What Is The Sin Of Pi 4
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
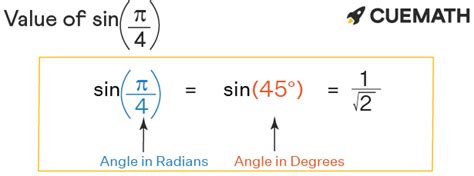
Table of Contents
What is the Sin of Pi/4? Unraveling Trigonometric Mysteries
The seemingly simple question, "What is the sin of pi/4?" opens a doorway to a fascinating world of trigonometry, mathematical history, and the elegance of the unit circle. This article delves deep into understanding this fundamental trigonometric concept, exploring its calculation, applications, and its significance within the broader landscape of mathematics.
Understanding the Basics: Angles, Radians, and the Unit Circle
Before we tackle the sin of pi/4, let's establish a solid foundation. Trigonometry, at its core, deals with the relationships between angles and sides of triangles. While degrees are a familiar unit for measuring angles, radians provide a more natural and mathematically convenient system. Radians express angles in terms of the ratio of arc length to radius on a circle. A full circle encompasses 2π radians, equivalent to 360 degrees.
The unit circle, a circle with a radius of 1, is a crucial tool for visualizing trigonometric functions. Each point on the unit circle can be represented by its coordinates (x, y), which are directly related to the cosine and sine of the angle formed between the positive x-axis and the line connecting the origin to that point. Specifically:
- cos θ = x (the x-coordinate)
- sin θ = y (the y-coordinate)
Calculating sin(π/4)
Now, let's focus on sin(π/4). π/4 radians is equivalent to 45 degrees. To find sin(π/4) using the unit circle:
-
Locate the 45-degree angle: Draw a line from the origin at a 45-degree angle to the positive x-axis. This line intersects the unit circle at a specific point.
-
Identify the coordinates: The coordinates of this intersection point are (√2/2, √2/2).
-
Extract the sine value: Remember, sin θ = y. Therefore, sin(π/4) = √2/2 (or approximately 0.707).
The Right-Angled Isosceles Triangle Approach
We can also derive sin(π/4) using a simple geometric approach. Consider a right-angled isosceles triangle, where two legs are of equal length (let's say 'a') and the hypotenuse is √2a (by the Pythagorean theorem). The angles in this triangle are 45°, 45°, and 90°. The sine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. Therefore:
sin(45°) = opposite/hypotenuse = a/(√2a) = 1/√2 = √2/2
This confirms our earlier result from the unit circle method.
Applications of sin(π/4) in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly simple value of sin(π/4) has far-reaching applications in various fields:
1. Physics and Engineering:
-
Projectile Motion: Understanding the trajectory of projectiles, crucial in fields like ballistics and aerospace engineering, heavily relies on trigonometric functions, including sin(π/4). The optimal launch angle for maximum range is 45 degrees, directly related to sin(π/4).
-
Wave Phenomena: Sinusoidal waves, fundamental to sound, light, and other wave phenomena, are described mathematically using sine and cosine functions. Calculations involving wave interference and superposition often involve sin(π/4).
-
Structural Analysis: Engineers utilize trigonometry to analyze stresses and strains within structures, employing sine and cosine functions to resolve forces into their components. Understanding sin(π/4) is essential in analyzing structures with 45-degree angles.
2. Computer Graphics and Game Development:
-
Rotation and Transformation: In computer graphics and game development, objects are rotated and transformed using trigonometric functions. Understanding the sine of specific angles, like π/4, is crucial for accurate calculations.
-
3D Modeling: Constructing and manipulating 3D models requires extensive use of trigonometric functions for precise positioning and orientation of objects in space.
3. Electrical Engineering:
- Alternating Current (AC) Circuits: AC circuits involve sinusoidal waveforms, and their analysis requires a thorough understanding of sine and cosine functions. Calculations involving phase shifts and impedance often use values like sin(π/4).
4. Navigation and Surveying:
- Distance and Angle Calculations: Surveyors and navigators employ trigonometry to determine distances and angles, relying on sine and cosine functions for calculations. Understanding sin(π/4) aids in accurate estimations when dealing with 45-degree angles.
Expanding Our Understanding: Beyond the Basics
While sin(π/4) = √2/2 is a fundamental result, understanding its broader context within trigonometry is equally important. This involves exploring concepts like:
1. The Sine Wave:
The sine function generates a periodic wave, a continuous oscillation. The value of sin(π/4) represents a specific point on this wave, highlighting the wave's amplitude and phase.
2. Trigonometric Identities:
Numerous trigonometric identities connect different trigonometric functions. Understanding these identities allows for manipulation and simplification of complex trigonometric expressions. For instance, the identity sin²θ + cos²θ = 1 is crucial in various calculations.
3. Inverse Trigonometric Functions:
Inverse trigonometric functions (arcsin, arccos, arctan) find the angle corresponding to a given trigonometric value. For example, arcsin(√2/2) = π/4.
The Historical Significance of Trigonometry
Trigonometry has a rich history, dating back to ancient civilizations. The Babylonians and Egyptians employed rudimentary forms of trigonometry for practical applications like land surveying and astronomy. The Greeks, particularly Ptolemy, made significant advancements in developing trigonometric tables and establishing fundamental trigonometric relationships. The development of trigonometry laid the foundation for many advancements in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of sin(π/4)
The seemingly simple question of "What is the sin of pi/4?" leads to a comprehensive exploration of trigonometry, its practical applications, and its historical significance. Understanding this fundamental concept is essential for anyone working in fields that involve angles, waves, or spatial relationships. While the value of √2/2 might appear straightforward, its implications within the broader mathematical and scientific landscape are far-reaching and continue to influence technological advancements and scientific discoveries. The elegance and utility of sin(π/4) underscore the profound beauty and practical power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons In P
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Causes The Alpha Particles To Deflect Backwards
Mar 26, 2025
-
64 To The Power Of 1 3
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Fraction Is Equal To 3 12
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Two Functional Groups Are Found In Amino Acids
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Sin Of Pi 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
