64 To The Power Of 1 3
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
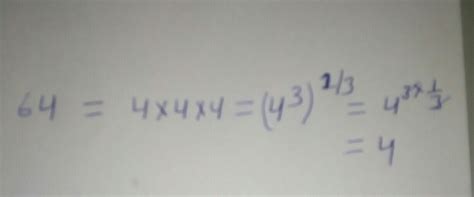
Table of Contents
64 to the Power of 1/3: Unpacking the Cube Root
The expression "64 to the power of 1/3" might seem daunting at first glance, but it represents a fundamental concept in mathematics: the cube root. Understanding this concept opens doors to a broader understanding of exponents, radicals, and their applications across various fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the meaning of 64<sup>1/3</sup>, explore its calculation, discuss its relevance in different mathematical contexts, and even touch upon its practical applications in real-world scenarios.
What Does 64<sup>1/3</sup> Mean?
Before jumping into the calculation, let's clarify what the expression signifies. The number 1/3 as an exponent indicates the cube root. In simpler terms, we're looking for a number that, when multiplied by itself three times (cubed), equals 64. The general form is:
x<sup>1/n</sup> = <sup>n</sup>√x
Where 'x' is the base number, 'n' is the root (in our case, 3 for the cube root), and the symbol '<sup>n</sup>√' denotes the nth root. Therefore, 64<sup>1/3</sup> is the same as the cube root of 64 (∛64).
Calculating 64<sup>1/3</sup>
Calculating 64<sup>1/3</sup> involves finding a number that, when multiplied by itself three times, results in 64. The most straightforward approach is to consider the factors of 64:
- 1 x 64 = 64
- 2 x 32 = 64
- 4 x 16 = 64
- 8 x 8 = 64
Notice that 8 multiplied by itself three times (8 x 8 x 8) equals 64. Therefore:
64<sup>1/3</sup> = 8
This demonstrates that 8 is the cube root of 64.
Understanding Exponents and Radicals
The concept of 64<sup>1/3</sup> is deeply intertwined with the broader understanding of exponents and radicals. Let's explore these concepts further:
Exponents:
Exponents represent repeated multiplication. For example, 2<sup>3</sup> (2 to the power of 3) means 2 x 2 x 2 = 8. The base is 2, and the exponent is 3. Fractional exponents, like 1/3, represent roots.
Radicals:
Radicals are the inverse operation of exponents. The cube root (∛) is a type of radical that finds a number which, when cubed, equals the radicand (the number under the radical symbol). Other common radicals include the square root (√), the fourth root (∜), and so on. The relationship between exponents and radicals is crucial for solving various mathematical problems.
Beyond 64<sup>1/3</sup>: Exploring Other Cube Roots
Understanding the calculation of 64<sup>1/3</sup> provides a foundation for calculating other cube roots. Let's explore some examples:
- The cube root of 27 (∛27): Since 3 x 3 x 3 = 27, the cube root of 27 is 3. Therefore, 27<sup>1/3</sup> = 3.
- The cube root of 125 (∛125): Since 5 x 5 x 5 = 125, the cube root of 125 is 5. Therefore, 125<sup>1/3</sup> = 5.
- The cube root of 1 (∛1): Since 1 x 1 x 1 = 1, the cube root of 1 is 1. Therefore, 1<sup>1/3</sup> = 1.
Applications of Cube Roots in Various Fields
The concept of cube roots, and fractional exponents more generally, has widespread applications across various fields, including:
Geometry:
Cube roots are frequently used in calculating volumes of cubes and other three-dimensional shapes. For example, if you know the volume of a cube, you can find the length of its side using the cube root.
Physics:
Cube roots appear in various physics equations, such as those related to the volume of objects, the relationship between density and mass, and calculations involving wave propagation.
Engineering:
Engineers utilize cube roots in structural design calculations, fluid dynamics, and many other engineering applications where the relationship between volume and dimensions is important.
Chemistry:
Cube roots find use in chemical calculations involving molarity, concentration, and reaction rates.
Finance:
Though less frequently used directly, the underlying principles of fractional exponents are crucial for compound interest calculations, which are fundamental to finance.
Solving Equations Involving Cube Roots
Cube roots often appear in equations that need to be solved. Here's how to tackle these:
Example:
Solve for x: x³ = 216
To solve for x, we take the cube root of both sides of the equation:
∛x³ = ∛216
x = 6
Therefore, the solution to the equation x³ = 216 is x = 6.
Advanced Concepts: Higher Roots and Fractional Exponents
The concept of cube roots extends to higher roots and more complex fractional exponents:
- Fourth Root: The fourth root of a number (x<sup>1/4</sup>) is a number that, when multiplied by itself four times, equals the original number.
- Fifth Root: The fifth root of a number (x<sup>1/5</sup>) is a number that, when multiplied by itself five times, equals the original number.
- General Fractional Exponents: Expressions like x<sup>m/n</sup> can be interpreted as (x<sup>1/n</sup>)<sup>m</sup>, meaning taking the nth root of x and then raising the result to the power of m.
Approximating Cube Roots for Numbers Without Perfect Cube Roots
Not all numbers have perfect cube roots (like 64, 27, or 125). For those numbers, approximation methods are needed. These methods often involve iterative calculations or numerical analysis techniques. Scientific calculators and computer software are invaluable for this process.
Conclusion: Mastering the Cube Root and Fractional Exponents
Understanding 64 to the power of 1/3 (or the cube root of 64) is a stepping stone to a deeper comprehension of exponents, radicals, and their vast applications. By grasping the fundamental principles explained here, you gain a more robust mathematical foundation applicable across numerous fields. Remember that practice is key to mastering these concepts, so tackle various problems and explore different applications to solidify your understanding. The journey to mastering mathematics is a continuous process of learning, exploring, and applying these core concepts to solve complex problems and unlock new possibilities. The world of numbers is rich and rewarding; this is just one example of the fascinating intricacies that await exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are 4 Agents Of Erosion
Mar 29, 2025
-
Molar Mass Of Sr No3 2
Mar 29, 2025
-
Is 2 3 Less Than 3 4
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Were These Elements In The First Periodic Table Arranged
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Percent Of 300 Is 51
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 64 To The Power Of 1 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
