What Is The Gcf Of 8 And 24
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
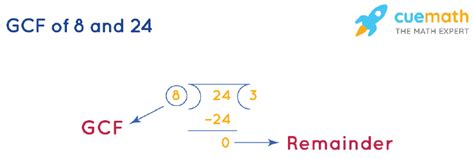
Table of Contents
What is the GCF of 8 and 24? A Deep Dive into Greatest Common Factors
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it is crucial for a strong foundation in mathematics. This comprehensive guide delves into the GCF of 8 and 24, explaining multiple approaches and exploring its relevance in broader mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond a simple answer and illuminate the 'why' behind the calculations, making this concept accessible and engaging for all levels of mathematical understanding.
Understanding Greatest Common Factors (GCF)
The greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest number that divides exactly into two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. It's a fundamental concept in number theory and has numerous applications in various fields, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations. Finding the GCF is essential for simplifying mathematical expressions and understanding the relationships between numbers.
Why is Finding the GCF Important?
The ability to efficiently determine the GCF is crucial for several reasons:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The GCF is used to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. By dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF, you obtain an equivalent fraction in its simplest form. This makes fractions easier to understand and work with.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: GCF plays a vital role in factoring algebraic expressions. Factoring allows us to simplify complex expressions and solve equations more readily.
-
Understanding Number Relationships: Determining the GCF helps us understand the relationships between different numbers. It reveals common divisors and provides insights into the structure of numbers.
-
Real-World Applications: GCF has applications in various real-world scenarios, such as dividing items equally amongst groups, determining the dimensions of objects, and planning projects involving equal divisions.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 8 and 24
Let's explore several methods to find the GCF of 8 and 24:
1. Listing Factors Method
This method involves listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the largest common factor.
Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8
Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Common Factors: 1, 2, 4, 8
Greatest Common Factor: 8
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers, but it becomes less efficient as the numbers grow larger.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method utilizes the prime factorization of each number. The prime factorization of a number is its expression as a product of prime numbers.
-
Prime Factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
-
Prime Factorization of 24: 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2³ x 3
The GCF is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. In this case, the common prime factor is 2, and the lowest power is 2³. Therefore:
GCF(8, 24) = 2³ = 8
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 8 and 24:
- 24 ÷ 8 = 3 with a remainder of 0
Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the smaller number, which is 8.
The Euclidean algorithm is particularly efficient for larger numbers because it reduces the size of the numbers involved with each step, making the calculations faster and simpler than the listing factors or prime factorization methods.
Applications of GCF in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of GCF extends far beyond theoretical mathematics. It finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Dividing Items Equally: Imagine you have 24 apples and 8 oranges, and you want to divide them equally among several baskets such that each basket has the same number of apples and oranges. The GCF(24, 8) = 8 tells you that you can create 8 baskets, each containing 3 apples and 1 orange.
-
Geometry and Measurement: When determining the dimensions of a rectangular area, finding the GCF can help in simplifying the measurements. For instance, if you have a rectangular plot of land with dimensions 24 meters by 8 meters, the GCF(24, 8) = 8 indicates that you can divide the plot into 8 equal square sections of 3 meters x 1 meter.
-
Project Planning: In project management, where tasks need to be divided equally among team members or resources allocated evenly, the GCF helps determine the optimal number of groups or the most efficient allocation strategy.
-
Music and Rhythm: In music theory, the GCF plays a role in determining common time signatures and rhythmic patterns. Understanding GCF allows for the creation of harmonious and mathematically consistent musical compositions.
GCF and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The GCF and the least common multiple (LCM) are closely related concepts. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. There is a useful relationship between the GCF and LCM of two numbers:
LCM(a, b) x GCF(a, b) = a x b
Using this relationship, if you know the GCF of two numbers, you can easily calculate their LCM. For example, since GCF(8, 24) = 8, then:
LCM(8, 24) = (8 x 24) / 8 = 24
This relationship provides a convenient way to find the LCM after calculating the GCF.
Expanding the Concept: GCF of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed earlier can be extended to find the GCF of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method remains particularly effective in these scenarios. You would find the prime factorization of each number, and the GCF is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
For example, let's find the GCF of 8, 24, and 32:
- Prime Factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime Factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
- Prime Factorization of 32: 2⁵
The only common prime factor is 2, and its lowest power is 2³. Therefore, GCF(8, 24, 32) = 8
Conclusion: Mastering the GCF
Understanding the greatest common factor is a cornerstone of mathematical fluency. This guide has explored various methods for calculating the GCF, emphasizing the importance of understanding the underlying principles. From simplifying fractions to solving complex problems, the GCF plays a pivotal role in numerous mathematical contexts and finds practical applications in many real-world scenarios. By mastering the techniques presented here, you can confidently tackle GCF problems and appreciate its significance in the broader world of mathematics. Remember to choose the method that best suits the numbers you are working with – the listing factors method is suitable for smaller numbers, prime factorization is generally versatile, and the Euclidean algorithm shines with larger numbers. The understanding of GCF is not merely about finding a numerical answer but rather about developing a deeper comprehension of number relationships and mathematical structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If The Median Is Greater Than The Mean
Mar 28, 2025
-
How To Find Number Of Core Electrons
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Formula For The Compound Magnesium Oxide
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Correct Formula For Calcium Oxide
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Si Base Unit Of Length
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Gcf Of 8 And 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
