What Is The Formula For The Compound Magnesium Oxide
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
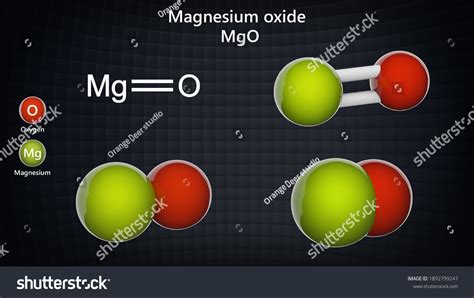
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for the Compound Magnesium Oxide?
Magnesium oxide, a compound with a myriad of applications, is a fascinating substance to study, from its simple chemical formula to its complex real-world uses. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of magnesium oxide, exploring its formula, properties, formation, and diverse applications. We will also touch upon related concepts to provide a thorough understanding of this important chemical compound.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: MgO
The chemical formula for magnesium oxide is simply MgO. This concise notation tells us everything we need to know about the basic composition of the compound: it contains one magnesium (Mg) atom for every one oxygen (O) atom. This 1:1 ratio reflects the ionic bonding between the two elements, where magnesium readily loses two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, and oxygen readily accepts those two electrons to achieve its own stable configuration.
This simple formula, however, hides a world of chemical and physical properties that make magnesium oxide so useful. Let's explore these properties in more detail.
Properties of Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide possesses several key properties that contribute to its widespread use:
-
High Melting Point: MgO boasts an exceptionally high melting point, around 2852 °C (5166 °F). This makes it incredibly stable at high temperatures, crucial for applications in refractory materials.
-
Insulating Properties: Magnesium oxide is an excellent electrical insulator, meaning it doesn't readily conduct electricity. This property makes it valuable in electrical applications. It also possesses good thermal insulation properties, making it useful in thermal applications.
-
Chemical Reactivity: While relatively stable, magnesium oxide does react with acids and water, forming magnesium hydroxide and magnesium salts. This reactivity is leveraged in various industrial processes.
-
White Crystalline Solid: In its pure form, magnesium oxide exists as a white crystalline solid. However, impurities can lead to variations in color.
Formation of Magnesium Oxide
The formation of magnesium oxide is a classic example of a redox reaction (reduction-oxidation reaction). This involves the transfer of electrons between the magnesium and oxygen atoms.
The Reaction: Burning Magnesium
The most common method for creating magnesium oxide is by burning magnesium metal in the presence of oxygen. The reaction is highly exothermic (releases heat), producing a bright white light and a white powder:
2Mg(s) + O₂(g) → 2MgO(s)
In this equation:
- Mg(s) represents solid magnesium.
- O₂(g) represents gaseous oxygen.
- MgO(s) represents solid magnesium oxide.
The reaction demonstrates the oxidation of magnesium (loss of electrons) and the reduction of oxygen (gain of electrons). The magnesium atoms each lose two electrons, becoming Mg²⁺ ions, while the oxygen atoms each gain two electrons, becoming O²⁻ ions. The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms the ionic bond that holds the MgO crystal lattice together.
Other Methods of Formation
While burning magnesium in air is the most straightforward method, magnesium oxide can also be formed through other chemical processes, including:
-
Thermal decomposition of magnesium hydroxide: Heating magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) drives off water, leaving behind magnesium oxide.
-
Reaction of magnesium salts with strong bases: Certain magnesium salts react with strong bases (like sodium hydroxide) to precipitate magnesium oxide.
Applications of Magnesium Oxide
The unique properties of magnesium oxide translate into a wide range of applications across numerous industries:
1. Refractory Materials
The high melting point and stability of magnesium oxide make it a crucial component in refractory materials. These are materials capable of withstanding extremely high temperatures without significant degradation. They are used in:
- Furnace linings: Protecting furnace walls from extreme heat.
- Crucibles: Containers for melting metals and other high-temperature processes.
- Kilns: Used in the manufacturing of ceramics and other materials.
2. Electronics Industry
Magnesium oxide's excellent insulating properties make it vital in various electronic applications, including:
- Insulators in electronic devices: Preventing short circuits and ensuring the safe operation of electronic components.
- Substrate materials: Providing a stable base for electronic circuits.
3. Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Magnesium oxide has several pharmaceutical applications:
- Antacid: Neutralizing stomach acid to alleviate heartburn and indigestion. (Note: always consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.)
- Laxative: Easing constipation. (Note: always consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.)
- Dietary supplement: Providing a source of magnesium, an essential mineral for numerous bodily functions. (Note: always consult a healthcare professional before taking any dietary supplement.)
4. Agriculture
Magnesium oxide is used in agriculture as a soil amendment, providing magnesium, an essential nutrient for plant growth. It helps to improve soil structure and pH levels.
5. Environmental Applications
Magnesium oxide finds applications in environmental remediation, including:
- Water treatment: Removing heavy metals and other contaminants from water.
- Air pollution control: Neutralizing acidic gases.
Safety Considerations
While magnesium oxide is generally considered safe in many applications, certain precautions should be taken:
-
Inhalation: Inhalation of magnesium oxide dust can cause respiratory irritation. Appropriate respiratory protection should be worn when handling MgO dust.
-
Skin Contact: Prolonged or repeated skin contact can cause irritation. Protective gloves should be used when handling MgO.
-
Eye Contact: Magnesium oxide dust can irritate the eyes. Safety glasses should always be worn.
Conclusion: The Significance of MgO
The simple formula MgO belies the complexity and importance of magnesium oxide. Its unique properties, ranging from its high melting point to its excellent insulating capabilities, have led to its wide adoption across diverse industries. From refractory materials to pharmaceuticals and beyond, magnesium oxide continues to play a critical role in modern technology and society. Understanding its formula and properties is essential for appreciating its diverse applications and for ensuring its safe and effective use. Further research into the synthesis and modification of magnesium oxide is ongoing, promising even more innovative applications in the future. This comprehensive exploration of magnesium oxide hopefully provides a solid foundation for understanding this fascinating and versatile compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Na H2o Naoh H2 Balanced Equation
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Type Of Medium Travels The Fastest
Mar 31, 2025
-
1 3 To The Power Of 3
Mar 31, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple For 18 And 24
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 3 4 Equivalent To In Fractions
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For The Compound Magnesium Oxide . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
