Oxidation Number Of Nitrogen In No2
listenit
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
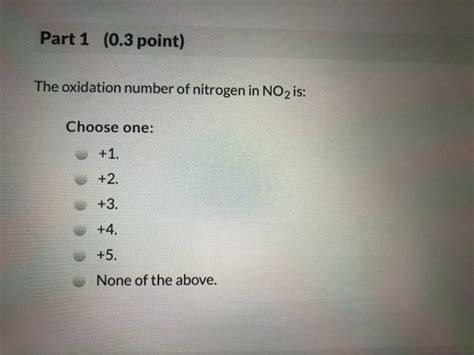
Table of Contents
Determining the Oxidation Number of Nitrogen in NO₂
Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) is a fascinating and important molecule, featuring prominently in various chemical processes and environmental phenomena. Understanding its properties, especially the oxidation state of nitrogen within the molecule, is crucial for comprehending its reactivity and role in different systems. This article will delve deep into the determination of the oxidation number of nitrogen in NO₂, exploring various approaches and clarifying potential misconceptions. We'll also touch upon the significance of this oxidation state in the context of NO₂'s chemical behavior and environmental impact.
Understanding Oxidation Numbers
Before we tackle the specific case of NO₂, let's establish a firm understanding of oxidation numbers. The oxidation number, also known as the oxidation state, is a hypothetical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule or ion. It represents the number of electrons an atom has gained, lost, or shared in a chemical bond. It's a crucial concept in redox chemistry (reduction-oxidation reactions), helping us understand electron transfer and predict reaction behavior.
Several rules guide the assignment of oxidation numbers:
-
Rule 1: The oxidation number of an atom in its elemental form is always zero. For example, the oxidation number of O₂ in oxygen gas is zero, and the same applies to N₂ in nitrogen gas.
-
Rule 2: The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. For instance, the oxidation number of Na⁺ is +1, and the oxidation number of Cl⁻ is -1.
-
Rule 3: The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, except in metal hydrides where it's -1. In H₂O, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1. In NaH, it's -1.
-
Rule 4: The oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2, except in peroxides (like H₂O₂) where it's -1 and in superoxides where it is -1/2. In most compounds, oxygen exhibits a -2 oxidation state.
-
Rule 5: The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral molecule is zero.
-
Rule 6: The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
Calculating the Oxidation Number of Nitrogen in NO₂
Now, let's apply these rules to determine the oxidation number of nitrogen (N) in nitrogen dioxide (NO₂).
We know that:
- The molecule is neutral (overall charge = 0).
- Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2.
Let's represent the oxidation number of nitrogen as 'x'. Using Rule 5, we can set up an equation:
x + 2(-2) = 0
Solving for x:
x - 4 = 0
x = +4
Therefore, the oxidation number of nitrogen in NO₂ is +4.
Different Approaches and Considerations
While the above method is straightforward, it's beneficial to explore other approaches to solidify our understanding. Let's consider the Lewis structure of NO₂:
Lewis Structure and Oxidation State
Drawing the Lewis structure of NO₂ reveals a resonance structure with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond and one nitrogen-oxygen single bond with an unpaired electron. While the Lewis structure doesn't directly give us the oxidation state, it helps visualize the bonding arrangement and electron distribution.
Formal Charge vs. Oxidation Number
It's crucial to differentiate between formal charge and oxidation number. Formal charge considers the number of electrons assigned to an atom in a Lewis structure based on a purely covalent bonding model. Oxidation number, on the other hand, considers the electrons as if they were completely transferred based on electronegativity differences. While the formal charge of nitrogen in NO₂ might vary depending on the resonance structure considered, the oxidation number remains consistently +4.
Significance of the +4 Oxidation State in NO₂'s Chemistry
The +4 oxidation state of nitrogen in NO₂ significantly influences its chemical behavior and reactivity.
Reactivity and Redox Reactions
The +4 oxidation state indicates that nitrogen is relatively high in its oxidation state, making NO₂ a potent oxidizing agent. It readily participates in redox reactions, either gaining electrons (reduction) or losing electrons (oxidation), depending on the reaction conditions and the other reactants involved. This reactivity is central to NO₂'s role in atmospheric chemistry and industrial processes.
Formation and Decomposition
The formation and decomposition of NO₂ often involve changes in nitrogen's oxidation state. For example, the oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) to NO₂ involves a change from +2 to +4. The decomposition of NO₂ can result in nitrogen's oxidation state decreasing.
Environmental Impact
NO₂ is a significant air pollutant, contributing to acid rain and respiratory problems. Its chemical properties, directly linked to the +4 oxidation state of nitrogen, are crucial in understanding its environmental impact. The reactions of NO₂ in the atmosphere, involving changes in the oxidation state of nitrogen, lead to the formation of other pollutants like nitric acid (HNO₃).
NO₂ in Various Chemical Contexts
The +4 oxidation state of nitrogen in NO₂ is not only important for its inherent properties but also for understanding its behavior in various chemical contexts.
Industrial Applications
NO₂ finds use in certain industrial processes. Its reactivity, stemming from the +4 oxidation state of nitrogen, makes it suitable for specific chemical transformations.
Laboratory Applications
In laboratories, NO₂ is used in various chemical experiments and as a reagent in specific reactions. Its oxidizing capacity and ability to participate in redox reactions are highly valued in these applications.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Oxidation States
Determining the oxidation number of nitrogen in NO₂ is a fundamental exercise in understanding the molecule's properties and its behavior in various chemical systems. The +4 oxidation state explains the molecule's oxidizing properties, its role in atmospheric chemistry, and its applications in industry and research. Understanding oxidation numbers, in general, is a critical skill in mastering the concepts of redox chemistry and predicting reaction outcomes. This article has highlighted not just the calculation of the oxidation state but also the broader significance of this concept within the context of NO₂'s chemical and environmental impact. The knowledge gained is critical for students, researchers, and anyone interested in chemical processes and environmental science. Understanding oxidation numbers provides a valuable framework for comprehending the complex world of chemistry and its impact on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find The Mass Of The Excess Reactant
Apr 02, 2025
-
Instantaneous Rate Of Change Vs Average Rate Of Change
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many D Orbitals Can Be In An Energy Level
Apr 02, 2025
-
Log Base 2 X 2 Graph
Apr 02, 2025
-
X 3 2x 2 5x 6
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Oxidation Number Of Nitrogen In No2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
