How Many Protons Does Neon Have
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
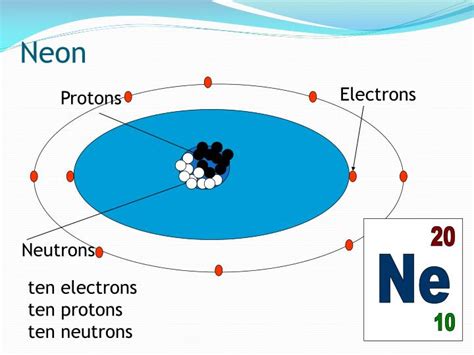
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Does Neon Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Neon's Properties
Neon, that vibrant gas used in signs and lasers, holds a fascinating place in the periodic table. But beyond its dazzling applications, understanding neon's atomic structure, particularly its proton count, unlocks a deeper understanding of its unique properties and behavior. So, how many protons does neon have? The simple answer is 10. But let's delve much deeper than that, exploring the implications of this number and its significance in chemistry and physics.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we focus specifically on neon, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. Every atom, the fundamental building block of matter, consists of three primary subatomic particles:
Protons: The Defining Characteristic
- Positive Charge: Protons carry a single positive electrical charge.
- Mass: A proton's mass is approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Location: Protons reside within the atom's nucleus, the dense central core.
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in an atom's nucleus defines its atomic number and uniquely identifies the element. This is crucial because it dictates the element's chemical properties and how it interacts with other elements.
Neutrons: Nuclear Stability
- Neutral Charge: Neutrons have no electrical charge; they are neutral.
- Mass: A neutron's mass is slightly larger than a proton's, also approximately 1 amu.
- Location: Neutrons, like protons, reside in the atom's nucleus.
- Isotopes: The number of neutrons can vary within an element, resulting in isotopes. Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. This affects the atom's mass but not its chemical behavior significantly.
Electrons: Chemical Reactivity
- Negative Charge: Electrons carry a single negative electrical charge, equal and opposite to a proton's positive charge.
- Mass: Electrons have a significantly smaller mass than protons and neutrons, approximately 1/1836 amu.
- Location: Electrons orbit the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The arrangement of electrons in these shells dictates the atom's chemical reactivity – its tendency to form bonds with other atoms.
Neon's Atomic Structure: 10 Protons and Beyond
Now, let's focus on neon (Ne), element number 10 on the periodic table. The fact that neon has an atomic number of 10 means it possesses 10 protons in its nucleus. This is fundamental to its identity as neon. This proton count determines its position in the periodic table, its electron configuration, and ultimately its chemical and physical properties.
Neon's Electron Configuration: A Stable Octet
With 10 protons, a neutral neon atom also has 10 electrons. These electrons are distributed in specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus. Neon's electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶. This configuration is incredibly stable because the outermost shell (the 2p subshell) is completely filled with eight electrons, achieving what's known as a stable octet. This full outer shell makes neon exceptionally unreactive, a characteristic that defines its noble gas nature.
Isotopes of Neon: Variations in Neutron Count
While the number of protons remains constant at 10 for all neon atoms, the number of neutrons can vary. This gives rise to different isotopes of neon. The most common isotopes are:
- Neon-20 (²⁰Ne): This is the most abundant isotope, making up about 90.48% of naturally occurring neon. It has 10 protons and 10 neutrons.
- Neon-21 (²¹Ne): This isotope accounts for approximately 0.27% of naturally occurring neon and has 10 protons and 11 neutrons.
- Neon-22 (²²Ne): Making up about 9.25% of naturally occurring neon, this isotope has 10 protons and 12 neutrons.
The different isotopes of neon have slightly different masses due to the varying neutron counts, but their chemical properties remain essentially identical because the number of protons and electrons doesn't change.
Neon's Properties and Applications: A Consequence of its 10 Protons
Neon's unique properties, stemming directly from its 10 protons and resulting electron configuration, make it highly valuable in various applications:
Inertness: A Key Feature
Neon's unreactive nature, a direct consequence of its stable electron configuration, makes it ideal for applications where inertness is crucial. It won't readily react with other substances, preventing unwanted chemical reactions.
Lighting Applications: The Glowing Neon Sign
Neon's most well-known application is in neon signs. When an electrical current passes through neon gas, the electrons become excited to higher energy levels. As these electrons return to their ground state, they emit light, producing the characteristic bright orange-red glow. This glow's color can be altered by using different gases or by coating the tube with phosphors.
Lasers: Precise and Powerful Light
Neon gas is also a crucial component in various types of lasers, including helium-neon lasers. These lasers produce a coherent and monochromatic beam of light, used in numerous applications, such as barcode scanners, laser pointers, and scientific research.
Cryogenics: Extremely Low Temperatures
Liquid neon, obtained by cooling neon gas to extremely low temperatures, finds applications in cryogenics – the study and application of very low temperatures. Its relatively low boiling point makes it a suitable refrigerant for certain specialized applications.
Other Applications
Neon's unique properties have led to applications in various other fields, including:
- Vacuum tubes: Due to its inertness.
- High-voltage indicators: Because of its ability to glow under high voltage.
- Diving gas mixtures: In specialized mixtures for deep-sea diving.
Conclusion: The Significance of Neon's 10 Protons
The seemingly simple fact that neon has 10 protons is fundamental to understanding its properties and applications. This proton count dictates its atomic number, its electron configuration, its inertness, and consequently, its widespread use in lighting, lasers, and cryogenics. By exploring neon's atomic structure, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationship between the subatomic world and the macroscopic properties we observe in everyday life. The seemingly simple number 10 holds a wealth of scientific significance. Understanding this helps us grasp the fundamental principles of chemistry and physics and appreciate the remarkable diversity and utility of the elements around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 To The Power Of Negative 1
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is A Common Property Of Metals
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Does The Coefficient In A Chemical Equation Represent
Mar 28, 2025
-
1 4 Pound Is How Many Ounces
Mar 28, 2025
-
Oxidation State Of Nitrogen In Ammonia
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Does Neon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
