What Is A Common Property Of Metals
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
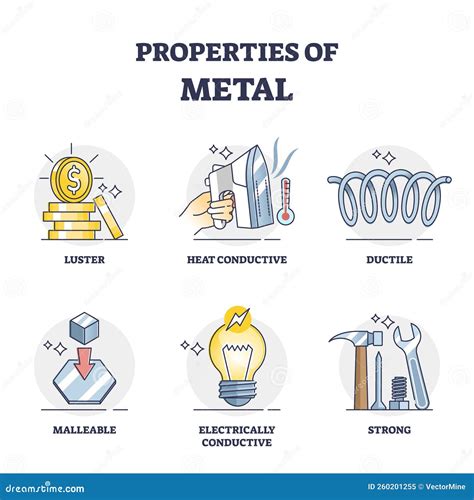
Table of Contents
What is a Common Property of Metals? Exploring the Characteristics that Define Metals
Metals are ubiquitous in our daily lives, from the smartphones in our pockets to the skyscrapers that define our skylines. Their widespread use stems from a unique set of properties that distinguish them from other materials. But what exactly is a common property of metals? It's not a single characteristic, but rather a collection of interrelated traits that contribute to their versatility and utility. This article will delve into the key properties that define metals, exploring their underlying causes and implications.
The Defining Characteristics of Metals
Several properties consistently appear across the vast majority of metallic elements, forming the basis of their classification. These include:
1. High Electrical Conductivity
One of the most prominent common properties of metals is their exceptional ability to conduct electricity. This arises from the unique structure of metallic bonding. In metals, the valence electrons (outermost electrons) are delocalized, meaning they are not bound to specific atoms but instead form a "sea" of electrons that are free to move throughout the metal lattice. This "sea" of mobile electrons acts as a conduit for electrical current, allowing electrons to flow easily when a potential difference is applied. Silver and copper, for example, are renowned for their exceptionally high electrical conductivity, making them ideal for electrical wiring and circuitry. This property is crucial in various technological applications, from power grids to microelectronics.
2. High Thermal Conductivity
Closely related to electrical conductivity is high thermal conductivity. The same mobile electrons responsible for electrical conduction also facilitate the efficient transfer of heat. When one part of a metal is heated, the kinetic energy of the electrons increases, and this energy is rapidly transferred throughout the metal via these mobile electrons. This rapid heat transfer is essential in applications requiring efficient heat dissipation, such as heat sinks in electronic devices or cooking utensils. Metals like aluminum and copper are frequently employed due to their superior thermal conductivity.
3. Malleability and Ductility
Metals are typically malleable, meaning they can be easily hammered or rolled into thin sheets without breaking. They are also ductile, meaning they can be drawn into wires. These properties are a direct consequence of the non-directional nature of metallic bonding. The "sea" of delocalized electrons allows the metal atoms to slide past each other relatively easily under stress, without disrupting the overall structure. This ability to deform without fracturing is vital in the shaping and forming of metal components for various industries, from automotive manufacturing to jewelry making.
4. Luster and Reflectivity
Metals possess a characteristic luster or shine, meaning they reflect light effectively. This is due to the interaction of light with the free electrons in the metal lattice. The electrons absorb light and then re-emit it, giving the metal its characteristic shiny appearance. This high reflectivity is exploited in various applications, from mirrors to decorative surfaces. The degree of luster and reflectivity can vary depending on the specific metal and its surface finish.
5. Hardness and Strength (with variations)
While not universally consistent across all metals, many possess significant hardness and strength. These properties arise from the strong metallic bonds holding the metal atoms together in a closely packed structure. However, the degree of hardness and strength varies considerably among different metals. Some metals, like iron and steel, are renowned for their high strength and are used in structural applications, while others, like gold and sodium, are relatively soft. The strength and hardness of a metal can be significantly improved through alloying—mixing it with other elements.
6. Metallic Bonding
Underlying all of these characteristic properties is the unique nature of metallic bonding. Unlike ionic or covalent bonding, where electrons are shared or transferred between specific atoms, metallic bonding involves a delocalized "sea" of electrons surrounding a lattice of positively charged metal ions. This unique bonding structure accounts for the high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster observed in metals.
Variations in Metallic Properties: The Role of Alloying and Other Factors
While the properties described above are common to most metals, the extent to which they are exhibited can vary significantly. This variation is influenced by several factors:
-
Type of Metal: Different metals have different numbers of valence electrons and different atomic sizes, leading to variations in the strength of metallic bonding and consequently affecting their properties. For example, copper exhibits higher electrical conductivity than iron.
-
Alloying: The addition of other elements (alloying) significantly alters the properties of a metal. Alloying can enhance strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, or other desired properties. Steel, an alloy of iron and carbon, is significantly stronger and harder than pure iron. Brass (copper and zinc) is more resistant to corrosion than pure copper.
-
Temperature: The properties of metals are also temperature-dependent. For example, the electrical conductivity of most metals decreases with increasing temperature.
-
Crystalline Structure: The arrangement of atoms in the metal lattice (crystalline structure) also influences its properties. Different crystal structures can lead to variations in strength, ductility, and other characteristics.
-
Presence of Impurities: The presence of impurities in a metal can significantly affect its properties. Even small amounts of impurities can alter the electrical conductivity, strength, or other characteristics.
Applications Based on Metallic Properties
The unique combination of properties exhibited by metals makes them indispensable across a wide array of applications:
-
Construction: Metals such as steel and aluminum are widely used in construction due to their high strength and relatively low weight.
-
Transportation: Steel, aluminum, and various alloys are crucial components in automobiles, airplanes, and ships.
-
Electronics: Copper and other metals are essential in electrical wiring and circuitry.
-
Packaging: Aluminum foil and tin cans are widely used for food packaging due to their corrosion resistance and malleability.
-
Medical Implants: Biocompatible metals such as titanium and stainless steel are used in medical implants due to their biocompatibility and strength.
-
Jewelry: Gold, silver, platinum, and various alloys are used in jewelry due to their luster, malleability, and resistance to corrosion.
Conclusion: The Versatility of Metals
The common properties of metals, stemming from their unique metallic bonding, have made them essential materials in human civilization. Their high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster have driven their use in a vast range of applications. While variations in these properties exist due to factors like alloying and temperature, understanding the fundamental characteristics of metals is crucial for designing and utilizing them effectively in modern technology and everyday life. The ongoing research and development in materials science continuously expands the possibilities of metal applications, making them an indispensable component of our future. Further exploration into the intricacies of metallic bonding and the influence of various factors on their properties will unlock even greater potential in this diverse and valuable class of materials.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple 16 And 24
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Name Of This Hydrocarbon
Mar 31, 2025
-
Columns Of Periodic Table Are Called
Mar 31, 2025
-
Difference Between Animal Mitosis And Plant Mitosis
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is Half Of One And A Half Teaspoons
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Common Property Of Metals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
