What Is The Valence Electrons Of Nitrogen
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
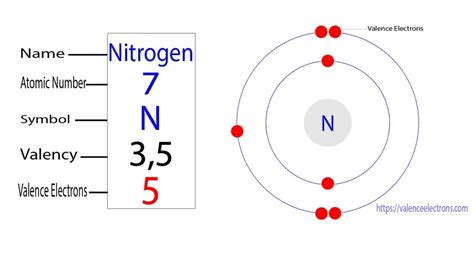
Table of Contents
What are the Valence Electrons of Nitrogen? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Chemical Behavior
Nitrogen, a ubiquitous element crucial for life as we know it, holds a fascinating position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly its valence electrons, is key to grasping its chemical reactivity and the formation of countless essential molecules. This comprehensive article will delve deep into the concept of valence electrons, focusing specifically on nitrogen, exploring its atomic structure, its role in bonding, and its implications in various chemical contexts.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Bonding
Before focusing on nitrogen, let's establish a firm understanding of valence electrons. These are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. They are the electrons most involved in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. The number of valence electrons dictates the element's position within the periodic table and greatly influences its chemical properties.
Atoms strive for stability, usually achieved by having a full outermost shell. This often involves gaining, losing, or sharing electrons to attain a stable configuration, often resembling the electron arrangement of a noble gas (group 18 elements). This drive towards stability is the fundamental driving force behind chemical bonding.
Nitrogen's Atomic Structure: Unveiling the Mystery of its Valence Electrons
Nitrogen (N), with an atomic number of 7, possesses seven electrons. To understand its valence electrons, we need to explore its electron configuration:
- 1s² 2s² 2p³
The electron configuration provides a detailed map of electron distribution within the atom's shells and subshells. The number preceding the letter (e.g., 1, 2) represents the principal energy level or shell. The letters (s, p, d, f) represent subshells within those energy levels. The superscript numbers indicate the number of electrons in each subshell.
Analyzing nitrogen's electron configuration:
- 1s²: Two electrons fill the first shell (n=1), which is the innermost and most stable shell.
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the 2s subshell in the second shell (n=2).
- 2p³: Three electrons are located in the 2p subshell within the second shell.
The key takeaway here is that the outermost shell (n=2) contains five electrons (2s² 2p³). Therefore, nitrogen has five valence electrons.
Significance of the 2p Subshell
The presence of three electrons in the 2p subshell is particularly crucial for nitrogen's chemical behavior. The p subshell has three orbitals, each capable of holding two electrons. Nitrogen's three 2p electrons occupy these orbitals individually, leading to three unpaired electrons. This unpaired electron configuration contributes significantly to nitrogen's ability to form three covalent bonds.
Nitrogen's Chemical Behavior: The Role of Valence Electrons
Nitrogen's five valence electrons dictate its strong tendency to form covalent bonds. To achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell), similar to the noble gas neon, it often shares electrons with other atoms. This explains why nitrogen is rarely found as a single atom but mostly exists as a diatomic molecule (N₂).
Formation of the N₂ Molecule: A Perfect Example
In the N₂ molecule, each nitrogen atom shares three electrons with the other, forming three covalent bonds. This triple bond is exceptionally strong, making N₂ incredibly stable and relatively unreactive under standard conditions. This explains why nitrogen gas constitutes a significant portion of Earth's atmosphere.
Other Chemical Compounds and Valence Electrons
Despite the stability of N₂, nitrogen's capacity to form covalent bonds also enables it to participate in various chemical reactions. The formation of ammonia (NH₃) is an excellent example. Here, nitrogen forms three single covalent bonds with three hydrogen atoms, utilizing three of its five valence electrons to complete the octet.
In other compounds like nitrogen oxides (e.g., NO, NO₂, N₂O₄), nitrogen's valence electrons are involved in forming bonds with oxygen atoms, exhibiting varying oxidation states depending on the specific compound. The number of bonds formed and the resulting oxidation state are directly related to nitrogen’s valence electrons.
Nitrogen's Role in Biological Systems: The Importance of Valence Electrons
Nitrogen's chemical properties, governed by its five valence electrons, are indispensable for life. It's a crucial component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), the carriers of genetic information. The ability of nitrogen to form stable bonds with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms makes it an essential element in constructing these complex biomolecules.
The nitrogen cycle, a fundamental process in ecosystems, involves the conversion of nitrogen between different forms, highlighting the continuous interplay of nitrogen's valence electrons in various chemical transformations. From atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates in the soil, nitrogen's ability to bond with different elements is essential for the growth and survival of plants and animals.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
While the basic concept of valence electrons is straightforward, a deeper understanding requires exploring advanced concepts:
Formal Charge and Oxidation State
The concept of formal charge and oxidation state helps in understanding the distribution of electrons in molecules. By considering the number of valence electrons and the number of bonds and lone pairs, we can assign formal charges and oxidation states to nitrogen atoms in various compounds. This provides further insight into the chemical bonding and reactivity of nitrogen compounds.
Hybridization and Molecular Geometry
Hybridization, a concept that describes the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals, plays a role in understanding the geometry of nitrogen-containing molecules. The hybridization of nitrogen's atomic orbitals influences the shape and properties of molecules like ammonia and amines.
Resonance Structures
In some nitrogen-containing molecules, resonance structures are needed to adequately represent the actual electron distribution. This occurs when the bonding electrons can be depicted in multiple ways without changing the arrangement of atoms. Resonance contributes to the stability and properties of such molecules.
Conclusion: Nitrogen’s Valence Electrons – A Cornerstone of Chemistry and Biology
In conclusion, understanding the five valence electrons of nitrogen is fundamental to comprehending its chemical behavior and biological significance. These electrons are the architects of nitrogen's ability to form strong bonds, leading to the formation of crucial molecules like ammonia, nitrogen oxides, and the building blocks of life. From the strong triple bond in N₂ to the versatile bonding in amino acids, the role of nitrogen's valence electrons is far-reaching and pivotal across various scientific disciplines. This article has only scratched the surface; further exploration into the world of nitrogen chemistry will undoubtedly unveil even more fascinating aspects of this critical element. The interplay of its valence electrons, governing its bonding capabilities and reactivity, remains a cornerstone of understanding chemistry and biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Round To The Nearest Cent
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 10
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Oz In 1 4 Pound
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 17 20
Mar 18, 2025
-
Integral Of Sec X Tan X
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Valence Electrons Of Nitrogen . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
