What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 10
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
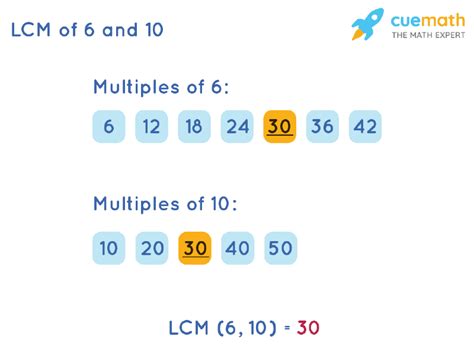
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 6 and 10? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly useful in simplifying fractions, solving problems involving cycles, and understanding rhythmic patterns. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of how to determine the LCM of 6 and 10, delving into various methods and explaining the underlying principles. We'll move beyond a simple answer and explore the broader implications of LCM calculations.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we calculate the LCM of 6 and 10, let's define what a least common multiple actually is. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, so the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
One of the simplest methods for finding the LCM, especially for smaller numbers like 6 and 10, is by listing their multiples.
Step 1: List the multiples of 6:
6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60…
Step 2: List the multiples of 10:
10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70…
Step 3: Identify the common multiples:
Notice that both lists share several multiples. Some common multiples of 6 and 10 are 30, 60, and so on.
Step 4: Determine the least common multiple:
The smallest common multiple in both lists is 30. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 10 is 30.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method is a more efficient approach for finding the LCM, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers. This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
Step 1: Find the prime factorization of 6:
6 = 2 x 3
Step 2: Find the prime factorization of 10:
10 = 2 x 5
Step 3: Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
The prime factors involved are 2, 3, and 5. The highest power of 2 is 2<sup>1</sup>, the highest power of 3 is 3<sup>1</sup>, and the highest power of 5 is 5<sup>1</sup>.
Step 4: Multiply the highest powers together:
LCM(6, 10) = 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
Method 3: Using the Formula with Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where:
- a and b are the two numbers.
- |a x b| represents the absolute value of the product of a and b.
- GCD(a, b) is the greatest common divisor of a and b.
Step 1: Find the GCD of 6 and 10:
The factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, 6. The factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, 10. The greatest common factor of 6 and 10 is 2. Therefore, GCD(6, 10) = 2.
Step 2: Apply the formula:
LCM(6, 10) = (6 x 10) / 2 = 60 / 2 = 30
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
Understanding LCM isn't just about abstract mathematical concepts; it has practical applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Timing:
Imagine two buses depart from a station at different intervals. One bus departs every 6 minutes, and the other every 10 minutes. To find out when both buses will depart simultaneously again, you need to find the LCM of 6 and 10. The LCM (30) indicates that both buses will depart together again after 30 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations:
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial for finding a common denominator, simplifying the calculation, and arriving at the correct answer.
3. Music and Rhythm:
In music, LCM is used to determine when different rhythmic patterns will coincide. For instance, if one instrument plays a pattern that repeats every 6 beats, and another plays a pattern repeating every 10 beats, the LCM helps determine when both patterns will align perfectly, creating a unified rhythmic effect.
4. Construction and Engineering:
In construction projects involving repetitive patterns like tiling or bricklaying, LCM can help determine the optimal size or spacing of elements to ensure a seamless and aesthetically pleasing result.
Extending the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, you'd find the prime factorization of each number, identify the highest power of each prime factor present, and then multiply those highest powers together. For the listing method, it becomes significantly more tedious as the number of integers increases.
For example, let's find the LCM of 6, 10, and 15:
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
The highest power of 2 is 2<sup>1</sup>, the highest power of 3 is 3<sup>1</sup>, and the highest power of 5 is 5<sup>1</sup>.
Therefore, LCM(6, 10, 15) = 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
The calculation of the least common multiple (LCM) is a vital skill in mathematics with numerous real-world applications. We've explored three efficient methods for calculating the LCM, particularly focusing on finding the LCM of 6 and 10. Understanding these methods empowers you to tackle more complex LCM problems involving larger numbers and multiple integers. The importance of LCM extends beyond simple calculations and plays a crucial role in various fields, highlighting its practical significance. Remember that mastering these methods will greatly enhance your mathematical problem-solving abilities and broaden your understanding of numerical relationships. The ability to swiftly and accurately calculate LCMs is a valuable asset in numerous mathematical and real-world contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 13 16 As A Decimal
Mar 18, 2025
-
5 6 Divided By 2 7
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Are Sublimation And Deposition Different From Each Other
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Yards In 7 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
2 X 2 X 3 0
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
