Integral Of Sec X Tan X
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 4 min read
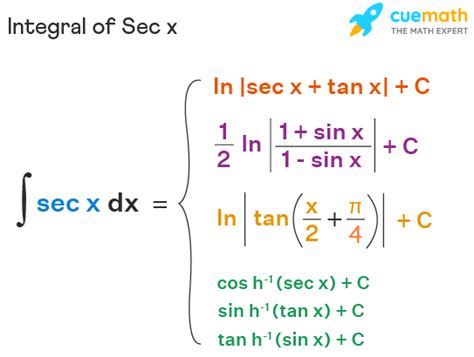
Table of Contents
The Indefinite Integral of sec(x)tan(x): A Comprehensive Guide
The integral of sec(x)tan(x) is a fundamental problem in calculus, frequently encountered in various applications. Understanding its derivation and properties is crucial for mastering integration techniques. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of this integral, exploring its solution, practical applications, and related concepts.
Understanding the Problem: ∫sec(x)tan(x) dx
The expression ∫sec(x)tan(x) dx represents the indefinite integral of the product of the secant and tangent functions. This seemingly simple integral holds significant importance due to its direct relationship with the derivative of the secant function.
Recall: The derivative of sec(x) with respect to x is given by:
d/dx [sec(x)] = sec(x)tan(x)
This crucial relationship provides the key to solving the integral. Since integration is the reverse process of differentiation, we can directly infer the solution.
Solving the Integral: A Step-by-Step Approach
The solution to the integral ∫sec(x)tan(x) dx is remarkably straightforward:
∫sec(x)tan(x) dx = sec(x) + C
where 'C' is the constant of integration. This constant is essential because the derivative of any constant is zero. Therefore, an infinite number of functions have the same derivative, differing only by a constant.
Why is the Constant of Integration Important?
The constant of integration, 'C', is a critical component of the indefinite integral. Without it, the solution is incomplete and doesn't represent the full family of antiderivatives. Consider the following:
- d/dx [sec(x) + 1] = sec(x)tan(x)
- d/dx [sec(x) - 5] = sec(x)tan(x)
- d/dx [sec(x) + π] = sec(x)tan(x)
Each of these functions, differing only by the constant term, has the same derivative: sec(x)tan(x). Including 'C' ensures we capture all possible antiderivatives.
Visualizing the Integral: Graphical Representation
Visualizing the integral can enhance understanding. Consider plotting the function y = sec(x)tan(x) and its antiderivative y = sec(x) + C for various values of C. You'll observe that the antiderivative functions are vertical translations of each other, differing only in their vertical position. This visual representation underscores the role of the constant of integration.
You can easily graph these using online graphing calculators or software like GeoGebra or Desmos. Experiment with different values of C to see how the graph shifts.
Applications of the Integral: Real-World Examples
The integral ∫sec(x)tan(x) dx isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Physics: In physics, particularly in mechanics and electromagnetism, this integral appears in problems involving forces and fields where the secant and tangent functions model the involved quantities. For instance, calculating work done along a curved path might involve this integral.
-
Engineering: Engineers encounter this integral in various calculations. Structural analysis, fluid mechanics, and electrical engineering often involve problems modeled using trigonometric functions where this integral is relevant.
-
Calculus and Differential Equations: The integral is frequently used as a building block in solving more complex integration problems. Mastering this foundational integral is crucial for tackling more challenging integration techniques like u-substitution, integration by parts, and trigonometric substitutions.
-
Computer Graphics and Animation: The representation of curves and surfaces often uses trigonometric functions. The integral can thus be part of calculations for rendering and animation.
Expanding on Related Integrals: Extensions and Variations
Understanding the integral of sec(x)tan(x) lays the foundation for solving several related integrals. Here are a few examples:
-
∫sec²(x) dx = tan(x) + C: This integral is another fundamental trigonometric integral, directly related to the derivative of the tangent function.
-
∫sec(x) dx: This integral is more challenging and requires a clever substitution technique. The solution involves natural logarithms.
-
∫tan²(x) dx: This integral can be solved using trigonometric identities to simplify the integrand.
Advanced Techniques: Utilizing Trigonometric Identities
While the integral ∫sec(x)tan(x) dx is solved directly using the knowledge of derivatives, more complex integrals involving secant and tangent functions require employing trigonometric identities for simplification. This often involves transforming the integrand into a form where the integral becomes solvable using basic integration rules or u-substitution.
Mastering Integration: Practice Problems
Practice is paramount in mastering integration. Here are a few problems for you to practice:
- Evaluate ∫ 2sec(x)tan(x) dx
- Evaluate ∫ sec(2x)tan(2x) dx (Hint: Use u-substitution)
- Evaluate ∫ sec(x)tan(x)√(sec(x)) dx (Hint: Use u-substitution)
Conclusion: The Significance of ∫sec(x)tan(x) dx
The integral of sec(x)tan(x) serves as a cornerstone of calculus, demonstrating the fundamental connection between differentiation and integration. Its solution, sec(x) + C, offers a valuable building block for solving more intricate integrals. Mastering this integral and its related concepts is crucial for success in calculus and its wide-ranging applications in various fields. Remember, consistent practice and exploration are key to deepening your understanding of this important concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Meters Is How Many Centimeters
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is 13 16 As A Decimal
Mar 18, 2025
-
5 6 Divided By 2 7
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Are Sublimation And Deposition Different From Each Other
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Yards In 7 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of Sec X Tan X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
