What Is The Most Abundant Gas In Air
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
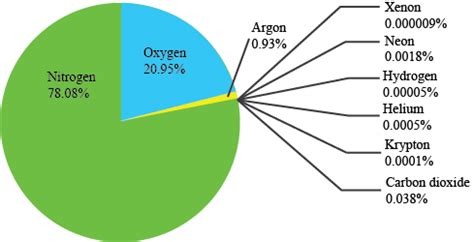
Table of Contents
What is the Most Abundent Gas in Air? A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Composition
The air we breathe, the invisible ocean surrounding our planet, is a complex mixture of gases. But one gas stands out above all others in terms of abundance: nitrogen. Understanding the composition of air, and the crucial role nitrogen plays, is fundamental to grasping various environmental processes, from weather patterns to the very sustenance of life on Earth. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the atmospheric composition, focusing specifically on nitrogen and its significance.
The Composition of Earth's Atmosphere: A Detailed Breakdown
Earth's atmosphere isn't a uniform entity; its composition varies slightly with altitude and location. However, a general approximation of the composition at sea level, by volume, is as follows:
- Nitrogen (N₂): Approximately 78.08%
- Oxygen (O₂): Approximately 20.95%
- Argon (Ar): Approximately 0.93%
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Approximately 0.04% (this is increasing due to human activity)
- Trace Gases: These include neon, helium, methane, krypton, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, xenon, and ozone, each present in minute quantities.
While the percentages might seem insignificant for trace gases, their impact on the environment and human health is far from negligible. For instance, the increasing concentration of carbon dioxide contributes significantly to global warming and climate change. Ozone, while vital in the stratosphere to protect us from harmful UV radiation, is a dangerous pollutant at ground level.
Nitrogen: The Dominant Player
As the data clearly shows, nitrogen gas (N₂) constitutes the overwhelming majority of Earth's atmosphere. Its inert nature, meaning it doesn't readily react with other substances under normal conditions, is a key factor in its abundance. This chemical stability has profound implications for life on Earth.
The Inert Nature of Nitrogen and its Significance
Nitrogen's inertness is a double-edged sword. While it prevents rapid reactions that could disrupt atmospheric balance, it also means that most organisms can't directly utilize atmospheric nitrogen for growth and metabolic processes. This is where the nitrogen cycle comes into play, a crucial biogeochemical cycle that transforms nitrogen into usable forms.
The Nitrogen Cycle: Transforming Inert Gas into Life's Building Blocks
The nitrogen cycle involves several intricate steps, converting atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms like ammonia (NH₃) and nitrates (NO₃⁻) through a process called nitrogen fixation. This process is primarily carried out by specialized bacteria living in soil and the roots of certain plants (legumes). These bacteria possess the unique ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, a readily available source of nitrogen for plants. Other bacteria then convert ammonia into nitrites and nitrates, which plants can absorb through their roots.
Animals obtain nitrogen by consuming plants or other animals. Finally, decomposers break down organic matter, releasing nitrogen back into the atmosphere as nitrogen gas through a process called denitrification. This continuous cycle ensures a constant supply of nitrogen for life on Earth.
The Importance of Nitrogen in Biological Systems
Nitrogen is a vital component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which carry genetic information. It's therefore an essential nutrient for all living organisms. Without a readily available source of nitrogen, plant growth would be severely limited, impacting the entire food chain.
Human Impact on the Nitrogen Cycle
Human activities have significantly altered the nitrogen cycle, primarily through the production and use of nitrogen fertilizers. Excessive use of these fertilizers leads to nitrogen runoff into waterways, causing eutrophication – a process where excessive nutrients fuel algal blooms, depleting oxygen levels and harming aquatic life. This highlights the delicate balance of the nitrogen cycle and the importance of sustainable agricultural practices.
Oxygen: The Essential Gas for Life
While nitrogen dominates the atmosphere, oxygen (O₂) is the second most abundant gas and arguably the most crucial for the majority of life on Earth. Oxygen is highly reactive, supporting respiration in most living organisms. The process of respiration utilizes oxygen to break down organic molecules, releasing energy that fuels life's processes.
The Oxygen Cycle: A Constant Exchange
The oxygen cycle involves a continuous exchange of oxygen between the atmosphere, the oceans, and living organisms. Photosynthesis in plants and algae plays a critical role, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) and oxygen using sunlight as an energy source. This oxygen is then released into the atmosphere, making it available for respiration.
The Importance of Oxygen for Respiration and other Processes
Oxygen's role in respiration is paramount. It acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, a series of chemical reactions that generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main energy currency of cells. Oxygen is also involved in other vital processes, such as the formation of ozone in the stratosphere, which protects us from harmful UV radiation.
Human Impact on Oxygen Levels
While human activities haven't significantly altered global oxygen levels, deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels consume oxygen and release carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change and potentially impacting future oxygen levels. Maintaining healthy forests and transitioning to renewable energy sources are crucial for preserving oxygen levels and mitigating climate change.
Argon and Other Trace Gases: Their Roles in the Atmosphere
Although present in smaller quantities, argon (Ar) and other trace gases play significant roles in the atmosphere. Argon, an inert gas like nitrogen, is a byproduct of radioactive decay of potassium-40 in the Earth's crust. It's chemically inactive and contributes little to atmospheric processes, but its presence is a consistent marker in atmospheric studies.
Other trace gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O), are potent greenhouse gases, trapping heat and contributing to global warming. Their concentrations are relatively low, but their impact on climate is disproportionately high. Understanding the sources and sinks of these gases is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change. Ozone (O₃), while vital in the stratosphere, is a harmful pollutant at ground level, contributing to respiratory problems.
Conclusion: Nitrogen's Reign and the Interconnectedness of Atmospheric Gases
In conclusion, nitrogen (N₂) is the most abundant gas in the air, making up approximately 78% of the atmosphere. Its inert nature has shaped the development of life on Earth, leading to the complex nitrogen cycle that converts atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for living organisms. While nitrogen's stability is crucial, the other atmospheric components, especially oxygen and the trace gases, play equally vital roles, highlighting the interconnectedness of atmospheric gases and the delicate balance that sustains life on our planet. Understanding this balance and the impact of human activities on atmospheric composition is crucial for ensuring a healthy and sustainable future. Further research and careful monitoring of atmospheric composition are needed to address the challenges posed by climate change and other environmental issues. The abundance of nitrogen might seem like a simple fact, but it opens a window into the intricate processes that govern our planet's atmosphere and the life it supports.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Number Of Protons In The Nucleus Of An Element
Mar 22, 2025
-
One Proton Weighs The Amount How Many Electrons
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Smallest Unit Of Element
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Do You Graph 2x Y
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is Hydrogen Chloride Soluble In Water
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Most Abundant Gas In Air . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
