What Is The Molar Mass Of Bf3
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
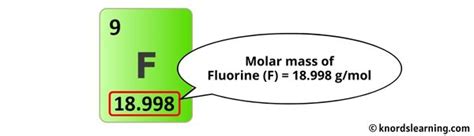
Table of Contents
What is the Molar Mass of BF₃? A Deep Dive into Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride (BF₃) is a colorless, toxic gas with a pungent odor. It's a crucial compound in various industrial applications, from the production of specialty polymers to the synthesis of other chemicals. Understanding its properties, particularly its molar mass, is essential for accurate calculations in chemistry and related fields. This comprehensive article will delve into the determination of BF₃'s molar mass, exploring the underlying concepts and calculations involved. We will also touch upon its uses and safety precautions.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before calculating the molar mass of BF₃, let's clarify the concept itself. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of entities, whether atoms, molecules, ions, or other specified particles. The molar mass is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
The molar mass of a substance is directly related to its atomic or molecular weight. For individual elements, the molar mass is numerically equivalent to the atomic weight found on the periodic table. For compounds, like BF₃, you need to sum the molar masses of each constituent atom, taking into account the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule.
Calculating the Molar Mass of BF₃
To calculate the molar mass of BF₃ (boron trifluoride), we need the atomic masses of boron (B) and fluorine (F) from the periodic table.
- Boron (B): The atomic mass of boron is approximately 10.81 g/mol. This value is an average considering the natural abundance of boron isotopes.
- Fluorine (F): The atomic mass of fluorine is approximately 19.00 g/mol.
The chemical formula BF₃ indicates that one molecule of boron trifluoride consists of one boron atom and three fluorine atoms. Therefore, to find the molar mass of BF₃, we perform the following calculation:
Molar mass of BF₃ = (1 x Atomic mass of B) + (3 x Atomic mass of F)
Molar mass of BF₃ = (1 x 10.81 g/mol) + (3 x 19.00 g/mol)
Molar mass of BF₃ = 10.81 g/mol + 57.00 g/mol
Molar mass of BF₃ = 67.81 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of BF₃ is approximately 67.81 g/mol. This means that one mole of BF₃ weighs approximately 67.81 grams.
Significance of Molar Mass in Chemical Calculations
The molar mass of BF₃ plays a vital role in various stoichiometric calculations. Here are a few examples:
-
Mass-to-Mole Conversions: If you know the mass of BF₃, you can use its molar mass to calculate the number of moles present. This is crucial in many chemical reactions where reactants are measured by mass.
-
Mole-to-Mass Conversions: Conversely, if you know the number of moles of BF₃ involved in a reaction, you can use the molar mass to determine its mass. This helps determine the amount of product formed or reactant needed.
-
Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas: Molar mass is a key factor in determining the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds, especially when analyzing experimental data from combustion or other analytical techniques.
-
Concentration Calculations: In solutions, the molar mass is used to calculate the molarity (moles of solute per liter of solution), a critical parameter in many chemical processes.
Applications of Boron Trifluoride
BF₃ finds widespread applications in various industries due to its unique chemical properties:
1. Polymer Chemistry:
-
Cationic Polymerization: BF₃ acts as a catalyst in cationic polymerization, which is essential for producing various polymers used in adhesives, coatings, and other applications. This process involves the initiation of a polymer chain using a carbocation, facilitated by BF₃. The precise control offered by BF₃ is vital for desired polymer properties.
-
Polymer Modification: BF₃ can be used to modify existing polymers, improving their properties such as thermal stability and reactivity. This is particularly valuable in creating specialized materials with tailored characteristics.
2. Organic Synthesis:
-
Lewis Acid Catalyst: BF₃ is a powerful Lewis acid catalyst, meaning it can accept electron pairs. This property makes it valuable in various organic reactions, accelerating the reaction rate and enhancing the yield of desired products. Examples include Friedel-Crafts reactions and other electrophilic aromatic substitutions.
-
Specific Reactions: It participates in many specific reactions, including the isomerization of alkenes and the preparation of certain organic compounds. Its role as a selective catalyst often allows for cleaner and more efficient synthesis pathways.
3. Other Industrial Applications:
-
Metal Refining: BF₃ plays a role in the purification and refining of certain metals. Its unique chemical interactions help remove impurities and increase the purity of the final product.
-
Electronics Industry: In semiconductor manufacturing, BF₃ is used in doping processes to enhance the conductivity of silicon and other materials. This is critical for the functionality of electronic components.
-
Nuclear Chemistry: While less common, BF₃ has some specialized applications in nuclear chemistry due to its ability to absorb neutrons, a property utilized in certain detector technologies.
Safety Precautions When Handling Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is a highly reactive and toxic gas. Strict safety precautions are essential when handling this compound:
-
Proper Ventilation: Work with BF₃ in well-ventilated areas or under a fume hood to prevent inhalation of the toxic gas. Even low concentrations can cause severe respiratory irritation.
-
Protective Equipment: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, eye protection, and a respirator designed to filter out BF₃. Skin contact can cause severe burns, and inhalation can lead to serious health issues.
-
Emergency Response: Be prepared for emergency situations, having readily available safety showers and eyewash stations. Understanding the proper procedures for handling spills and leaks is crucial for mitigating risks.
-
Storage: Store BF₃ in properly labeled and sealed cylinders in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials. Improper storage can lead to leaks and potential hazards.
-
Disposal: Dispose of BF₃ and any contaminated materials according to local, regional, and national regulations. Improper disposal can have serious environmental consequences.
Conclusion
The molar mass of BF₃, calculated as approximately 67.81 g/mol, is a fundamental piece of information for various chemical calculations and applications. This value is essential for converting between mass and moles, enabling accurate stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions, and determining concentrations in solutions. Understanding the properties and applications of boron trifluoride is critical in many industrial processes, particularly in polymer chemistry and organic synthesis. However, it's crucial to remember the inherent dangers associated with this compound and to always prioritize safety when handling BF₃. By adhering to proper safety protocols and utilizing appropriate protective measures, the risks associated with BF₃ can be minimized, ensuring safe and effective use in various applications. Remember to always consult relevant safety data sheets (SDS) and follow established safety guidelines when working with this chemical.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 12 5 Is 39
Mar 26, 2025
-
Empirical And Molecular Formula Of Ibuprofen
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of So2
Mar 26, 2025
-
Electrons In The Outermost Energy Level Are Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
Express The Integral As A Limit Of Riemann Sums
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molar Mass Of Bf3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
