What Is The Molar Mass Of So2
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
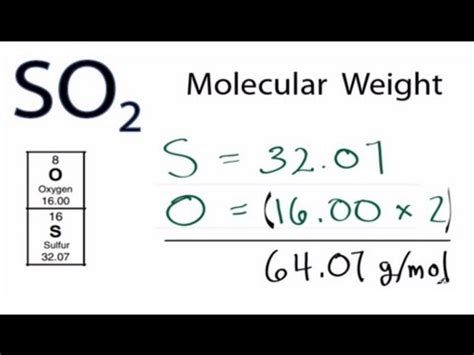
Table of Contents
What is the Molar Mass of SO2? A Deep Dive into Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colorless gas with a pungent, suffocating odor. It's a crucial compound in various industrial processes and a significant atmospheric pollutant. Understanding its properties, particularly its molar mass, is vital in many scientific and engineering applications. This comprehensive article will delve into the concept of molar mass, calculate the molar mass of SO2, and explore its relevance in different fields.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before calculating the molar mass of SO2, let's establish a solid understanding of the fundamental concept. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup>) of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). Essentially, the molar mass tells us the mass of 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup> molecules of a particular substance. It's usually expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
The molar mass of an element is numerically equal to its atomic weight (found on the periodic table) in grams. For compounds, the molar mass is the sum of the molar masses of all the atoms present in the molecule.
Calculating the Molar Mass of SO2
SO2, sulfur dioxide, is a molecule composed of one sulfur atom (S) and two oxygen atoms (O). To calculate its molar mass, we need the atomic masses of sulfur and oxygen from the periodic table.
- Atomic mass of Sulfur (S): Approximately 32.06 g/mol
- Atomic mass of Oxygen (O): Approximately 16.00 g/mol
Now, let's calculate the molar mass of SO2:
Molar mass of SO2 = (1 x atomic mass of S) + (2 x atomic mass of O)
Molar mass of SO2 = (1 x 32.06 g/mol) + (2 x 16.00 g/mol)
Molar mass of SO2 = 32.06 g/mol + 32.00 g/mol
Molar mass of SO2 = 64.06 g/mol
Therefore, one mole of sulfur dioxide (SO2) weighs approximately 64.06 grams.
Significance of Molar Mass in Various Applications
The molar mass of SO2 is a critical parameter in numerous scientific and industrial applications. Let's explore some of them:
1. Stoichiometry and Chemical Reactions
In stoichiometry, the molar mass is essential for converting between mass and moles in chemical reactions. Knowing the molar mass of SO2 allows us to calculate the amount of SO2 involved in a reaction, determine the limiting reactant, and predict the yield of products. For example, in a reaction involving the oxidation of SO2 to SO3, the molar mass helps determine the amount of SO3 produced from a given mass of SO2.
2. Environmental Monitoring and Pollution Control
SO2 is a major air pollutant contributing to acid rain and respiratory problems. Understanding its molar mass is crucial for environmental monitoring and pollution control. Measuring the concentration of SO2 in the atmosphere often involves converting measured masses to moles for accurate analysis and comparison. This data is then used to develop and implement strategies for reducing SO2 emissions from industrial sources.
3. Industrial Processes
SO2 is used in various industrial processes, including the production of sulfuric acid, a vital chemical used in countless applications. Accurate calculations involving the molar mass of SO2 are crucial for optimizing these industrial processes, ensuring efficiency, and minimizing waste. For instance, determining the optimal amount of SO2 needed for a specific reaction in sulfuric acid production requires precise knowledge of its molar mass.
4. Gas Laws and Thermodynamics
The molar mass of SO2 is essential when applying gas laws, such as the Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT), to understand its behavior under different conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature. The molar mass is incorporated in the calculation of the number of moles (n) in the Ideal Gas Law, allowing for accurate predictions of the gas's properties.
5. Spectroscopy and Analytical Chemistry
Molar mass is relevant in various spectroscopic techniques used for analyzing the composition of samples. In techniques like mass spectrometry, the molar mass helps identify and quantify different components in a mixture, including SO2.
Beyond the Basics: Isotopes and Molar Mass
The molar mass we calculated (64.06 g/mol) is an average molar mass. This is because sulfur and oxygen have different isotopes, each with slightly different masses. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is a weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element.
The presence of isotopes slightly affects the precision of molar mass calculations. For instance, sulfur has several isotopes, including <sup>32</sup>S (the most abundant), <sup>33</sup>S, <sup>34</sup>S, and <sup>36</sup>S. Oxygen also has isotopes like <sup>16</sup>O, <sup>17</sup>O, and <sup>18</sup>O.
While the average molar mass is sufficient for most calculations, highly precise measurements might require considering the isotopic composition of the sample. This is particularly relevant in specialized fields such as nuclear chemistry or mass spectrometry, where isotope ratios are crucial.
Practical Applications and Examples
Let's illustrate the practical use of SO2's molar mass with a couple of examples:
Example 1: Determining Moles from Mass
Suppose we have 10 grams of SO2. How many moles of SO2 do we have?
We use the following formula:
Moles = Mass / Molar Mass
Moles = 10 g / 64.06 g/mol
Moles ≈ 0.156 moles of SO2
Example 2: Determining Mass from Moles
If we have 0.5 moles of SO2, what is its mass in grams?
Mass = Moles x Molar Mass
Mass = 0.5 mol x 64.06 g/mol
Mass ≈ 32.03 grams of SO2
Safety Considerations with SO2
It is crucial to remember that sulfur dioxide is a toxic gas. It is important to handle it with caution and follow appropriate safety protocols. Direct inhalation can cause severe respiratory irritation, and exposure should be minimized. Proper ventilation is essential when working with SO2 in any environment.
Conclusion
The molar mass of SO2, approximately 64.06 g/mol, is a fundamental property with far-reaching implications in chemistry, environmental science, and industrial applications. Understanding its calculation and significance is crucial for anyone working in these fields. From stoichiometric calculations to environmental monitoring and industrial process optimization, the molar mass of SO2 serves as a cornerstone for numerous critical calculations and analyses. This knowledge empowers scientists and engineers to make accurate predictions, improve efficiency, and contribute to safer and more sustainable practices. The importance of safety protocols when working with SO2 should never be overlooked.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 8
Mar 29, 2025
-
Name 3 Ways To Dissolve Something Faster
Mar 29, 2025
-
Charged Language In I Have A Dream
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 38 Out Of 40
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Does The Prefix Hydro Mean
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molar Mass Of So2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
