Empirical And Molecular Formula Of Ibuprofen
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
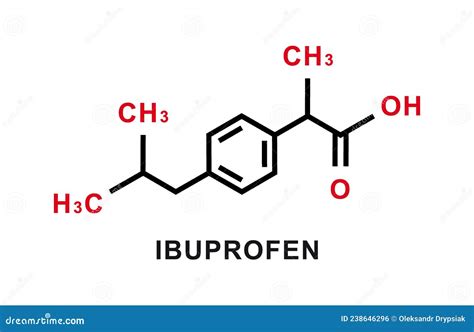
Table of Contents
Empirical and Molecular Formula of Ibuprofen: A Deep Dive
Ibuprofen, a globally recognized nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), is a common household remedy for pain and fever. Understanding its chemical composition, particularly its empirical and molecular formulas, provides valuable insight into its properties and pharmacological actions. This article will delve deep into the empirical and molecular formula of ibuprofen, exploring its derivation, significance, and relation to its medicinal properties.
What are Empirical and Molecular Formulas?
Before we dive into the specifics of ibuprofen, let's establish a clear understanding of empirical and molecular formulas. These are two crucial ways to represent the composition of a chemical compound.
Empirical Formula
The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound. It doesn't necessarily reflect the actual number of atoms in a molecule, only their relative proportions. Think of it as a simplified representation of the compound's composition. For example, the empirical formula of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is HO, showing a 1:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms.
Molecular Formula
The molecular formula, on the other hand, gives the actual number of atoms of each element present in one molecule of the compound. This represents the true composition of a single molecule. For hydrogen peroxide, the molecular formula is H₂O₂, accurately reflecting two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms per molecule.
Determining the Empirical and Molecular Formula of Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen's chemical name is (RS)-2-(4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl)propanoic acid. This complex name hints at its intricate molecular structure. To determine its empirical and molecular formulas, we need to understand its constituent elements and their proportions.
Step-by-Step Determination
-
Identify the Elements: Ibuprofen contains carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
-
Determine the Number of Atoms of Each Element: Analyzing the chemical structure of ibuprofen reveals the following atom counts:
- Carbon (C): 13 atoms
- Hydrogen (H): 18 atoms
- Oxygen (O): 2 atoms
-
Write the Molecular Formula: Based on the atom counts, the molecular formula of ibuprofen is C₁₃H₁₈O₂.
-
Derive the Empirical Formula: To find the empirical formula, we need to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the subscripts in the molecular formula. In this case, the GCD of 13, 18, and 2 is 1. Since the GCD is 1, the empirical formula is the same as the molecular formula: C₁₃H₁₈O₂.
This indicates that the simplest whole-number ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in ibuprofen is 13:18:2. While this is a relatively simple case, it's important to remember that in other compounds, the empirical and molecular formulas might differ significantly.
The Significance of Ibuprofen's Formula
Knowing ibuprofen's empirical and molecular formulas is crucial for several reasons:
-
Synthesis and Production: The molecular formula guides the precise synthesis of ibuprofen in pharmaceutical laboratories. It dictates the exact amounts of each element required for the chemical reaction.
-
Dosage and Pharmacokinetics: The molecular weight (calculated from the molecular formula) is vital in determining appropriate dosages and understanding how ibuprofen is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body (pharmacokinetics).
-
Purity and Quality Control: The formulas are used in quality control tests to ensure the purity and consistency of ibuprofen produced. Analysis techniques like elemental analysis verify the correct composition, guaranteeing the drug's efficacy and safety.
-
Drug Interactions: Understanding ibuprofen's chemical structure (implied by its formula) is essential in predicting potential interactions with other drugs. Its molecular interactions with biological targets are directly related to its chemical composition.
-
Structural Analysis and Modifications: The molecular formula is the foundation for further research into modifying ibuprofen's structure to improve its properties, such as reducing side effects or enhancing its effectiveness.
Ibuprofen's Structure and its Impact on Properties
Ibuprofen's molecular structure directly influences its pharmacological activity. The presence of a chiral carbon atom leads to two enantiomers (mirror-image isomers), (S)-ibuprofen and (R)-ibuprofen. (S)-ibuprofen is the significantly more potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory isomer, while (R)-ibuprofen has weaker activity. Most commercial ibuprofen preparations are racemic mixtures, containing equal amounts of both isomers.
The propionic acid group (-CH₂CH₂COOH) is responsible for ibuprofen's anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. It interacts with cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, reducing the production of prostaglandins, which are involved in pain and inflammation. The aromatic ring contributes to the molecule's overall lipophilicity (fat solubility), influencing its absorption and distribution in the body. The isobutyl group ((CH₃)₂CHCH₂) further modulates the molecule's interaction with COX enzymes and influences its overall pharmacological profile.
Analytical Techniques Used to Determine Ibuprofen's Formula
Determining the molecular formula of ibuprofen and other complex organic molecules often involves a combination of techniques:
-
Elemental Analysis: This technique determines the percentage composition of each element (C, H, O) in ibuprofen. By knowing the percentages and the atomic weights of the elements, the empirical formula can be calculated.
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS): MS provides the molecular weight of ibuprofen. This is crucial in distinguishing between the empirical and molecular formulas, particularly when they are not identical. High-resolution MS can provide accurate mass measurements, further confirming the molecular formula.
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: NMR provides detailed information about the structure of the molecule, including the number and types of atoms and their connectivity. This data helps confirm the arrangement of atoms, providing further confidence in the molecular formula.
-
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: IR spectroscopy provides information about the functional groups present in the molecule, which can be used to support the proposed structure and formula.
By combining the results from these analytical techniques, scientists can confidently determine the empirical and molecular formulas of ibuprofen and other complex compounds.
Conclusion
The empirical and molecular formula of ibuprofen, C₁₃H₁₈O₂, is not just a set of symbols but a cornerstone of its understanding and application. It is fundamental to its synthesis, quality control, dosage determination, and further research into its pharmacological properties and potential modifications. Understanding the relationship between its chemical structure, as revealed by its formula, and its biological activity is essential for advancing its therapeutic uses and developing newer, improved NSAIDs. The analytical techniques described above are invaluable tools in confirming this critical information, ensuring the safety and efficacy of this widely used medication. The detailed understanding of ibuprofen's formula and structure serves as a powerful example of how chemical information underpins advancements in medicine and pharmaceutical science.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Standard Enthalpy Of Formation Of Ethanol
Mar 29, 2025
-
Do Parallelograms Have 4 Right Angles
Mar 29, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 8
Mar 29, 2025
-
Name 3 Ways To Dissolve Something Faster
Mar 29, 2025
-
Charged Language In I Have A Dream
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Empirical And Molecular Formula Of Ibuprofen . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
