What Is The Difference Between Diction And Syntax
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
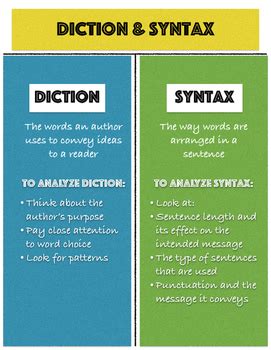
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Diction and Syntax? A Deep Dive into Language's Building Blocks
Understanding the nuances of language requires delving into its fundamental components. While often used interchangeably, diction and syntax represent distinct yet interconnected aspects of writing and speech. Mastering both is crucial for crafting clear, compelling, and effective communication, whether in creative writing, academic essays, or everyday conversation. This article will explore the differences between diction and syntax, offering practical examples to illuminate their individual roles and combined power.
Diction: The Art of Word Choice
Diction refers to the choice and use of words and phrases in speech or writing. It encompasses the style, tone, and clarity of language used. Think of diction as the what of your communication – the specific words you select to convey your message. The impact of your diction is profound; it dictates the overall impression your writing or speech leaves on the audience.
Types of Diction
Diction can be categorized into several types, each serving a distinct purpose and evoking a particular response from the reader or listener:
-
Formal Diction: Characterized by precise, sophisticated vocabulary and complex sentence structures. It’s often used in academic papers, legal documents, and formal speeches. Examples include words like "utilize," "endeavor," and "commensurate."
-
Informal Diction: Uses simpler, everyday language, often including colloquialisms, slang, and contractions. It creates a more relaxed and conversational tone, suitable for informal essays, personal letters, and casual conversations. Examples include words like "use," "try," and "equal."
-
Informal Diction: Uses simpler, everyday language, often including colloquialisms, slang, and contractions. It creates a more relaxed and conversational tone, suitable for informal essays, personal letters, and casual conversations. Examples include words like "use," "try," and "equal."
-
Poetic Diction: Employs vivid, evocative language, often including figurative language like metaphors, similes, and personification. It's commonly used in poetry and other creative writing to enhance imagery and emotional impact.
-
Technical Diction: Utilizes precise and specialized vocabulary specific to a particular field or profession. It's essential in scientific reports, medical journals, and technical manuals.
Impact of Diction on Writing
Effective diction goes beyond simply choosing words; it involves considering the connotation and denotation of words. Denotation is the literal meaning of a word, while connotation refers to the emotional associations and cultural implications attached to it.
For example, the words "house" and "home" both denote a dwelling place, but "home" carries a stronger connotation of warmth, comfort, and belonging. Choosing between these words significantly impacts the overall feeling and message of your writing.
Consider these examples:
-
"The man walked down the street." This sentence uses neutral diction.
-
"The weary traveler trudged along the desolate road." This sentence uses more evocative diction, painting a clearer picture and conveying a sense of hardship.
The careful selection of words drastically affects the reader’s understanding and emotional response, demonstrating the power of diction in shaping meaning and tone.
Syntax: The Art of Sentence Structure
Syntax, on the other hand, concerns the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences. It's the how of your communication – the grammatical structure you use to convey your message. Syntax dictates the flow, rhythm, and emphasis of your writing or speech.
Elements of Syntax
Several key elements contribute to the effectiveness of syntax:
-
Sentence Length: Varying sentence lengths – short, concise sentences juxtaposed with longer, more complex ones – keeps the reader engaged and prevents monotony.
-
Sentence Structure: Different sentence structures, such as simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex, offer diverse ways to express ideas and create rhythm.
-
Word Order: The order in which words appear in a sentence influences the emphasis and meaning. Changing word order can significantly alter the impact of a sentence.
-
Parallelism: Using similar grammatical structures to express related ideas creates a sense of balance and clarity.
-
Punctuation: Punctuation marks are crucial in guiding the reader's understanding of sentence structure and meaning. They signal pauses, breaks, and shifts in thought.
Impact of Syntax on Writing
Mastering syntax allows you to control the pace, rhythm, and emphasis of your writing. Consider the following examples:
-
"The cat sat on the mat." This is a simple sentence, straightforward and concise.
-
"On the mat, the cat sat." This alters the emphasis slightly, placing more focus on the location.
-
"Slowly, deliberately, the cat settled onto the warm mat." This sentence uses modifiers and a different sentence structure to convey a sense of leisurely action.
Effective syntax avoids ambiguity and ensures the clear and concise transmission of information. It's the foundation of readability and comprehension. Complex syntax can add layers of meaning and stylistic flair, while simple syntax can provide clarity and impact.
The Interplay of Diction and Syntax
While distinct, diction and syntax are intrinsically linked. Your choice of words (diction) directly impacts how you structure your sentences (syntax). For instance, using formal diction often necessitates more complex sentence structures. Conversely, informal diction often aligns with simpler, shorter sentences.
Consider this example:
-
Formal Diction & Complex Syntax: "The proliferation of misinformation necessitates the implementation of robust fact-checking mechanisms to mitigate the dissemination of unsubstantiated claims and thereby preserve the integrity of public discourse."
-
Informal Diction & Simple Syntax: "Fake news is a problem. We need better fact-checking to stop it."
Both sentences convey a similar message, but their distinct diction and syntax create vastly different impressions. The first is formal and scholarly, while the second is informal and direct.
The skillful combination of diction and syntax allows writers and speakers to craft messages that are not only grammatically correct but also stylistically effective and impactful. It's through the thoughtful integration of these two elements that writers can truly master the art of communication.
Conclusion: Mastering the Building Blocks of Language
Diction and syntax are the cornerstones of effective communication. While diction focuses on word choice, creating tone and conveying meaning through careful selection, syntax deals with the arrangement of those words, shaping the rhythm, flow, and impact of the message. Understanding and skillfully employing both are crucial for any writer or speaker aiming to create engaging, clear, and persuasive content. By mastering these fundamental elements, you unlock the potential to communicate effectively and powerfully, regardless of your audience or purpose. The ability to adapt your diction and syntax to different contexts is a key skill in achieving communicative excellence. Therefore, constant practice and mindful attention to these elements are vital steps on the path to becoming a skilled and articulate communicator.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 15 4 As A Mixed Number
Apr 06, 2025
-
Sublimation Is Physical Or Chemical Change
Apr 06, 2025
-
Write 2 1 2 As An Improper Fraction
Apr 06, 2025
-
For Which Of The Mixtures Will Ag2so4 S Precipitate
Apr 06, 2025
-
Is The Square Root Of 16 A Rational Number
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Diction And Syntax . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
