What Is The Derivative Of Cosecant
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
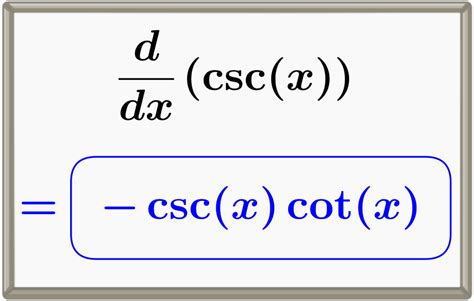
Table of Contents
What is the Derivative of Cosecant? A Comprehensive Guide
The cosecant function, denoted as csc(x), is a crucial trigonometric function with significant applications in calculus, physics, and engineering. Understanding its derivative is essential for solving various problems involving rates of change and optimization. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the derivation of the cosecant's derivative, explore its properties, and showcase its practical applications.
Understanding the Cosecant Function
Before diving into the derivative, let's refresh our understanding of the cosecant function itself. The cosecant of an angle x (csc(x)) is defined as the reciprocal of the sine function:
csc(x) = 1/sin(x)
This means that the cosecant function is undefined wherever the sine function is equal to zero. This occurs at integer multiples of π (i.e., x = nπ, where n is an integer). The cosecant function exhibits a periodic behavior, repeating its values every 2π interval. Its graph displays vertical asymptotes at these points of undefined values.
Deriving the Derivative of Cosecant using the Quotient Rule
The most straightforward method to derive the derivative of csc(x) is by employing the quotient rule of differentiation. The quotient rule states that the derivative of a function f(x) / g(x) is given by:
d/dx [f(x)/g(x)] = [g(x)f'(x) - f(x)g'(x)] / [g(x)]²
In our case, f(x) = 1 and g(x) = sin(x). Therefore, f'(x) = 0 and g'(x) = cos(x). Substituting these values into the quotient rule, we get:
d/dx [csc(x)] = d/dx [1/sin(x)] = [sin(x)(0) - 1(cos(x))] / [sin(x)]² = -cos(x) / [sin(x)]²
Since cos(x)/sin(x) = cot(x), we can simplify this expression further:
d/dx [csc(x)] = -cot(x)csc(x)
Therefore, the derivative of cosecant(x) is -cot(x)csc(x). This is a fundamental result in calculus and is frequently used in various applications.
Deriving the Derivative using the Chain Rule
The chain rule is another powerful tool that can be used to derive the derivative of the cosecant function. Remember the chain rule states:
d/dx [f(g(x))] = f'(g(x)) * g'(x)
We can express csc(x) as (sin(x))⁻¹. Applying the chain rule:
d/dx [csc(x)] = d/dx [(sin(x))⁻¹] = -1(sin(x))⁻² * cos(x) = -cos(x) / (sin(x))²
This result is identical to the one obtained using the quotient rule, again yielding:
d/dx [csc(x)] = -cot(x)csc(x)
Understanding the Result: -cot(x)csc(x)
The derivative of csc(x), -cot(x)csc(x), provides valuable information about the instantaneous rate of change of the cosecant function at any given point. The negative sign indicates that the function is generally decreasing where it is defined. The presence of cot(x) and csc(x) reflects the inherent relationship between the cosecant, cotangent, and sine functions.
Analyzing the Derivative's Behavior
The derivative, -cot(x)csc(x), is undefined at the same points as the cosecant function itself (integer multiples of π). This is expected because the function has vertical asymptotes at these points, and the instantaneous rate of change becomes undefined at such points. Analyzing the derivative's behavior in the intervals between these asymptotes helps understand the function's increasing or decreasing nature.
Applications of the Cosecant Derivative
The derivative of the cosecant function finds numerous applications in various fields. Some key examples include:
1. Physics and Engineering:
In physics and engineering, the cosecant function appears in problems involving waves, oscillations, and signal processing. The derivative helps determine the instantaneous rate of change of these phenomena. For instance, in analyzing the motion of a pendulum, the cosecant function and its derivative play a crucial role in understanding the angular velocity and acceleration.
2. Calculus and Optimization Problems:
Finding maxima and minima of functions involving cosecants requires calculating the derivative and setting it to zero. This technique is essential for solving optimization problems in various fields.
3. Differential Equations:
The cosecant function and its derivative appear in certain types of differential equations which describe physical systems, such as those found in wave mechanics and electrical circuit analysis. Solving these equations often involves using the derivative to find the solution that satisfies the initial conditions.
4. Geometry and Trigonometry:
Understanding the cosecant function and its derivative enhances the ability to analyze geometric problems involving triangles, circles, and other shapes where trigonometric functions are used to define relationships between sides and angles.
5. Computer Graphics and Game Development:
The cosecant function and its derivative play a role in creating realistic simulations and animations. These functions can be used to model the movements of objects and the behaviour of light, where accurate derivatives are crucial for realistic animation.
Higher-Order Derivatives of Cosecant
While the first derivative is most commonly used, it's possible to calculate higher-order derivatives of the cosecant function. This involves repeatedly applying the derivative rules. The second derivative, for instance, involves the derivative of -cot(x)csc(x), requiring application of the product rule and further simplification. Higher-order derivatives become increasingly complex but are sometimes necessary in advanced applications like Taylor series expansions of the cosecant function.
Conclusion
The derivative of the cosecant function, -cot(x)csc(x), is a fundamental result in calculus with wide-ranging applications. Understanding its derivation, properties, and applications is crucial for anyone working with trigonometric functions and their applications in various fields. Whether you're a physics student, an engineer, or a mathematician, mastering the derivative of cosecant enhances your ability to analyze and solve problems involving rates of change and optimization. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for understanding and applying this important concept effectively. By understanding the derivations using both the quotient rule and the chain rule, you have a deeper comprehension of this essential concept and its application in complex problem-solving scenarios. Remember to practice and apply these concepts to various problems to strengthen your understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Rate Of Change The Same As Slope
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is Difference Between Atom And Ion
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Gas Is Used In The Process
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Is The Electron Configuration For Bromine
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Protons Does Mercury Have
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Derivative Of Cosecant . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
