Which Is The Electron Configuration For Bromine
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
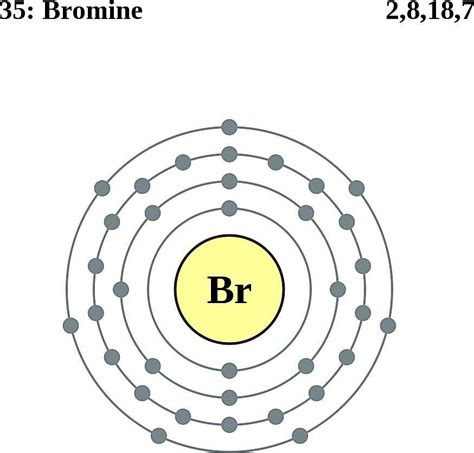
Table of Contents
Which is the Electron Configuration for Bromine? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Bromine, a fascinating element with a rich history and diverse applications, holds a unique place in the periodic table. Understanding its electron configuration is key to unlocking its chemical properties and behavior. This article will delve deep into the electron configuration of bromine, exploring the underlying principles of atomic structure and illustrating its significance in determining bromine's reactivity and characteristics.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before diving into bromine's specific configuration, let's establish a foundational understanding of what electron configuration represents. An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in the various energy levels and sublevels within an atom. This arrangement is governed by several fundamental principles:
- The Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. This is like filling a building from the ground floor up, before moving to higher levels.
- Hund's Rule: Within a subshell (like a floor in our building analogy), electrons will individually occupy each orbital before pairing up. Think of it as each person getting their own room before sharing.
- The Pauli Exclusion Principle: Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, and these electrons must have opposite spins (represented as ↑ and ↓). This is like a room having a maximum occupancy of two people.
These principles dictate the order in which electrons fill the various atomic orbitals, resulting in a unique electron configuration for each element.
Determining the Electron Configuration of Bromine
Bromine (Br) has an atomic number of 35, meaning it possesses 35 protons and 35 electrons in a neutral atom. To determine its electron configuration, we follow the Aufbau principle and fill the orbitals according to their energy levels:
1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶, 4s², 3d¹⁰, 4p⁵
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: The first energy level (n=1) contains the 1s subshell, which holds a maximum of two electrons.
- 2s²: The second energy level (n=2) begins with the 2s subshell, also holding two electrons.
- 2p⁶: The 2p subshell has three orbitals, each capable of holding two electrons, resulting in a total of six electrons.
- 3s², 3p⁶: The third energy level (n=3) follows the same pattern, with the 3s and 3p subshells holding two and six electrons respectively.
- 4s²: The fourth energy level (n=4) starts with the 4s subshell, accommodating two electrons.
- 3d¹⁰: The 3d subshell, despite being in the third energy level, has a higher energy than the 4s subshell and is filled next, holding ten electrons.
- 4p⁵: Finally, the 4p subshell, part of the fourth energy level, holds the remaining five electrons.
Orbital Diagram of Bromine
A more visual representation of bromine's electron configuration uses an orbital diagram. This shows the individual orbitals and the arrangement of electrons within them:
1s: ↑↓
2s: ↑↓
2p: ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓
3s: ↑↓
3p: ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓
4s: ↑↓
3d: ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓
4p: ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↑
Each arrow represents an electron, and the paired arrows indicate electrons with opposite spins. Notice the 4p subshell has one orbital with only one electron, demonstrating Hund's rule in action.
Significance of Bromine's Electron Configuration
Bromine's electron configuration is not merely a theoretical arrangement; it directly dictates its chemical properties and reactivity:
-
Valence Electrons: The outermost electrons, those in the 4s and 4p subshells (7 electrons in total), are called valence electrons. These electrons are responsible for bromine's chemical bonding and reactivity. Having seven valence electrons makes bromine highly reactive, as it readily gains one electron to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons) in its outermost shell, similar to the noble gas krypton.
-
Oxidation States: Bromine's electron configuration explains its ability to exhibit various oxidation states. It can easily gain one electron to form the bromide ion (Br⁻), with an oxidation state of -1. It can also lose electrons, although less readily, resulting in positive oxidation states.
-
Chemical Bonding: Bromine's tendency to gain one electron leads to the formation of ionic bonds with metals and covalent bonds with nonmetals. The resulting compounds have properties dictated by the nature of the bonds formed.
-
Reactivity: The relatively high electronegativity of bromine (its ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond) is a direct consequence of its electron configuration. This contributes to its reactivity with a wide range of elements and compounds.
Bromine's Role in Chemical Reactions and Compounds
The unique characteristics stemming from its electron configuration make bromine vital in various chemical reactions and compounds:
-
Halogen Family: Bromine belongs to the halogen family (Group 17), a group of highly reactive nonmetals. Its properties share similarities with other halogens, like chlorine and iodine, but also exhibit distinct differences.
-
Formation of Bromides: Bromine's strong tendency to gain an electron leads to the formation of various bromides. For instance, sodium bromide (NaBr) is a common ionic compound used in various applications.
-
Organic Chemistry: Bromine plays a crucial role in organic chemistry, often used as a reagent in halogenation reactions, where it adds a bromine atom to organic molecules. This is widely utilized in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
-
Industrial Applications: Bromine and its compounds find extensive applications in diverse industries, including agriculture (as fumigants), pharmaceuticals (in the synthesis of drugs), and water treatment (as disinfectants).
Beyond the Basic Configuration: Excited States and Ions
While the ground state electron configuration describes the most stable arrangement, bromine can also exist in excited states. In these states, one or more electrons are promoted to higher energy levels, resulting in a different electron configuration. These excited states play a role in bromine's interactions with light and in specific chemical reactions.
Furthermore, bromine can form ions, most notably the bromide ion (Br⁻), which has gained one electron and a complete octet in its outermost shell. This ion exhibits properties distinct from the neutral bromine atom.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Bromine's Electron Configuration
Understanding the electron configuration of bromine is paramount to comprehending its chemical behavior and its wide array of applications. From its reactivity and bonding to its role in chemical reactions and industrial processes, the arrangement of its electrons fundamentally determines its properties. This fundamental understanding is crucial in various scientific fields, particularly chemistry and materials science. The information presented here serves as a comprehensive guide, providing a deep understanding of bromine's electron configuration and its implications for its behavior and applications in diverse settings. This article's comprehensive coverage is designed for students, researchers and anyone seeking a detailed understanding of this crucial element. The clear explanation, combined with illustrative examples, aims to demystify the concept of electron configuration and its significance in understanding the properties and behaviors of bromine.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 2 10 As A Decimal
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is The O H Bond Polar Or Nonpolar
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 5 Percent Of 120
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Present In A Prokaryotic Cell
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Are Monomers And Polymers Related
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is The Electron Configuration For Bromine . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
