Is The O-h Bond Polar Or Nonpolar
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
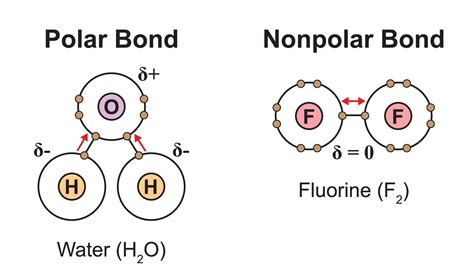
Table of Contents
Is the O-H Bond Polar or Nonpolar? A Deep Dive into Bond Polarity
The question of whether the O-H bond is polar or nonpolar is fundamental to understanding chemical bonding and the properties of numerous molecules crucial to life and various industrial applications. This article will delve deep into the concept of bond polarity, exploring the electronegativity differences that dictate bond character, and ultimately definitively answer the question regarding the O-H bond. We will also explore the implications of this polarity on the properties of molecules containing this bond, such as water.
Understanding Bond Polarity: Electronegativity's Crucial Role
The polarity of a chemical bond arises from the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond. Atoms with high electronegativity strongly pull electrons towards themselves, creating a partial negative charge (δ-), while the atom with lower electronegativity develops a partial positive charge (δ+).
A purely nonpolar covalent bond exists when the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is negligible, meaning the electrons are shared almost equally. This typically occurs when identical atoms bond (e.g., H₂ or O₂). Conversely, a polar covalent bond forms when there's a significant electronegativity difference, resulting in an uneven distribution of electron density. The greater the electronegativity difference, the more polar the bond.
Finally, an ionic bond represents the extreme case of polarity, where the electronegativity difference is so large that one atom essentially steals an electron from the other, forming ions with full positive and negative charges.
Electronegativity Values and the O-H Bond
To determine the polarity of the O-H bond, we need to examine the electronegativity values of oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H). Oxygen has a significantly higher electronegativity than hydrogen. While the exact values vary slightly depending on the scale used (Pauling, Mulliken, etc.), the relative difference remains consistent: oxygen is substantially more electronegative than hydrogen.
This significant electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen leads to an unequal sharing of electrons in the O-H bond. The oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, resulting in a partial negative charge (δ-) on the oxygen and a partial positive charge (δ+) on the hydrogen.
Therefore, the O-H bond is definitively polar.
Consequences of O-H Bond Polarity: Water as a Prime Example
The polar nature of the O-H bond has profound consequences for the properties of molecules containing this bond, most notably water (H₂O). Water's unique properties are directly attributable to the polarity of its O-H bonds and its resulting bent molecular geometry.
Hydrogen Bonding: A Consequence of Polarity
The partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom in one water molecule is attracted to the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom in a neighboring water molecule. This attractive force is called a hydrogen bond, a special type of dipole-dipole interaction. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds but significantly stronger than other intermolecular forces like van der Waals forces.
Hydrogen bonding is responsible for many of water's exceptional properties:
- High boiling point: The strong hydrogen bonds require considerable energy to break, leading to a relatively high boiling point compared to other molecules of similar molar mass.
- High surface tension: Hydrogen bonds create a strong cohesive force between water molecules, resulting in high surface tension.
- Excellent solvent: The polar nature of water allows it to effectively dissolve many ionic and polar substances. The partial charges in water molecules can interact with and surround ions or polar molecules, breaking them apart and keeping them in solution.
- High specific heat capacity: Water can absorb a significant amount of heat energy without a large temperature increase, due to the energy required to break the hydrogen bonds. This property is crucial for regulating temperature in living organisms.
- Density anomaly: Ice is less dense than liquid water, a phenomenon attributed to the hydrogen bonding network in ice, which creates a more open structure compared to liquid water.
Other Molecules with Polar O-H Bonds
The polar O-H bond is not limited to water. Many other important molecules contain this bond and exhibit properties influenced by its polarity. Examples include:
-
Alcohols (ROH): Alcohols, such as methanol (CH₃OH) and ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH), contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group, contributing to their polarity and solubility in water. The O-H bond in alcohols allows for hydrogen bonding with water molecules, enhancing their solubility.
-
Carboxylic acids (RCOOH): Carboxylic acids, such as acetic acid (CH₃COOH), possess both a carbonyl (C=O) and a hydroxyl (-OH) group. The polar O-H bond enables hydrogen bonding, contributing to the higher boiling points of carboxylic acids compared to aldehydes and ketones with similar molecular weights.
-
Sugars: Sugars, like glucose and fructose, contain multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups. The presence of these polar O-H bonds makes sugars readily soluble in water, a critical aspect of their biological roles.
-
Phenols (ArOH): Phenols contain a hydroxyl group directly attached to a benzene ring. The polarity of the O-H bond makes phenols weakly acidic.
Distinguishing Polar O-H Bonds from Nonpolar Bonds
It's crucial to contrast the polar O-H bond with examples of nonpolar bonds to solidify the understanding of electronegativity's role. A nonpolar bond, like the C-H bond, exhibits minimal electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen. The electrons are shared almost equally, resulting in a nonpolar bond with no significant dipole moment.
The presence of polar O-H bonds significantly alters the overall polarity and properties of a molecule compared to molecules with primarily nonpolar bonds. This difference in polarity has crucial implications for solubility, boiling points, intermolecular forces, and reactivity.
Applications and Importance
The understanding of the O-H bond's polarity is not merely an academic exercise; it has numerous practical applications across various fields:
- Chemistry: The knowledge of bond polarity is crucial for predicting the reactivity and behavior of molecules in chemical reactions.
- Biochemistry: Understanding the polarity of O-H bonds in biological molecules such as sugars, proteins, and nucleic acids is vital for comprehending their structure, function, and interactions.
- Materials Science: The properties of materials are often dictated by the types of bonds present. The polarity of O-H bonds plays a significant role in the design and synthesis of materials with specific properties, like solubility, hydrophilicity, and reactivity.
- Medicine: Many drugs and pharmaceuticals contain O-H bonds and their properties are directly influenced by this polarity. Understanding this aspect is key for drug design and delivery.
Conclusion: The Definitive Polarity of O-H
In conclusion, the O-H bond is unequivocally polar due to the substantial electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen. This polarity leads to crucial consequences for the properties of molecules containing O-H bonds, particularly hydrogen bonding, which influences many key properties like boiling point, solubility, and intermolecular interactions. The understanding of this polarity is central to various scientific fields, emphasizing its importance in both theoretical and practical contexts. From the life-sustaining properties of water to the design of new materials and pharmaceuticals, the polar nature of the O-H bond remains a cornerstone of chemical understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Gcf Of 36 And 54
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does N Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Horizontal Rows Of The Periodic Table Are Called
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Do Neon Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is 53 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The O-h Bond Polar Or Nonpolar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
