What Is Terminal Side Of An Angle
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
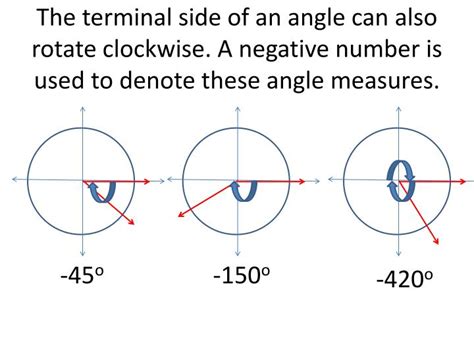
Table of Contents
What is the Terminal Side of an Angle? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the terminal side of an angle is fundamental to grasping trigonometry and its applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition, properties, and significance of the terminal side, providing you with a solid foundation for further exploration of trigonometric concepts. We'll explore various scenarios, including angles in standard position and angles exceeding 360 degrees. By the end, you'll be confident in identifying and working with the terminal side of any angle.
Defining the Terminal Side of an Angle
Before diving into the specifics of the terminal side, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes an angle in the context of trigonometry. An angle is formed by two rays originating from a common point called the vertex. One ray is considered the initial side, typically lying along the positive x-axis, and the other is the terminal side, which rotates around the vertex. The direction of rotation determines whether the angle is positive (counterclockwise) or negative (clockwise).
Think of it like the hands of a clock. The initial side is like the hour hand at 12 o'clock, always pointing to the right along the positive x-axis. The terminal side is like the minute hand, which sweeps around the clock face. The extent to which the minute hand sweeps indicates the measure of the angle.
The terminal side, therefore, is the ray that results after the rotation from the initial side to define the angle's measure. Its position uniquely identifies the angle in a coordinate plane. This position is crucial because it dictates the values of trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, etc.) associated with that angle.
Standard Position: The Foundation for Understanding
Angles are often drawn in standard position, meaning the initial side aligns with the positive x-axis, and the vertex is located at the origin (0,0) of the coordinate plane. This convention simplifies calculations and allows for a consistent understanding of the angle's properties. Once an angle is in standard position, locating the terminal side becomes a straightforward task involving rotating counterclockwise (for positive angles) or clockwise (for negative angles).
Angles Greater Than 360 Degrees (or 2π radians)
It's important to remember that angles are not limited to a single rotation. An angle can rotate multiple times around the origin. For instance, an angle of 450 degrees represents one full rotation (360 degrees) plus an additional 90-degree rotation. Even though the angle has rotated more than once, the terminal side's position is what determines the trigonometric values. In this case, the terminal side would be the same as for a 90-degree angle.
Similarly, negative angles can also exceed a full rotation. For example, an angle of -450 degrees represents a full clockwise rotation (-360 degrees) followed by another -90-degree rotation. Again, the terminal side determines the trigonometric values, which will be the same as for a -90-degree angle.
Determining the Quadrant of the Terminal Side
The location of the terminal side within the four quadrants of the coordinate plane (I, II, III, and IV) significantly impacts the signs of the trigonometric functions. Understanding how to determine the quadrant is key to successfully solving trigonometric problems.
-
Quadrant I (0° < θ < 90° or 0 < θ < π/2): The terminal side lies in the upper-right quadrant. All trigonometric functions are positive.
-
Quadrant II (90° < θ < 180° or π/2 < θ < π): The terminal side lies in the upper-left quadrant. Only sine and cosecant are positive.
-
Quadrant III (180° < θ < 270° or π < θ < 3π/2): The terminal side lies in the lower-left quadrant. Only tangent and cotangent are positive.
-
Quadrant IV (270° < θ < 360° or 3π/2 < θ < 2π): The terminal side lies in the lower-right quadrant. Only cosine and secant are positive.
By knowing the angle's measure, you can easily determine the quadrant in which the terminal side resides and, consequently, anticipate the signs of the trigonometric functions. This is especially crucial when solving trigonometric equations or interpreting trigonometric graphs.
The Terminal Side and Trigonometric Functions
The terminal side's position is inextricably linked to the values of the trigonometric functions. Consider a point (x, y) on the terminal side of an angle θ, where r is the distance from the origin to this point (r = √(x² + y²)). Then:
-
sin θ = y/r
-
cos θ = x/r
-
tan θ = y/x
-
csc θ = r/y
-
sec θ = r/x
-
cot θ = x/y
These ratios are defined based on the coordinates of the point on the terminal side and the distance from the origin. The values of these functions directly reflect the position and angle of the terminal side.
Applications of Terminal Side Understanding
The concept of the terminal side is not merely a theoretical construct; it has numerous practical applications across various fields:
1. Navigation and Surveying
In navigation and surveying, angles are used to determine positions and distances. Understanding the terminal side allows for accurate calculations of bearings and coordinates, crucial for tasks such as mapping, route planning, and land surveying.
2. Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, angles and their terminal sides play a vital role in analyzing forces, velocities, and other vector quantities. Understanding the terminal side facilitates resolving vectors into their components and performing vector calculations. This is applicable to fields like mechanics, electricity, and optics.
3. Computer Graphics and Game Development
The terminal side concept is fundamental in computer graphics and game development for transformations, rotations, and positioning of objects in 2D and 3D spaces. Precise control over the terminal side allows for the creation of realistic and visually appealing graphics.
4. Astronomy
In astronomy, the positions of celestial bodies are often described using angles. Understanding the terminal side helps in determining the apparent positions of stars and planets, crucial for navigation and astronomical observations.
Solving Problems Involving Terminal Sides
Let's illustrate the practical application with a few examples:
Example 1: Find the terminal side's quadrant for an angle of 225°.
Solution: 225° lies between 180° and 270°, placing it in Quadrant III.
Example 2: An angle has a terminal side passing through the point (-3, 4). Find the trigonometric functions.
Solution: First, find r: r = √((-3)² + 4²) = 5. Then:
- sin θ = 4/5
- cos θ = -3/5
- tan θ = -4/3
- csc θ = 5/4
- sec θ = -5/3
- cot θ = -3/4
Example 3: Determine the angle if its terminal side passes through (1, -√3).
Solution: Calculate r: r = √(1² + (-√3)²) = 2. We have cos θ = 1/2 and sin θ = -√3/2. This indicates θ = 300° (or 5π/3 radians).
Conclusion: Mastering the Terminal Side
The terminal side of an angle is a cornerstone concept in trigonometry. Understanding its definition, properties, and relationship with trigonometric functions is crucial for mastering trigonometry and its various applications. By consistently practicing problem-solving and visualizing angles in standard position, you will develop a strong intuitive grasp of this vital concept. This will empower you to tackle complex trigonometric problems with confidence and apply trigonometric principles in various real-world scenarios. Remember to always visualize the angle and its terminal side in the coordinate plane to solidify your understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Half A Mile In Feet
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Percent Of 12 5 Is 39
Mar 26, 2025
-
Empirical And Molecular Formula Of Ibuprofen
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of So2
Mar 26, 2025
-
Electrons In The Outermost Energy Level Are Called
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Terminal Side Of An Angle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
