What Is Prime Factorization Of 63
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
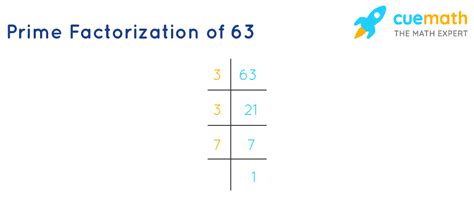
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 63? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, plays a crucial role in various mathematical fields and applications. Understanding this concept unlocks doors to more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques. This article will explore the prime factorization of 63, explaining the process in detail, discussing its significance, and exploring related concepts within number theory.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before diving into the prime factorization of 63, it's essential to grasp the definition of a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite.
The concept of prime numbers is fundamental because every other natural number greater than 1 can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This unique representation is the essence of prime factorization.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, give the original number. Every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be uniquely factored into a product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
The prime factorization of a number is typically expressed using exponents to indicate repeated prime factors. For instance, the prime factorization of 12 is 2² x 3, meaning 2 multiplied by itself twice (2 x 2), then multiplied by 3, equals 12.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 63
Now, let's determine the prime factorization of 63. We can use a few methods:
Method 1: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until we reach 1.
- Start with 63. The smallest prime number is 2. 63 is not divisible by 2 (it's an odd number).
- Try the next prime number, 3. 63 divided by 3 is 21.
- Now we have 21. 21 is also divisible by 3, resulting in 7.
- We are left with 7. 7 is a prime number itself.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 63 is 3 x 3 x 7, which can be written as 3² x 7.
Method 2: Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual representation of the factorization process.
63
/ \
3 21
/ \
3 7
We start with 63 and find two factors (3 and 21). We continue breaking down composite factors until we're left with only prime numbers at the bottom of the tree. Again, this leads us to the prime factorization: 3² x 7.
Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number might seem like a simple concept, but its implications are far-reaching:
-
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (disregarding the order of the factors). This unique representation forms the basis for many other mathematical concepts.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization simplifies the calculation of the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is divisible by all the given numbers.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are crucial in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The security of these systems relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Prime factorization is essential in various applications of modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory dealing with remainders after division.
-
Algebra and Polynomial Factorization: The concepts used in prime factorization extend to factoring polynomials, a crucial skill in algebra.
Beyond 63: Exploring Other Factorizations
Let's briefly explore the prime factorizations of some numbers related to 63:
- 62: 2 x 31
- 64: 2⁶
- 65: 5 x 13
- 66: 2 x 3 x 11
Notice how each number has its unique prime factorization, highlighting the fundamental theorem of arithmetic.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
While prime factorization might seem abstract, its applications are surprisingly practical:
-
Simplifying Fractions: To simplify a fraction, find the GCD of the numerator and denominator using prime factorization. Dividing both by the GCD reduces the fraction to its simplest form.
-
Solving Word Problems: Many word problems involving ratios, proportions, or divisibility can be solved more efficiently using prime factorization.
-
Computer Science: Prime factorization algorithms are used in various areas of computer science, including cryptography and data compression.
Advanced Concepts Related to Prime Factorization
For those interested in delving deeper, here are some advanced concepts connected to prime factorization:
-
The Riemann Hypothesis: This unsolved problem in number theory deals with the distribution of prime numbers and has significant implications for various mathematical fields.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm is an efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
-
Miller-Rabin Primality Test: This probabilistic test is used to determine whether a given number is likely prime. It's particularly useful for testing very large numbers.
Conclusion
The prime factorization of 63, 3² x 7, serves as a simple yet powerful illustration of a fundamental concept in number theory. Understanding prime factorization unlocks the ability to solve a wide range of mathematical problems and provides a foundation for more advanced concepts in algebra, number theory, and cryptography. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, impacting various fields from computer science to cryptography. By exploring this seemingly simple concept, we gain access to a world of mathematical richness and complexity. The unique factorization of numbers into primes is a testament to the beauty and elegance of mathematics itself. Further exploration into these concepts will undoubtedly reveal even more fascinating aspects of this fundamental mathematical principle.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Terminal Side Of An Angle
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Monomers And Polymers Are Related
Mar 25, 2025
-
Elements In Group 3 12 Are Called
Mar 25, 2025
-
List The Color Of The Stars From Hottest To Coldest
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Trunk In Anatomy
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 63 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
