Number Of Valence Electrons In Calcium
listenit
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
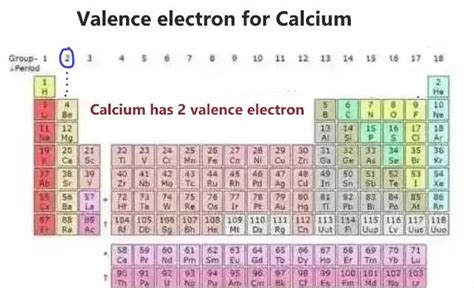
Table of Contents
Number of Valence Electrons in Calcium: A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
Calcium, a vital element for life and a cornerstone of many industrial processes, plays a significant role in various chemical reactions. Understanding its behavior necessitates a thorough understanding of its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons. This article delves deep into the concept of valence electrons, explains how to determine the number of valence electrons in calcium, and explores its implications for calcium's chemical reactivity and bonding characteristics.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Behavior
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. They are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. These electrons reside in the highest principal energy level (shell) of an atom's electron configuration. The number of valence electrons directly influences an element's position on the periodic table and its chemical properties. Elements in the same group (vertical column) share the same number of valence electrons, explaining their similar chemical behaviors.
Importance of Valence Electrons in Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonds are formed through the interaction of valence electrons. These interactions can take several forms:
- Ionic Bonds: Formed by the transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions (charged atoms). This is common between atoms with significantly different electronegativities, typically a metal and a nonmetal.
- Covalent Bonds: Formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms. This is common between nonmetals where the electronegativity difference is small.
- Metallic Bonds: Found in metals where valence electrons are delocalized and form a "sea" of electrons that are shared among many metal atoms.
The number of valence electrons an atom possesses dictates the number of bonds it can form and the geometry of the resulting molecule or crystal structure.
Determining the Number of Valence Electrons in Calcium (Ca)
Calcium (Ca) is an alkaline earth metal located in Group 2 of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 20, indicating it has 20 protons and, in a neutral atom, 20 electrons. To determine the number of valence electrons, we need to examine its electron configuration.
Electron Configuration of Calcium
The electron configuration of calcium is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s². This notation describes the arrangement of electrons within different energy levels and sublevels:
- 1s²: Two electrons in the first energy level (n=1), in the s sublevel.
- 2s²2p⁶: Eight electrons in the second energy level (n=2), two in the s sublevel and six in the p sublevel.
- 3s²3p⁶: Eight electrons in the third energy level (n=3), two in the s sublevel and six in the p sublevel.
- 4s²: Two electrons in the fourth energy level (n=4), in the s sublevel.
The outermost electrons are located in the 4s sublevel. Therefore, calcium has two valence electrons.
Understanding the Periodic Table and Valence Electrons
The periodic table is organized in a way that simplifies the determination of valence electrons. Group numbers (using the American system) directly relate to the number of valence electrons for main group elements (Groups 1-2 and 13-18).
- Group 1 (Alkali Metals): 1 valence electron
- Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals): 2 valence electrons
- Group 13 (Boron Group): 3 valence electrons
- Group 14 (Carbon Group): 4 valence electrons
- Group 15 (Pnictogens): 5 valence electrons
- Group 16 (Chalcogens): 6 valence electrons
- Group 17 (Halogens): 7 valence electrons
- Group 18 (Noble Gases): 8 valence electrons (except Helium with 2)
Since Calcium belongs to Group 2, we can immediately infer that it possesses two valence electrons. This is a convenient shortcut for determining valence electrons for main group elements.
Chemical Implications of Calcium's Two Valence Electrons
The presence of two valence electrons significantly influences calcium's chemical properties and reactivity:
Reactivity and Ionic Bonding
Calcium readily loses its two valence electrons to achieve a stable octet (a full outer shell of eight electrons) similar to the noble gas Argon. This loss of electrons leads to the formation of a Ca²⁺ ion, a cation with a +2 charge. This tendency to lose electrons makes calcium highly reactive, especially with nonmetals that have a high electronegativity, such as oxygen and chlorine.
The reaction with oxygen, for instance, produces calcium oxide (CaO), an ionic compound where calcium loses two electrons to oxygen, forming ionic bonds.
Metallic Bonding and Properties
Calcium, being a metal, also exhibits metallic bonding. Its two valence electrons are delocalized, contributing to the "sea" of electrons that bind the calcium atoms together. This explains calcium's characteristic metallic properties such as:
- Good electrical conductivity: The delocalized electrons are free to move and carry an electric current.
- Good thermal conductivity: The delocalized electrons can efficiently transfer thermal energy.
- Malleability and ductility: The metallic bonding allows the atoms to slide past each other without breaking the bonds.
- Luster: The delocalized electrons interact with light, giving calcium its characteristic metallic sheen.
Calcium's Role in Biological Systems and Industrial Applications
The chemical properties stemming from its two valence electrons make calcium crucial for various biological and industrial processes.
Biological Significance
Calcium is an essential element for numerous biological functions. Its role in maintaining strong bones and teeth is well known. However, its involvement extends far beyond skeletal structure, including:
- Muscle contraction: Calcium ions act as a signaling molecule in muscle cells, initiating muscle contraction.
- Nerve impulse transmission: Calcium ions play a crucial role in the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Blood clotting: Calcium ions are essential for the coagulation process.
- Enzyme activation: Many enzymes require calcium ions for their activity.
Industrial Applications
Calcium's reactivity and properties make it valuable in various industrial applications:
- Production of steel: Calcium is used as an alloying element in steel production, enhancing its properties.
- Cement production: Calcium compounds are major components of cement, providing strength and durability.
- Dehydrating agent: Calcium oxide (quicklime) is a potent dehydrating agent, absorbing water from various substances.
- Reducing agent: Calcium is used as a reducing agent in the extraction of certain metals from their ores.
Conclusion: The Significance of Valence Electrons in Understanding Calcium
The number of valence electrons in an atom is fundamental to understanding its chemical behavior. Calcium, with its two valence electrons, exhibits properties typical of alkaline earth metals – high reactivity, tendency to form +2 ions, and metallic bonding. These properties lead to its crucial roles in biological systems and various industrial processes. Understanding the electron configuration and the implications of valence electrons provides a crucial foundation for comprehending the chemical and physical characteristics of calcium and its importance in the world around us. From the strength of our bones to the construction of modern buildings, calcium’s chemical behavior, dictated by its two valence electrons, plays a critical and multifaceted role.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Dissolution Of Sodium Chloride In Water
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which State Of Matter Takes The Shape Of Its Container
Apr 03, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 145
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 24 And 32
Apr 03, 2025
-
X 3y 9 In Slope Intercept Form
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Valence Electrons In Calcium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
