Mars Distance From The Sun In Au
listenit
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
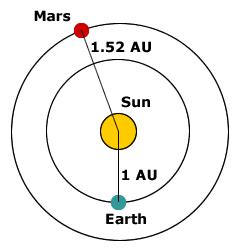
Table of Contents
Mars' Distance from the Sun in AU: A Comprehensive Exploration
Mars, the fourth planet from our Sun, holds a captivating allure for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. Its reddish hue, potential for past or present life, and intriguing geological features have fueled countless explorations and scientific investigations. Understanding Mars' orbital characteristics, particularly its distance from the Sun, is crucial to comprehending its climate, geological processes, and potential for habitability. This article delves deep into Mars' distance from the Sun, expressed in astronomical units (AU), exploring its variations, implications, and the methods used to determine this vital parameter.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
Before we embark on our exploration of Mars' distance, let's establish a clear understanding of the astronomical unit (AU). An AU is a unit of length roughly equal to the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. It's a crucial measurement in astronomy because it provides a convenient scale for expressing the vast distances within our solar system. While the exact value of an AU is constantly being refined through increasingly precise measurements, it's generally accepted to be approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles).
Using AU as a unit simplifies calculations and comparisons of planetary distances. Instead of dealing with cumbersome numbers in kilometers or miles, we can express distances in terms of the relatively familiar Earth-Sun distance. For example, Jupiter's average distance from the Sun might be described as 5.2 AU, meaning it's about 5.2 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
Mars' Average Distance from the Sun in AU
Mars' orbit around the Sun is elliptical, meaning it's not a perfect circle. This elliptical shape results in variations in Mars' distance from the Sun throughout its orbital journey. However, we can define an average distance, which is approximately 1.52 AU. This means that on average, Mars is about 1.52 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
This seemingly small difference in distance has profound consequences for Mars' environment. The reduced solar radiation received by Mars compared to Earth leads to significantly colder temperatures and a thinner atmosphere. This difference also plays a significant role in the planet's seasonal variations and the dynamics of its thin atmosphere.
Variations in Mars' Distance from the Sun
The elliptical nature of Mars' orbit means its distance from the Sun is not constant. At its perihelion (closest point to the Sun), Mars is approximately 1.38 AU away. Conversely, at its aphelion (farthest point from the Sun), it reaches a distance of roughly 1.67 AU. This variation of about 0.29 AU represents a considerable difference in solar radiation received by the planet.
These variations in distance influence the intensity of solar radiation impacting Mars' surface, affecting its temperature and influencing the processes within its thin atmosphere. The difference between perihelion and aphelion also contributes to the length of Martian seasons, as Mars moves faster when closer to the Sun and slower when farther away. The seasonal variations on Mars are more pronounced than on Earth because of the combination of its elliptical orbit and axial tilt.
Calculating Mars' Distance from the Sun
Determining Mars' distance from the Sun is a complex process involving sophisticated astronomical techniques. Historically, astronomers used methods like parallax and Kepler's laws to estimate planetary distances. Parallax involves measuring the apparent shift in a planet's position as observed from different points on Earth's orbit. Kepler's laws, derived from observations of planetary motion, provide a mathematical framework for calculating planetary distances based on their orbital periods.
Modern methods utilize advanced techniques such as radar ranging, spacecraft tracking, and astrometric observations. Radar ranging involves sending radio waves to a planet and measuring the time it takes for the signal to return. This provides a highly accurate measurement of the distance. Spacecraft tracking involves monitoring the precise position and velocity of spacecraft orbiting Mars, which provides detailed information about the planet's orbit and distance from the Sun. Astrometric observations use highly sensitive telescopes to measure the precise positions of celestial bodies, providing data that refine our understanding of planetary orbits.
These sophisticated techniques have greatly improved the accuracy of Mars' distance calculations, leading to increasingly precise values for its average, perihelion, and aphelion distances. The ongoing refinement of these measurements contributes to our evolving understanding of the Martian environment and its potential for past or present life.
Implications of Mars' Distance from the Sun
The distance of Mars from the Sun profoundly influences several key aspects of the planet:
1. Temperature and Climate:
The decreased solar radiation at Mars' greater distance results in significantly lower average surface temperatures compared to Earth. Mars experiences extreme temperature variations between day and night, and the thin atmosphere provides minimal insulation.
2. Atmospheric Pressure:
The reduced solar radiation likely contributes to Mars' thin atmosphere. The weak gravitational pull coupled with the lack of a global magnetic field means that solar wind can easily strip away atmospheric particles.
3. Water and Ice:
Mars' distance from the Sun plays a crucial role in the planet's water cycle, or lack thereof. The low temperatures mean that liquid water is generally unstable on the surface, primarily existing as ice in the polar regions and possibly underground.
4. Seasonal Variations:
The combination of Mars' elliptical orbit and axial tilt leads to pronounced seasonal variations in temperature and atmospheric conditions. The length of Martian seasons is also affected by the variations in its orbital speed.
Future Missions and Research
The ongoing exploration of Mars involves numerous missions aimed at deepening our understanding of its geology, climate, and potential for life. Future missions will continue to refine our measurements of Mars' distance from the Sun and its implications for the planet's environment. Data from orbiters, landers, and rovers will contribute to increasingly accurate models of Mars' climate and geological history.
The study of Mars' distance from the Sun isn't just about a simple numerical value; it's about understanding the fundamental forces that shape a planet's environment and its potential for life. Every refinement of this measurement brings us closer to unlocking the secrets of the red planet.
Conclusion
Mars' distance from the Sun, expressed in AU, is a fundamental parameter in understanding its environment. While its average distance is approximately 1.52 AU, the elliptical nature of its orbit results in significant variations throughout its year. These variations in distance have profound consequences for Mars' temperature, atmosphere, water cycle, and seasonal changes. The precise determination of Mars' distance relies on advanced astronomical techniques, and ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of this crucial factor. By continuing to explore and study this fascinating planet, we can gain valuable insights into the formation and evolution of planetary systems, and the potential for life beyond Earth. The ongoing quest to unravel the mysteries of Mars promises exciting discoveries in the years to come, and the simple yet crucial measurement of its distance from the Sun remains a central element in this ongoing scientific endeavor. Understanding this distance is not merely an academic exercise; it's the cornerstone of our efforts to understand Mars' past, present, and potential future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Unpaired Electrons Does Manganese Have
Apr 04, 2025
-
Water Is Made Up Of Which Two Elements
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is 9 Percent Of 50
Apr 04, 2025
-
Distance From Earth To Pluto In Light Years
Apr 04, 2025
-
Molar Mass Of Copper 2 Sulfate
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mars Distance From The Sun In Au . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
