Lowest Common Multiple Of 21 And 28
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
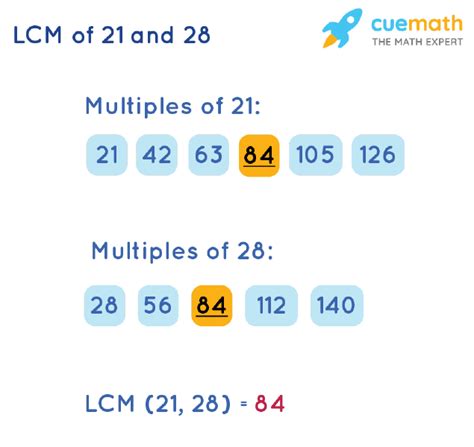
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 21 and 28: A Comprehensive Guide
The lowest common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in algebra and number theory. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods of calculating the LCM of 21 and 28, providing a thorough understanding of the underlying principles and showcasing multiple approaches for finding the solution. We'll also explore the broader significance of LCM and its practical applications.
Understanding the Concept of LCM
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 21 and 28, let's establish a clear understanding of what the lowest common multiple actually is. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be divided evenly by all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 21 and 28
Several methods can be employed to determine the LCM of 21 and 28. We will explore three prominent approaches: the listing method, the prime factorization method, and the greatest common divisor (GCD) method.
1. The Listing Method
This method, while straightforward for smaller numbers, can become cumbersome for larger ones. It involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
Multiples of 21: 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, 126, 147, 168, 189, 210...
Multiples of 28: 28, 56, 84, 112, 140, 168, 196, 224, 252, 280...
By comparing the lists, we can observe that the smallest common multiple is 84. Therefore, the LCM of 21 and 28 is 84.
While this method is simple to understand, it's not the most efficient, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
2. The Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient and systematic, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present in the factorizations.
Prime factorization of 21: 3 x 7
Prime factorization of 28: 2 x 2 x 7 = 2² x 7
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7
Now, we multiply these highest powers together: 2² x 3 x 7 = 4 x 3 x 7 = 84
Therefore, the LCM of 21 and 28 using the prime factorization method is 84. This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and systematic approach.
3. The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two numbers. The formula connecting LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
First, we need to find the GCD of 21 and 28. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- 28 = 21 x 1 + 7
- 21 = 7 x 3 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 7, so the GCD(21, 28) = 7.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(21, 28) x GCD(21, 28) = 21 x 28
LCM(21, 28) x 7 = 588
LCM(21, 28) = 588 / 7 = 84
This method provides another efficient way to calculate the LCM, especially when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization might be more challenging.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has far-reaching applications in various fields:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires finding the LCM of the denominators.
-
Scheduling Problems: Determining when events with different repeating cycles will coincide (e.g., two buses arriving at a stop at different intervals).
-
Gear Ratios: Calculating gear ratios in mechanical engineering often involves the concept of LCM.
-
Music Theory: Understanding rhythmic patterns and finding common musical phrases involves the LCM of note durations.
-
Computer Science: LCM is used in algorithms and data structures, especially in tasks involving modular arithmetic.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements and alignments in construction projects often require the use of LCM for accurate calculations.
Conclusion: The LCM of 21 and 28 is 84
We have explored three different methods to calculate the lowest common multiple of 21 and 28, demonstrating that the LCM is 84. The choice of method depends on the context and the complexity of the numbers involved. The prime factorization method is generally recommended for its efficiency and systematic approach, while the listing method is useful for simpler cases. Understanding the LCM and its calculation is essential for various mathematical and practical applications, making it a fundamental concept to grasp. The significance of LCM extends beyond simple mathematical exercises, highlighting its practical utility in diverse fields. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for anyone seeking to understand and apply the concept of LCM in various situations. Remember to choose the method that best suits your needs and always double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Decay Of Carbon 14 By Beta Emission Equation
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 192
Mar 26, 2025
-
Neurotransmitter That Stimulates Skeletal Muscle Contraction
Mar 26, 2025
-
Can Steroid Hormones Cross The Cell Membrane
Mar 26, 2025
-
4a 3 A 2 2 3a 2
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 21 And 28 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
