Is Sohcahtoa Only For Right Triangles
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
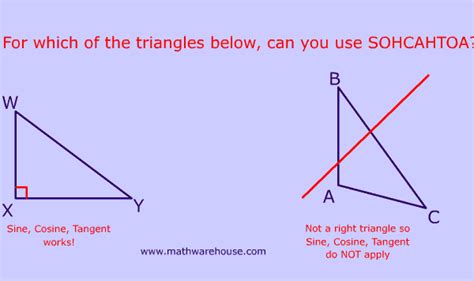
Table of Contents
Is SOHCAHTOA Only for Right Triangles? Understanding Trigonometric Functions in Different Contexts
SOHCAHTOA, the mnemonic device for remembering the fundamental trigonometric ratios (Sine, Cosine, and Tangent), is deeply ingrained in the minds of anyone who's taken high school trigonometry. But a common question arises: Is SOHCAHTOA only for right-angled triangles? The short answer is yes, in its basic, introductory form. However, the trigonometric functions themselves are far more versatile and applicable to a much broader range of scenarios beyond the right-angled triangle. Let's delve deeper into this fascinating topic.
Understanding SOHCAHTOA and its Limitations
SOHCAHTOA provides a simple framework for understanding sine, cosine, and tangent in the context of a right-angled triangle:
- Sine (sin) = Opposite / Hypotenuse
- Cosine (cos) = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
- Tangent (tan) = Opposite / Adjacent
Where:
- Opposite refers to the side opposite the angle in question.
- Adjacent refers to the side adjacent to the angle in question.
- Hypotenuse is the longest side, opposite the right angle.
This mnemonic is incredibly useful for solving problems involving right-angled triangles, allowing us to find unknown angles or side lengths given sufficient information. But its reliance on the right angle inherently limits its direct application to other triangle types.
Extending Trigonometry Beyond Right Triangles: The Unit Circle
To understand how trigonometry extends beyond right triangles, we need to introduce the unit circle. The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin (0,0) of a Cartesian coordinate system. This seemingly simple construct is the key to unlocking the true power and generality of trigonometric functions.
By placing an angle θ (theta) in standard position (with its vertex at the origin and its initial side along the positive x-axis), we can define the trigonometric functions in terms of the coordinates of the point where the terminal side of the angle intersects the unit circle.
Let's call this point (x, y). Then:
- cos θ = x (the x-coordinate of the point)
- sin θ = y (the y-coordinate of the point)
- tan θ = y/x (the ratio of the y-coordinate to the x-coordinate)
This definition holds true regardless of whether the angle is acute, obtuse, reflex, or even negative. The unit circle provides a consistent framework for defining trigonometric functions for any angle.
Applying Trigonometric Functions to Oblique Triangles: The Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines
Oblique triangles, triangles without a right angle, require different approaches for solving. Here's where two powerful tools come into play:
The Law of Sines
The Law of Sines establishes a relationship between the angles and sides of any triangle:
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
where:
- a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides opposite angles A, B, and C respectively.
This law is particularly useful when we know two angles and one side (AAS or ASA) or two sides and an angle opposite one of them (SSA – ambiguous case).
The Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines provides another crucial relationship for solving oblique triangles:
a² = b² + c² - 2bc cos A
(and similarly for b² and c²)
This law is essential when we know three sides (SSS) or two sides and the included angle (SAS).
Understanding the Relationship between SOHCAHTOA and the Unit Circle
While SOHCAHTOA is limited to right-angled triangles, it provides the foundational understanding for grasping the unit circle definition. Consider a right-angled triangle inscribed within the unit circle. The hypotenuse becomes the radius (1 unit), and the opposite and adjacent sides directly correlate with the x and y coordinates on the unit circle. This clarifies how the ratios from SOHCAHTOA seamlessly transition into the unit circle definitions of sine, cosine, and tangent.
Trigonometric Functions in Higher Dimensions and Calculus
The applications of trigonometric functions extend far beyond the realm of triangles. They are fundamental tools in:
- Calculus: Derivatives and integrals of trigonometric functions are crucial for solving numerous problems in physics, engineering, and other fields.
- Vectors and Linear Algebra: Trigonometric functions play a vital role in representing and manipulating vectors, particularly in determining their components and magnitudes.
- Complex Numbers: Trigonometric functions form the basis of Euler's formula, which connects complex exponentials and trigonometric functions, providing powerful tools for analyzing and manipulating complex numbers.
- Physics and Engineering: From analyzing wave phenomena (sound, light, electromagnetism) to solving problems involving rotational motion and projectile trajectories, trigonometric functions are indispensable.
Advanced Applications: Beyond the Basics
The power of trigonometric functions becomes even more apparent in advanced applications:
- Fourier Analysis: This technique uses trigonometric functions to decompose complex periodic functions into simpler sinusoidal components, enabling the analysis of various signals and data sets.
- Signal Processing: Trigonometric functions are critical for understanding and manipulating signals in areas like audio processing, image processing, and telecommunications.
- Computer Graphics: Trigonometric functions are essential for rendering 3D graphics, calculating transformations, and defining curves and surfaces.
- Cartography and Navigation: Trigonometry plays a significant role in mapping, geodesy, and navigation systems by enabling precise calculations of distances, angles, and locations.
Conclusion: SOHCAHTOA is a Starting Point
While SOHCAHTOA serves as an excellent introduction to trigonometry and is perfectly suited for solving problems involving right-angled triangles, it's essential to recognize its limitations. The unit circle definition of trigonometric functions provides a more robust and comprehensive framework, applicable to any angle and extending the power of trigonometry to far-reaching applications across diverse fields. Understanding this broader context allows you to appreciate the true versatility and significance of trigonometric functions in mathematics, science, and engineering. The fundamental ratios established by SOHCAHTOA remain valuable, but they form only the foundation upon which a more complete and powerful understanding of trigonometry is built. Moving beyond this basic introduction unlocks the vast potential of this crucial mathematical tool.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Factor Of 7 And 9
Mar 28, 2025
-
2 Protons 2 Neutrons 2 Electrons
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Can The P Orbital Hold
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is Another Name For Newtons First Law
Mar 28, 2025
-
Earth Would Not Have Seasons If It
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Sohcahtoa Only For Right Triangles . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
