2 Protons 2 Neutrons 2 Electrons
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
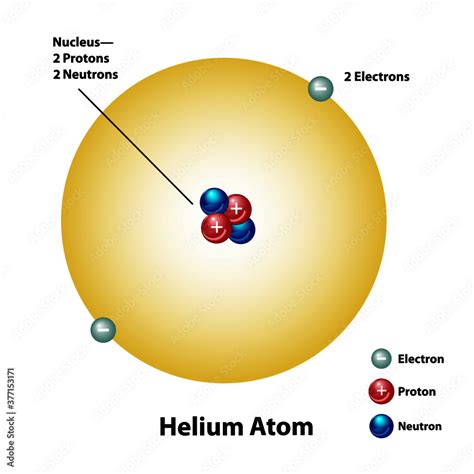
Table of Contents
2 Protons, 2 Neutrons, 2 Electrons: Delving into the World of Helium
The seemingly simple combination of 2 protons, 2 neutrons, and 2 electrons might appear unremarkable at first glance. However, this configuration defines helium, a noble gas with profound implications across various scientific fields and everyday life. This article delves deep into the properties, behaviors, and significance of helium, exploring its atomic structure, unique characteristics, and widespread applications.
Understanding the Atomic Structure of Helium
Helium's atomic structure, with its 2 protons, 2 neutrons (in the most common isotope, Helium-4), and 2 electrons, is the foundation for its unique properties. Let's break it down:
Protons: The Defining Identity
The two protons in the nucleus define helium as a chemical element. The atomic number of an element corresponds to the number of protons in its nucleus, and for helium, this number is 2. This is what distinguishes helium from all other elements on the periodic table. The positive charge carried by these protons is crucial for the atom's overall neutrality, balanced by the negative charge of the electrons.
Neutrons: Nuclear Stability
The two neutrons residing alongside the protons within the helium nucleus contribute to its stability. Neutrons, while electrically neutral, play a significant role in holding the nucleus together against the electrostatic repulsion between the positively charged protons. The presence of neutrons is vital for the nuclear stability of most atoms, and their absence or imbalance can lead to radioactivity. The common isotope of helium, Helium-4, has a particularly stable nucleus due to its even number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes with a different number of neutrons, like Helium-3 (one neutron), exist, though they are less common.
Electrons: Defining Chemical Behavior
The two electrons in helium orbit the nucleus in a configuration dictated by quantum mechanics. In helium's case, these two electrons fill the lowest energy level, the 1s orbital. This complete electron shell is the key to understanding helium's inertness and remarkable chemical stability. A filled electron shell represents a highly stable electronic configuration; electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus, making it extremely difficult for helium to participate in chemical reactions.
Unique Properties of Helium: Inertness and Low Density
Helium's atomic structure directly contributes to its distinctive physical and chemical properties. Two key characteristics stand out:
Chemical Inertness: The Noble Gas
Helium's inertness is perhaps its most defining characteristic. Due to its completely filled electron shell, helium rarely interacts with other atoms to form chemical compounds. This makes it a noble gas, a group of elements known for their stability and reluctance to react. This lack of reactivity has profound consequences for its use in various applications, where its inertness prevents unwanted chemical reactions.
Low Density: Lighter Than Air
Helium possesses an exceptionally low density, making it lighter than air. This property is crucial for its use in balloons, airships, and other applications where buoyancy is required. The low density arises from the small mass of the helium atom, a consequence of its small number of protons and neutrons. This low density also influences helium's behavior in other contexts, impacting its diffusion rate and its use in specific scientific instruments.
The Significance of Helium in Various Fields
Helium's unique properties make it invaluable across a diverse range of fields:
Scientific and Industrial Applications
-
Cryogenics: Helium's extremely low boiling point (-268.93 °C or -452.07 °F) makes it essential as a cryogenic refrigerant. It is used to cool superconducting magnets in MRI machines, particle accelerators, and other scientific instruments. The ability to achieve extremely low temperatures with helium is critical for many advanced technologies.
-
Welding: Helium is used as a shielding gas in welding processes, preventing oxidation and contamination of the weld. Its inertness protects the weld metal from atmospheric reactions, ensuring high-quality welds.
-
Leak Detection: Helium's small atomic size and inertness allow it to penetrate even tiny leaks, making it ideal for leak detection in various systems, from vacuum chambers to industrial pipelines.
-
Calibration of Instruments: The precise and predictable behavior of helium under varying conditions make it a standard for calibrating various scientific instruments and equipment.
Medical Applications
-
MRI Machines: As mentioned above, helium is crucial in the cooling of superconducting magnets in MRI machines, enabling the production of strong magnetic fields essential for generating clear medical images.
-
Respiratory Therapy: Helium-oxygen mixtures are sometimes used in respiratory therapy to reduce the work of breathing in patients with obstructive airway diseases. The lower density of helium compared to air allows for easier breathing.
Everyday Applications
-
Balloons: Helium's buoyancy makes it the preferred gas for inflating balloons, giving them their characteristic upward lift.
-
Airships: Though less common now, helium was and remains an essential lifting gas for airships and blimps. Its inertness and non-flammability are crucial safety features compared to the previously used hydrogen.
Helium's Scarcity and Conservation
Despite its seemingly ubiquitous presence in balloons and some scientific applications, helium is a scarce resource. It's not easily synthesized and is primarily extracted from natural gas reserves. This scarcity necessitates careful conservation efforts and responsible management of existing helium reserves. The demand for helium continues to grow, particularly in technologically advanced sectors, highlighting the need for sustainable practices.
Future of Helium: Research and Innovation
Ongoing research focuses on several aspects related to helium:
-
Helium Recycling: Developing efficient methods for recycling helium from various applications is crucial to mitigating its scarcity. Improving the collection and purification processes for used helium will contribute significantly to its sustainability.
-
Helium Substitutes: Research into finding suitable alternatives for helium in certain applications is also underway. However, finding a perfect substitute that matches helium's unique properties across all applications remains challenging.
-
Improved Extraction Techniques: Innovations in extraction techniques can help improve the efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of helium extraction from natural gas wells.
Conclusion: The Invaluable and Irreplaceable Helium
The humble combination of 2 protons, 2 neutrons, and 2 electrons gives rise to helium, a remarkable element with far-reaching implications. Its inertness, low density, and cryogenic properties make it essential in numerous scientific, medical, and industrial applications. Understanding helium's atomic structure and unique characteristics is crucial for appreciating its significance and for developing strategies for its responsible and sustainable use. The ongoing challenges associated with helium scarcity highlight the need for continued research and innovation in this vital area, ensuring that this invaluable resource remains available for future generations. Further research into helium's properties and applications promises to uncover even more exciting uses for this remarkable and irreplaceable element in the future. The journey of understanding helium is far from over, and its future implications are vast and exciting.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Percentage Of 4 Out Of 20
Mar 31, 2025
-
How To Find The Restricted Domain
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 1 3 4 In Decimal Form
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Derivative Of X 5
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Even Numbers Are On A Dice
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 Protons 2 Neutrons 2 Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
