Is Hbr An Acid Or A Base
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
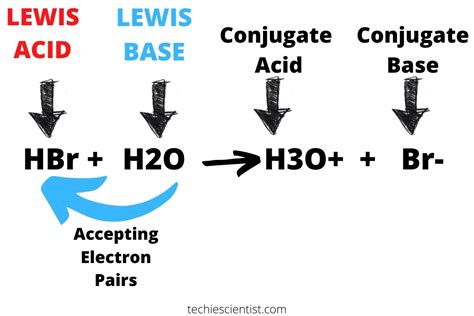
Table of Contents
Is HBr an Acid or a Base? Understanding the Properties of Hydrobromic Acid
Determining whether a chemical compound acts as an acid or a base is crucial in chemistry. This understanding is fundamental to predicting chemical reactions and understanding their behavior in various systems. This article delves into the properties of hydrobromic acid (HBr), exploring its classification as a strong acid, its reactions, and its applications. We will examine the theoretical underpinnings behind acid-base classifications to provide a comprehensive understanding.
What is HBr?
Hydrobromic acid, commonly denoted as HBr, is a strong inorganic acid. It's a colorless, corrosive, and fuming liquid solution of hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. The pure hydrogen bromide gas is a colorless compound with a pungent, irritating odor. HBr is highly soluble in water, readily forming hydrobromic acid. This solubility is a key factor in its behavior as a strong acid. Understanding the properties of the constituent elements, hydrogen and bromine, is crucial to grasping HBr's acidic nature.
Understanding Acids and Bases: A Brief Overview
Before classifying HBr, let's briefly review the different definitions of acids and bases. Several theories define acids and bases, most notably:
1. Arrhenius Theory:
The Arrhenius theory defines an acid as a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water. A base, conversely, is a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water. While simple, this theory has limitations, as it only applies to aqueous solutions.
2. Brønsted-Lowry Theory:
The Brønsted-Lowry theory offers a broader definition. It defines an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. This theory is applicable even in non-aqueous solutions, expanding the scope of acid-base chemistry.
3. Lewis Theory:
The Lewis theory provides the most comprehensive definition. A Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor, while a Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. This theory encompasses a wider range of reactions, including those that don't involve protons.
HBr as a Brønsted-Lowry Acid: The Proton Donor
HBr's classification as a strong acid firmly rests within the Brønsted-Lowry framework. When HBr dissolves in water, it readily donates a proton (H⁺) to a water molecule. This is depicted in the following reaction:
HBr(aq) + H₂O(l) → H₃O⁺(aq) + Br⁻(aq)
This reaction shows that HBr acts as a proton donor, transferring its proton to water, forming the hydronium ion (H₃O⁺) and the bromide ion (Br⁻). The formation of hydronium ions is characteristic of acidic solutions. The ease with which HBr donates this proton is what categorizes it as a strong acid, meaning it almost completely dissociates in water. This high degree of dissociation is crucial in understanding its reactivity and applications.
The Strength of HBr: Complete Dissociation
The strength of an acid is determined by its degree of dissociation in water. Strong acids, like HBr, undergo almost complete dissociation, meaning nearly all HBr molecules donate their protons in aqueous solution. Weak acids, on the other hand, only partially dissociate. This complete dissociation of HBr directly contributes to its high acidity and its ability to readily participate in acid-base reactions. The high concentration of H₃O⁺ ions produced accounts for the strong acidic properties of HBr.
Comparing HBr to other acids: HCl and HI
To further understand HBr's classification, comparing it to similar acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hydroiodic acid (HI) is insightful. These are also strong acids that undergo almost complete dissociation in water. The similarities in their structure and behavior stem from the halogens (Cl, Br, I) having similar electronegativity differences with hydrogen, leading to relatively weak H-X bonds. This weak bond readily breaks, facilitating proton donation. However, there are subtle differences in their acid strength, with HI being the strongest among the three, followed by HBr and then HCl. This difference is linked to the size and electronegativity of the halide ion. The larger the halide, the weaker the H-X bond, leading to greater ease of dissociation.
Reactions of Hydrobromic Acid: Illustrating its Acidity
The acidic nature of HBr is demonstrated through its numerous reactions:
1. Reaction with Bases: Neutralization
HBr readily reacts with bases (proton acceptors) in a neutralization reaction. For example, its reaction with sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
HBr(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaBr(aq) + H₂O(l)
This reaction produces sodium bromide (NaBr) and water. The heat released during this reaction indicates a strong acid-base interaction.
2. Reaction with Metals: Hydrogen Gas Evolution
HBr reacts with many active metals (such as zinc and magnesium) to produce hydrogen gas (H₂) and the corresponding metal bromide salt:
2HBr(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnBr₂(aq) + H₂(g)
The evolution of hydrogen gas is a characteristic reaction of acids with active metals.
3. Reaction with Carbonates and Bicarbonates: Carbon Dioxide Evolution
HBr reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates, producing carbon dioxide (CO₂), water, and the corresponding metal bromide salt. For example, the reaction with sodium carbonate:
2HBr(aq) + Na₂CO₃(aq) → 2NaBr(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
The evolution of CO₂ is a common observation in reactions between acids and carbonates.
Applications of Hydrobromic Acid: Utilizing its Properties
HBr's strong acidic properties find applications in various fields:
- Chemical Synthesis: HBr serves as a crucial reagent in organic synthesis, often used for the bromination of organic compounds, introducing bromine atoms into the molecule. This is critical in the production of various pharmaceuticals and industrial chemicals.
- Metal Cleaning and Etching: Its corrosive nature makes HBr useful in metal cleaning and etching processes. It can remove surface oxides and impurities from metal surfaces.
- Production of Inorganic Bromides: HBr is employed in the production of various inorganic bromides, such as metal bromides, used in various applications, including photography.
- Petroleum Industry: It has applications in the petroleum refining industry.
- Analytical Chemistry: HBr finds applications as a reagent in various analytical procedures.
Safety Precautions: Handling Hydrobromic Acid
HBr is a highly corrosive and hazardous substance. Safety precautions are essential when handling it:
- Eye protection: Always wear appropriate eye protection, such as safety goggles or a face shield.
- Protective clothing: Wear protective clothing, including gloves, lab coats, and aprons, to prevent skin contact.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or use a fume hood to avoid inhaling the fumes, which are highly irritating and corrosive.
- Storage: Store HBr in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible materials.
Conclusion: HBr is unequivocally an acid.
In conclusion, hydrobromic acid (HBr) is definitively classified as a strong acid. Its ability to readily donate protons (Brønsted-Lowry theory) and its high degree of dissociation in water confirm its acidic nature. Its reactions with bases, metals, and carbonates showcase its characteristic acidic behavior. While powerful, its corrosive nature necessitates careful handling and appropriate safety precautions. The diverse applications of HBr in various industries highlight its importance in both chemical synthesis and industrial processes. The information provided here aims to comprehensively address the question of whether HBr is an acid or a base, providing a detailed analysis backed by chemical principles and practical applications. Understanding its properties allows for safe and efficient usage across various scientific and industrial settings.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Derivative Of Xe X
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Be
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Do You Find Total Pressure
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Improper Fraction For 2 1 4
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 20 Is 18
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Hbr An Acid Or A Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
