What Is The Improper Fraction For 2 1/4
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
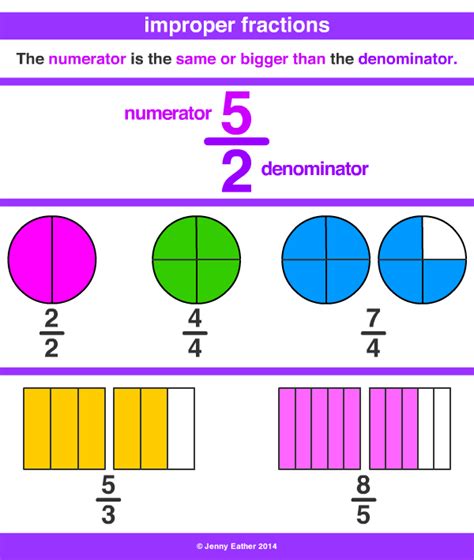
Table of Contents
What is the Improper Fraction for 2 1/4? A Deep Dive into Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Understanding fractions is fundamental to mathematics, and mastering the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a crucial skill. This article will comprehensively explore the conversion of the mixed number 2 1/4 into an improper fraction, delving into the underlying concepts and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We’ll also touch upon the broader applications of this conversion in various mathematical contexts.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before we delve into the specific conversion, let's define our terms:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (the top number) smaller than its denominator (the bottom number). For example, 2 1/4 is a mixed number; 2 is the whole number, and 1/4 is the proper fraction.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator. For example, 9/4 is an improper fraction. Improper fractions represent values greater than or equal to one.
The ability to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is essential for performing various arithmetic operations, especially addition and subtraction of fractions with different denominators.
Converting 2 1/4 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of 2 1/4 to an improper fraction involves a simple two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 2, and the denominator of the fraction is 4. Multiplying these together gives us: 2 * 4 = 8
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 1. Adding this to the result from Step 1 (which was 8), we get: 8 + 1 = 9
This '9' becomes the new numerator of our improper fraction. The denominator remains the same as the original fraction.
Step 3: Write the Improper Fraction.
Therefore, the improper fraction equivalent of 2 1/4 is 9/4.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have two whole pizzas and one-quarter of a pizza. This represents the mixed number 2 1/4. To express this as an improper fraction, we need to divide each pizza into quarters (the denominator).
Each whole pizza has 4 quarters. Therefore, two whole pizzas have 2 * 4 = 8 quarters. Adding the extra quarter, we have a total of 8 + 1 = 9 quarters. Since each quarter is represented by 1/4, we have 9/4 quarters – our improper fraction.
Practical Applications of Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
The ability to seamlessly convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial in various mathematical contexts:
-
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, converting them to improper fractions with a common denominator simplifies the process significantly. Trying to directly add 2 1/4 and 1 3/4 without conversion would be far more complex.
-
Multiplication and Division of Fractions: While not strictly necessary, converting mixed numbers to improper fractions often makes multiplication and division of fractions simpler and less prone to errors.
-
Algebra: Solving algebraic equations involving fractions often requires converting mixed numbers into improper fractions to streamline the solution process. The consistency of working with improper fractions aids in simplification and prevents confusion.
-
Geometry and Measurement: In geometry problems involving areas, volumes, or lengths, measurements are often expressed as mixed numbers. Converting them into improper fractions allows for easier calculations.
-
Everyday Life: Many real-world applications involve fractions, from baking recipes (requiring precise measurements) to calculating fuel efficiency or dividing resources fairly. Understanding the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial for accurate calculations in these situations.
Further Exploration: Other Examples and Practice Problems
Let's consider a few more examples to reinforce your understanding:
Example 1: Converting 3 2/5 to an Improper Fraction
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 3 * 5 = 15
- Add the numerator: 15 + 2 = 17
- The improper fraction is 17/5
Example 2: Converting 1 7/8 to an Improper Fraction
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 1 * 8 = 8
- Add the numerator: 8 + 7 = 15
- The improper fraction is 15/8
Example 3: Converting 5 1/3 to an Improper Fraction
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 5 * 3 = 15
- Add the numerator: 15 + 1 = 16
- The improper fraction is 16/3
Practice Problems:
Try converting the following mixed numbers to improper fractions:
- 4 1/2
- 2 3/7
- 6 5/9
- 1 1/10
- 10 2/3
Solutions:
- 9/2
- 17/7
- 59/9
- 11/10
- 32/3
Converting Improper Fractions Back to Mixed Numbers
It's equally important to know how to convert an improper fraction back to a mixed number. This involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the proper fraction, retaining the original denominator.
For example, to convert 9/4 back to a mixed number:
- Divide 9 by 4: 9 ÷ 4 = 2 with a remainder of 1.
- The quotient (2) is the whole number.
- The remainder (1) is the numerator of the proper fraction.
- The denominator remains 4.
- Therefore, 9/4 = 2 1/4
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions for Mathematical Success
Understanding the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This process, while seemingly simple, underpins a wide range of mathematical operations and applications. By mastering this conversion, you'll strengthen your foundational mathematical skills, paving the way for tackling more complex problems with confidence. Remember to practice regularly and visualize the concepts to solidify your understanding. This will not only improve your mathematical abilities but also boost your problem-solving skills across various disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Sohcahtoa Only For Right Triangles
Mar 24, 2025
-
Organisms That Cannot Produce Their Own Food
Mar 24, 2025
-
1 2 3g 2 G 2
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Em Wave Has The Longest Wavelength
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Organelles Are Involved In Energy Conversion
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Improper Fraction For 2 1/4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
