1 2 3g 2 G 2
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
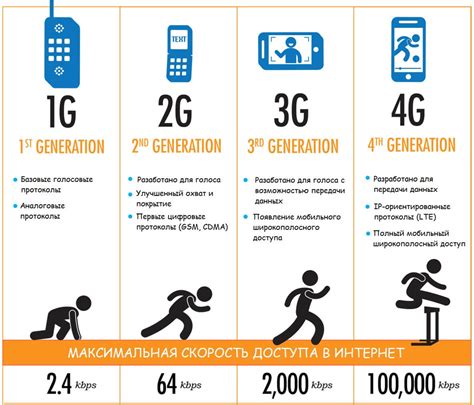
Table of Contents
Decoding the 1 2 3G 2G 2 Enigma: A Deep Dive into Cellular Network Generations
The seemingly random string "1 2 3G 2G 2" might seem nonsensical at first glance. However, for those familiar with the evolution of cellular technology, it hints at a journey through the generations of mobile networks, highlighting both advancements and the persistent relevance of older technologies. This article will unravel the meaning behind this sequence, exploring the history, characteristics, and lasting impact of each generation, from the primitive 1G to the sophisticated 5G (although 5G isn't explicitly mentioned in the sequence, its presence is implicitly understood as the successor to 4G). We'll delve into their technical specifications, applications, and ultimately, why understanding this progression is crucial in today's hyper-connected world.
1G: The Dawn of Mobile Communication
1G, or first-generation cellular networks, marked the humble beginnings of mobile telephony. Emerging in the early 1980s, 1G systems primarily utilized analog technology. This meant that voice calls were transmitted as analog signals, leading to several limitations:
- Limited Capacity: The analog nature restricted the number of simultaneous calls a network could handle. Congestion was a common issue, especially during peak hours.
- Poor Security: Analog signals were vulnerable to eavesdropping and interception. Privacy was a significant concern.
- Lack of Data Capabilities: 1G networks were primarily designed for voice communication. Data transmission was virtually nonexistent.
- Short Range: Cell towers had limited range, requiring frequent handoffs between cells, often resulting in dropped calls.
Despite its limitations, 1G represented a monumental leap forward, freeing communication from the constraints of landlines. It laid the foundation for the subsequent generations of cellular technology.
The Legacy of 1G:
While technologically outdated, 1G's legacy lies in its pioneering role. It proved the viability of mobile communication on a large scale, setting the stage for the explosive growth seen in later generations. It’s a reminder that even seemingly primitive technologies can pave the way for significant innovation.
2G: The Rise of Digital Communication
2G, or second-generation cellular networks, marked a paradigm shift in mobile technology by transitioning to digital signal processing. This transition brought about significant improvements:
- Increased Capacity: Digital signals allowed for more efficient use of radio frequencies, increasing the number of simultaneous calls and users a network could support.
- Enhanced Security: Digital encryption provided greater security and privacy for voice calls.
- Introduction of Data Services: 2G networks introduced the ability to transmit data, albeit at relatively low speeds. This paved the way for SMS (Short Message Service) text messaging and early mobile internet access using technologies like GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) and EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution).
- Improved Coverage: Advances in antenna technology and network infrastructure led to improved coverage and reduced dropped calls.
Popular 2G technologies included GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access), which became the dominant standards globally.
2G's Enduring Influence:
Even in the age of 5G, 2G networks still maintain a presence in many parts of the world. Their low cost and wide coverage make them suitable for applications where high speeds are not essential, such as SMS messaging and IoT (Internet of Things) devices with minimal data requirements. The enduring legacy of 2G highlights the importance of considering cost-effectiveness and coverage alongside technological advancements.
3G: The Mobile Internet Revolution
3G, or third-generation cellular networks, brought about a true mobile internet revolution. Building upon the digital foundations of 2G, 3G introduced:
- Significantly Higher Data Speeds: 3G networks offered significantly faster data speeds compared to 2G, enabling more robust mobile internet browsing, email, and multimedia applications.
- Broader Bandwidth: Increased bandwidth allowed for greater capacity and more simultaneous users.
- Enhanced Multimedia Capabilities: 3G facilitated the transmission of video and audio streams, opening the door for mobile video calling and streaming services.
- Mobile Broadband: 3G provided a stepping stone toward mobile broadband, making mobile internet access a mainstream reality.
Popular 3G technologies included UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) and CDMA2000.
3G's Impact on Mobile Usage:
3G profoundly transformed mobile usage. The increased data speeds and broader bandwidth enabled the rise of mobile applications, social media, and mobile gaming. It ushered in an era of constant connectivity and changed how people communicate, access information, and conduct business.
The Significance of the "1 2 3G 2G 2" Sequence
The sequence "1 2 3G 2G 2" reflects the reality of cellular network deployments and evolution. While newer technologies offer superior capabilities, older generations often persist for various reasons:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Maintaining older networks is significantly cheaper than upgrading to the latest technologies everywhere.
- Coverage: Older networks often offer superior coverage in remote or sparsely populated areas.
- Backward Compatibility: Older devices may not support the latest network technologies.
- Specific Applications: Some applications require only basic data capabilities, making older networks sufficient.
The continued presence of 2G highlights the complex interplay between technological advancements, economic factors, and the need for widespread connectivity. It underscores that technological progress is not always a linear replacement of old with new; instead, it's a layered evolution where different generations coexist and serve various needs.
4G and Beyond: The Continuous Evolution
While not explicitly mentioned in the sequence, 4G (fourth-generation) networks represent a quantum leap in mobile technology. 4G brought:
- Significantly Increased Data Speeds: 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) offered substantially faster speeds than 3G, enabling high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and other bandwidth-intensive applications.
- Low Latency: 4G LTE reduced latency, making real-time applications more responsive.
- Increased Capacity: Advanced network technologies like MIMO (Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) significantly increased network capacity.
4G has fundamentally reshaped our interaction with the digital world, enabling high-speed mobile data access for a wider range of applications.
5G, the current leading edge, takes things even further, promising significantly higher speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, which will pave the way for new technologies and applications like the Internet of Things (IoT) on an unprecedented scale.
Conclusion: A Multi-Generational Mobile Ecosystem
The "1 2 3G 2G 2" sequence, although seemingly arbitrary, effectively illustrates the dynamic and multifaceted nature of cellular technology evolution. While newer generations offer superior capabilities, older generations continue to play vital roles. Understanding this multi-generational ecosystem is crucial for comprehending the complexities of mobile connectivity, developing effective strategies for network deployment, and appreciating the continual progress in this ever-evolving field. The future of mobile communication likely involves a continued interplay of different generations, each fulfilling specific needs and catering to various user requirements, ensuring widespread connectivity and access to information for billions worldwide. The journey from 1G to 5G is not merely a technological advancement but a testament to human ingenuity and the unrelenting pursuit of seamless communication.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Factor 1 X 3
Mar 29, 2025
-
How To Find A Boiling Point
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is 85 In Fraction Form
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Coefficients In A Chemical Equation Represent The
Mar 29, 2025
-
Maximum Number Of Electrons In P Orbital
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 2 3g 2 G 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
