What Is The Derivative Of Xe X
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
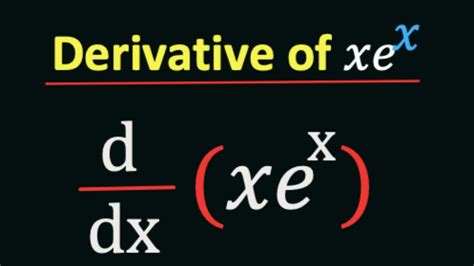
Table of Contents
What is the Derivative of xeˣ? Understanding the Product Rule and its Application
The derivative of xeˣ is a classic example demonstrating the application of the product rule in calculus. While seemingly simple at first glance, understanding its derivation reveals fundamental principles vital for tackling more complex differentiation problems. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the process, providing a step-by-step explanation, exploring related concepts, and offering practical applications.
Understanding the Product Rule
Before tackling the derivative of xeˣ, let's solidify our understanding of the product rule. This rule is essential for finding the derivatives of functions that are products of two or more functions. The rule states:
If we have a function h(x) = f(x)g(x), then its derivative h'(x) is given by:
h'(x) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)
In simpler terms, the derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function multiplied by the second function, plus the first function multiplied by the derivative of the second function.
Deriving the Derivative of xeˣ
Now, let's apply the product rule to find the derivative of xeˣ. Here, we consider:
- f(x) = x
- g(x) = eˣ
First, we find the derivatives of f(x) and g(x):
- f'(x) = 1 (The derivative of x with respect to x is 1)
- g'(x) = eˣ (The derivative of eˣ with respect to x is eˣ)
Now, we substitute these into the product rule formula:
h'(x) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x) = (1)(eˣ) + (x)(eˣ) = eˣ + xeˣ
Therefore, the derivative of xeˣ is eˣ + xeˣ. This can also be factored as eˣ(1 + x).
Simplifying and Understanding the Result
The derivative, eˣ + xeˣ or eˣ(1 + x), might seem initially complex. However, understanding its components allows for deeper insights. The term eˣ represents the contribution from the exponential function, while xeˣ highlights the interplay between the linear and exponential components. The factored form, eˣ(1 + x), beautifully demonstrates the common factor present in both terms. This factored form is often preferred due to its conciseness and elegance.
Visualizing the Derivative
Graphing both the original function, xeˣ, and its derivative, eˣ(1 + x), provides valuable visual understanding. The original function represents an exponential growth that is increasingly rapid. The derivative function, showing the rate of change, confirms this rapid growth, illustrating how the rate itself also increases over time. The points where the derivative equals zero indicate potential extrema (minima or maxima) in the original function.
Applications of the Derivative
Understanding the derivative of xeˣ extends far beyond a simple calculus exercise. It finds practical applications in various fields:
1. Differential Equations:
The derivative of xeˣ frequently appears in the solutions to differential equations, particularly those modeling exponential growth or decay with time-dependent factors.
2. Physics:
In physics, exponential functions are ubiquitous, often describing radioactive decay, capacitor discharge, or other processes governed by exponential relationships. The derivative helps quantify the rate of these processes.
3. Economics and Finance:
Exponential growth models are used in economics and finance to predict the future values of investments or the growth of populations. The derivative aids in calculating rates of return, growth rates, and other crucial economic indicators.
4. Statistics and Probability:
Certain probability distributions, like the exponential distribution or variations thereof, involve exponential functions. The derivative plays a vital role in calculating probabilities and analyzing statistical properties.
5. Computer Science:
In algorithms and numerical methods, understanding derivatives is critical for optimization processes. Efficient algorithms often leverage derivatives to find optimal solutions.
Extending the Concept: Higher-Order Derivatives
We can extend our understanding by calculating higher-order derivatives of xeˣ. Let's find the second derivative:
To find the second derivative, we differentiate the first derivative, eˣ + xeˣ or eˣ(1 + x). Using the product rule again on the eˣ(1+x) form:
- Let f(x) = eˣ and g(x) = (1+x)
- f'(x) = eˣ and g'(x) = 1
Then the second derivative is:
h''(x) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x) = eˣ(1+x) + eˣ(1) = eˣ(1+x) + eˣ = eˣ(2+x)
Similarly, we can compute third, fourth, and even higher-order derivatives. Each successive derivative reveals further insights into the function's behavior and curvature.
Relating to Other Derivative Rules
The derivative of xeˣ showcases the product rule's power. It's also important to consider its relationship to other derivative rules:
-
Chain Rule: Although not directly used in this specific case, the chain rule is crucial when dealing with composite functions involving eˣ. For instance, finding the derivative of e^(x²).
-
Quotient Rule: While we didn't use it here, the quotient rule becomes relevant when dealing with functions expressed as ratios, such as (xeˣ)/(x² + 1).
Mastering the product rule and its interplay with other derivative rules is fundamental to calculus proficiency.
Practical Exercises
To solidify your understanding, consider practicing these exercises:
- Find the derivative of x²eˣ.
- Find the derivative of (x³ + 2x)e⁻ˣ.
- Find the second derivative of xe²ˣ.
- Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve y = xeˣ at x = 1.
Conclusion: Mastering the Derivative of xeˣ and Beyond
The derivative of xeˣ, while seemingly a simple problem, provides a solid foundation for understanding the product rule and its broader applications. Through this step-by-step guide, we've not only derived the derivative but also explored its implications, visualization, practical applications, and its relation to other fundamental calculus rules. Mastering this concept will empower you to tackle more complex differentiation problems and deepen your understanding of calculus's power and relevance in various fields. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your knowledge and confidently apply these techniques in your academic or professional endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Is Water Molecule Like A Magnet
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 23 Out Of 30
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are The Common Factors Of 16 And 20
Mar 24, 2025
-
30 Is 40 Of What Number
Mar 24, 2025
-
Is Sohcahtoa Only For Right Triangles
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Derivative Of Xe X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
