Is 2 3 Same As 3 4
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
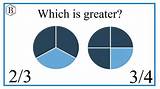
Table of Contents
Is 2/3 the Same as 3/4? A Deep Dive into Fraction Comparison
The question, "Is 2/3 the same as 3/4?" seems deceptively simple. A quick glance might lead some to assume they're equal, but a closer examination reveals a fascinating exploration into the world of fractions, ratios, and mathematical comparisons. This article will not only answer the question definitively but also delve into the methods for comparing fractions, their applications, and the underlying mathematical principles.
Understanding Fractions: A Foundation
Before we dive into comparing 2/3 and 3/4, let's solidify our understanding of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates the number of parts we have, while the denominator indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For instance, in the fraction 2/3, the numerator (2) represents two parts, and the denominator (3) means the whole is divided into three equal parts. Similarly, in 3/4, we have three parts out of a total of four equal parts.
Comparing Fractions: Multiple Methods
Several methods exist for comparing fractions. Let's explore the most common and effective techniques:
1. Finding a Common Denominator
This is arguably the most straightforward method. To compare fractions, we need to express them with a common denominator – a number that is a multiple of both denominators. Once we have a common denominator, we can directly compare the numerators.
Let's apply this to our problem: Comparing 2/3 and 3/4.
-
Find the least common multiple (LCM) of 3 and 4: The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
-
Convert both fractions to have a denominator of 12:
- 2/3 = (2 * 4) / (3 * 4) = 8/12
- 3/4 = (3 * 3) / (4 * 3) = 9/12
-
Compare the numerators: Since 8 < 9, we conclude that 8/12 < 9/12, meaning 2/3 < 3/4.
2. Converting to Decimals
Another effective method is converting fractions to decimals. This allows for a direct numerical comparison.
-
Convert 2/3 to a decimal: 2 ÷ 3 ≈ 0.6667 (repeating decimal)
-
Convert 3/4 to a decimal: 3 ÷ 4 = 0.75
-
Compare the decimals: Since 0.6667 < 0.75, we again conclude that 2/3 < 3/4.
3. Visual Representation
While not as precise as the previous methods, visualizing fractions using diagrams or models can provide a helpful intuitive understanding. Imagine two circles. Divide one into three equal parts and shade two of them (representing 2/3). Divide the other circle into four equal parts and shade three of them (representing 3/4). Visually comparing the shaded areas will clearly demonstrate that 3/4 represents a larger portion than 2/3.
The Significance of the Inequality: Practical Applications
The fact that 2/3 is not equal to 3/4 has significant implications across various fields:
1. Construction and Engineering
Precision is paramount in construction and engineering. Accurate fraction comparisons ensure correct measurements and prevent structural errors. Miscalculating fractions, even slightly, can lead to significant problems.
2. Cooking and Baking
Following recipes accurately requires precise measurements. Understanding the relationship between fractions is crucial for achieving desired results in baking, where even small variations in ingredient ratios can drastically alter the final product.
3. Finance and Economics
Fractions are fundamental in financial calculations. Interest rates, stock prices, and financial ratios all involve fractions. Accurate comparisons are essential for making sound financial decisions.
4. Data Analysis and Statistics
In statistical analysis, fractions often represent proportions or probabilities. Understanding fraction comparisons is essential for interpreting data accurately and drawing meaningful conclusions.
Beyond the Basic Comparison: Exploring Ratios and Proportions
The comparison of 2/3 and 3/4 extends beyond a simple numerical inequality. It highlights the concept of ratios and proportions. A ratio is a comparison of two quantities, while a proportion is a statement that two ratios are equal.
While 2/3 and 3/4 are not equal ratios, they can be used to explore related proportions. For example, we can ask: "What is the ratio of 2/3 to 3/4?" This can be calculated as (2/3) / (3/4) = 8/9. This shows that 2/3 is 8/9 of 3/4.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions often arise when comparing fractions:
-
Ignoring the denominator: Some mistakenly compare only the numerators, disregarding the denominators entirely. This is incorrect; the denominator plays a crucial role in determining the fraction's value.
-
Assuming equal parts imply equal value: The size of the parts depends on the denominator. A larger denominator signifies smaller parts of the whole.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Fractions
The seemingly simple question, "Is 2/3 the same as 3/4?" has led us on a journey exploring fundamental concepts in mathematics. We've learned multiple methods for comparing fractions, examined their practical applications, and uncovered the underlying principles of ratios and proportions. Mastering fraction comparison is not just about solving mathematical problems; it's about developing a deeper understanding of numerical relationships and their relevance in various aspects of life. The inequality of 2/3 and 3/4 underscores the importance of precise calculations and careful consideration of the denominator when working with fractions. Remember, a firm grasp of these concepts is essential for success in numerous fields, from construction to finance, highlighting the far-reaching influence of basic arithmetic. Furthermore, the ability to accurately compare fractions showcases a valuable skill set: attention to detail, logical reasoning, and a strong mathematical foundation. This foundation paves the way for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and enhances problem-solving capabilities across numerous disciplines. The seemingly simple comparison of two fractions has therefore illuminated a wealth of important mathematical principles and their real-world applications, reinforcing the significance of this fundamental aspect of arithmetic.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electros In Hydrogen
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do Animals Get The Nitrogen They Need
Mar 17, 2025
-
Nucleotides Are Attached By Bonds Between The
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Sum Of A Number And Four
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Can Each Ring Hold
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 2 3 Same As 3 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
