Integral Of Sin 3x Cos 2x
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 4 min read
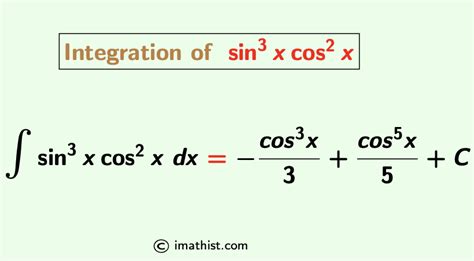
Table of Contents
Solving the Integral of sin 3x cos 2x: A Comprehensive Guide
The integral of sin 3x cos 2x presents a classic example of how trigonometric identities can simplify seemingly complex integration problems. This comprehensive guide will walk you through multiple methods of solving this integral, explaining the underlying principles and offering detailed step-by-step solutions. We'll also explore the broader context of integrating trigonometric functions and highlight key concepts for tackling similar problems.
Understanding the Problem: ∫sin 3x cos 2x dx
Our objective is to evaluate the indefinite integral: ∫sin 3x cos 2x dx. Direct integration isn't feasible; we need to employ trigonometric identities to simplify the integrand before proceeding. This problem highlights the importance of mastering trigonometric manipulation in calculus.
Method 1: Using the Product-to-Sum Formula
The most straightforward approach involves using the product-to-sum trigonometric identity:
sin A cos B = (1/2)[sin(A + B) + sin(A - B)]
Applying this to our integral, where A = 3x and B = 2x:
sin 3x cos 2x = (1/2)[sin(3x + 2x) + sin(3x - 2x)] = (1/2)[sin 5x + sin x]
Now our integral becomes significantly simpler:
∫sin 3x cos 2x dx = (1/2)∫[sin 5x + sin x] dx
This can be integrated term by term:
(1/2)∫sin 5x dx + (1/2)∫sin x dx
The integral of sin(kx) is -(1/k)cos(kx) + C, where C is the constant of integration. Therefore:
(1/2)[- (1/5)cos 5x - cos x] + C
Simplifying, we arrive at the final solution:
∫sin 3x cos 2x dx = (-1/10)cos 5x - (1/2)cos x + C
This method is generally preferred for its simplicity and direct application of a well-known identity.
Method 2: Employing Complex Exponentials (Euler's Formula)
A more advanced, yet elegant, approach uses Euler's formula:
e^(ix) = cos x + i sin x
From this, we can derive expressions for sin x and cos x:
sin x = (e^(ix) - e^(-ix)) / (2i) cos x = (e^(ix) + e^(-ix)) / 2
Substituting these into our integral:
∫[(e^(i3x) - e^(-i3x)) / (2i)] * [(e^(i2x) + e^(-i2x)) / 2] dx
Expanding and simplifying (remembering that i² = -1):
(1/4i)∫[e^(i5x) + e^(ix) - e^(-ix) - e^(-i5x)] dx
Integrating term by term:
(1/4i)[(1/5i)e^(i5x) + (1/i)e^(ix) + (1/i)e^(-ix) + (1/5i)e^(-i5x)] + C
Now, we can use Euler's formula in reverse to convert back to trigonometric functions:
(1/4i)[(1/5i)(cos 5x + i sin 5x) + (1/i)(cos x + i sin x) + (1/i)(cos x - i sin x) + (1/5i)(cos 5x - i sin 5x)] + C
Further simplification, remembering that 1/i = -i, yields:
(-1/10)cos 5x - (1/2)cos x + C
This method, while more involved, showcases the power of complex analysis in solving trigonometric integrals. It's a valuable technique to understand for more advanced calculus problems.
Comparing the Methods
Both methods yield the same result: (-1/10)cos 5x - (1/2)cos x + C. The product-to-sum formula is generally more efficient and easier to understand for introductory calculus students. However, the complex exponential method demonstrates a powerful alternative approach that becomes essential in more advanced mathematical contexts.
Generalizing the Approach: ∫sin ax cos bx dx
The techniques demonstrated above can be generalized to solve integrals of the form ∫sin ax cos bx dx, where 'a' and 'b' are constants. Using the product-to-sum formula:
∫sin ax cos bx dx = (1/2)∫[sin(a+b)x + sin(a-b)x] dx = (-1/2)[cos(a+b)x/(a+b) + cos(a-b)x/(a-b)] + C (assuming a ≠ b)
If a = b, the integral simplifies to:
∫sin ax cos ax dx = (1/2)∫sin 2ax dx = (-1/4a)cos 2ax + C
This general formula provides a quick and efficient way to solve a broad class of similar integrals.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
The integral of sin 3x cos 2x, while seemingly abstract, finds applications in various fields, including:
- Signal Processing: Trigonometric functions are fundamental in representing and analyzing signals. This type of integral might arise when dealing with the convolution or correlation of two signals.
- Physics: Oscillatory systems, such as those involving waves or vibrations, often involve trigonometric functions in their mathematical descriptions. Solving such integrals is crucial for understanding these systems' behavior.
- Engineering: Many engineering problems, particularly in electrical and mechanical engineering, involve solving differential equations that contain trigonometric terms. The ability to integrate these functions is essential.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
For more complex integrals involving trigonometric functions, you might explore:
- Integration by Parts: This technique is valuable when dealing with products of trigonometric and other functions.
- Trigonometric Substitution: Substituting trigonometric functions can simplify certain integrals involving square roots and other expressions.
- Reduction Formulas: Recursively reducing the complexity of the integral can be helpful for certain types of trigonometric integrals.
Mastering the integration of trigonometric functions is a cornerstone of calculus. The examples presented here serve as a foundation for tackling more advanced problems and gaining a deeper understanding of this essential mathematical concept. Consistent practice and a thorough understanding of trigonometric identities are key to success in this area. Remember to always check your work and ensure that your solutions are consistent with the fundamental principles of calculus.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Factor X 2
Mar 22, 2025
-
Geometric Mean Of 5 And 15
Mar 22, 2025
-
Least Common Factor Of 3 And 8
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 31
Mar 22, 2025
-
Graph The Parabola Y 3x 2
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of Sin 3x Cos 2x . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
