How Do You Factor X 2
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
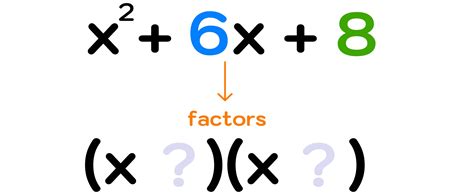
Table of Contents
How Do You Factor x²? A Comprehensive Guide
Factoring quadratic expressions, especially those as simple as x², might seem trivial at first glance. However, understanding the underlying principles is crucial for tackling more complex algebraic manipulations and solving various mathematical problems. This comprehensive guide will explore different methods to factor x², expand on its implications, and demonstrate its application in solving equations and simplifying expressions. We'll cover everything from the basics for beginners to more advanced techniques for seasoned math enthusiasts.
Understanding What Factoring Means
Before delving into the specifics of factoring x², let's establish a fundamental understanding of what factoring actually is. In mathematics, factoring (or factorisation) involves expressing a number or algebraic expression as a product of simpler numbers or expressions. Think of it like reverse multiplication. If you multiply 2 by 3 to get 6, factoring 6 would be finding those original factors, 2 and 3.
In the context of algebra, we’re usually working with polynomials (expressions with variables and coefficients). Factoring a polynomial means rewriting it as a product of simpler polynomials. This process is invaluable for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and uncovering underlying mathematical structures.
Factoring x²: The Simplest Case
The simplest form of factoring involves x². Since x² represents x multiplied by itself (x * x), its prime factorization is straightforward. The factors of x² are simply x and x. We can represent this as:
x² = x * x
This might seem too obvious to warrant discussion, but grasping this fundamental concept lays the groundwork for understanding more complex factoring scenarios. It's the building block upon which all other quadratic factoring techniques are built.
Expanding the Concept: Introducing Coefficients and Constants
While x² is the simplest case, we frequently encounter quadratic expressions with coefficients and constants. These are expressed in the general form:
ax² + bx + c
where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants (numbers). Let's consider a few examples of how the principles of factoring x² extend to these more complex expressions.
Example 1: Factoring 2x² + 4x
In this expression, we have a common factor of 2x:
2x² + 4x = 2x(x + 2)
Notice that we've essentially factored out 2x from each term. The original expression is now expressed as a product of 2x and (x + 2). Understanding this process is crucial for factoring more complicated quadratic expressions.
Example 2: Factoring x² + 5x + 6
This example requires a different approach than simply factoring out a common term. We need to find two numbers that add up to 5 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 6 (the constant term). These numbers are 2 and 3. Therefore, the factored form is:
x² + 5x + 6 = (x + 2)(x + 3)
This method is known as the sum-product method or factoring by grouping. It's a common technique for factoring quadratic trinomials (expressions with three terms).
Example 3: Factoring x² - 4
This example involves the difference of squares. The expression x² - 4 can be rewritten as x² - 2² (since 4 is 2 squared). The difference of squares formula states:
a² - b² = (a + b)(a - b)
Applying this formula to x² - 4 gives us:
x² - 4 = (x + 2)(x - 2)
Advanced Factoring Techniques
While the examples above cover common scenarios, factoring can become significantly more challenging with higher-degree polynomials or more complex coefficients. Several advanced techniques can be employed:
The Quadratic Formula
For quadratic equations in the standard form ax² + bx + c = 0, the quadratic formula provides a reliable method for finding the roots (solutions). These roots can then be used to factor the quadratic expression. The quadratic formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Once you find the roots (x1 and x2), the factored form of the quadratic is:
a(x - x1)(x - x2)
Completing the Square
Completing the square is another powerful technique for factoring and solving quadratic equations. This method involves manipulating the quadratic expression to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored.
Factoring by Grouping
As mentioned earlier, factoring by grouping is a useful method for factoring polynomials with four or more terms. It involves grouping terms with common factors and then factoring out those common factors.
The Significance of Factoring x² and Beyond
The ability to factor x² and other polynomial expressions is fundamental to many areas of mathematics and its applications. Here are a few key applications:
Solving Quadratic Equations
Factoring is a crucial step in solving quadratic equations. By factoring the quadratic expression, you can find the values of x that make the equation equal to zero. These values are the roots or solutions of the equation.
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Factoring allows us to simplify complex algebraic expressions by reducing them to simpler, more manageable forms. This simplification can make further calculations and analysis easier.
Calculus and Advanced Mathematics
Factoring plays a vital role in calculus, especially when dealing with derivatives, integrals, and limits. The ability to factor expressions quickly and accurately is crucial for success in these areas.
Real-World Applications
Factoring has practical applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and computer science, where it helps to model and solve real-world problems. For example, in physics, factoring may be used to solve problems related to projectile motion or oscillations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Factoring
Factoring, particularly understanding how to factor x², forms the bedrock of many algebraic manipulations and problem-solving techniques. While the simple case of x² = x * x might seem elementary, its implications extend far beyond this basic representation. Mastering different factoring methods, from simple common factoring to the quadratic formula and completing the square, equips you with invaluable skills for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide serves as a stepping stone to further explore the fascinating world of algebra and its wide-ranging applications. Consistent practice and a deep understanding of the underlying principles will ultimately lead to proficiency in this crucial area of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Common Factor Of 24 And 32
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Intermolecular Force Is The Strongest
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Ribs Does A Pig Have
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Color Of Light Has The Highest Energy
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Gas Is Most Abundant In Earths Atmosphere
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Factor X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
