What Is The Square Root Of 31
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
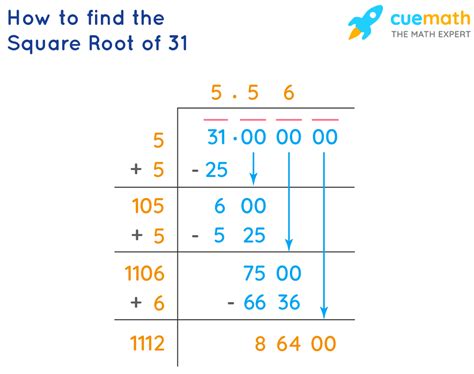
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 31? A Deep Dive into Irrational Numbers
The question, "What is the square root of 31?" seems simple enough. However, delving into this seemingly straightforward mathematical problem reveals a fascinating journey into the world of irrational numbers and the complexities of numerical approximation. This article will explore not only the answer but also the methods used to arrive at it, the implications of its irrationality, and the practical applications of understanding square roots in various fields.
Understanding Square Roots
Before we tackle the square root of 31 specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of square roots. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 multiplied by 3 (3²) equals 9. This is often represented as √9 = 3.
This concept is relatively straightforward for perfect squares – numbers that result from squaring an integer. However, the situation becomes more complex when dealing with numbers that are not perfect squares, like 31. These numbers have square roots that are irrational.
Irrational Numbers: The Nature of √31
An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Its decimal representation neither terminates nor repeats. The square root of 31 falls into this category. This means we cannot express √31 as a fraction like 3/4 or 7/2. Its decimal representation goes on forever without any repeating pattern.
This inherent characteristic of irrational numbers poses a challenge when trying to find the exact value of √31. We can only approximate its value using various methods.
Approximating √31: Different Methods
Several methods can be employed to approximate the square root of 31. Let's examine a few:
1. Using a Calculator: The Easiest Approach
The most straightforward way to find an approximate value is by using a calculator. Most scientific calculators have a square root function (√). Inputting 31 and pressing the square root button will provide a decimal approximation, typically to several decimal places. This might yield a result like 5.56776436283...
While convenient, this method doesn't offer insight into the underlying mathematical processes involved in calculating the square root.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): An Iterative Approach
The Babylonian method is an ancient algorithm for approximating square roots. It's an iterative process, meaning it refines its approximation with each step. Here's how it works:
-
Make an initial guess: Start with a reasonable guess for the square root of 31. Since 5² = 25 and 6² = 36, a good starting point is 5.5.
-
Iterate: Use the following formula to refine the guess:
Next guess = (Previous guess + (Number / Previous guess)) / 2 -
Repeat: Repeat step 2 until the desired level of accuracy is achieved. Each iteration brings the approximation closer to the true value.
Let's illustrate with a few iterations:
- Iteration 1: (5.5 + (31 / 5.5)) / 2 ≈ 5.568
- Iteration 2: (5.568 + (31 / 5.568)) / 2 ≈ 5.567764
- Iteration 3: (5.567764 + (31 / 5.567764)) / 2 ≈ 5.56776436
As you can see, the approximation quickly converges to the value obtained using a calculator.
3. The Method of Linear Interpolation: A Simpler Approach
This method uses a linear approximation based on nearby perfect squares. Since 31 lies between 25 (5²) and 36 (6²), we can estimate the square root using linear interpolation:
-
Find the difference: The difference between 31 and 25 is 6, and the difference between 36 and 25 is 11.
-
Calculate the proportion: The proportion is 6/11.
-
Add to the lower bound: Add this proportion to the lower bound square root (5): 5 + (6/11) ≈ 5.545
This method provides a rougher approximation than the Babylonian method but is simpler to understand and calculate.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
Understanding irrational numbers like √31 is crucial for several reasons:
-
Foundation of Mathematics: Irrational numbers are fundamental components of the real number system, which forms the basis of much of higher-level mathematics.
-
Geometry and Measurement: Irrational numbers frequently appear in geometric calculations, such as calculating the diagonal of a square or the circumference of a circle. The famous irrational number π (pi) is a prime example.
-
Physics and Engineering: Many physical phenomena and engineering calculations involve irrational numbers. For instance, the calculation of wave frequencies and the analysis of oscillatory systems often require the use of irrational numbers.
-
Computer Science and Numerical Analysis: Approximating irrational numbers accurately is crucial in computer science and numerical analysis for developing efficient algorithms and achieving high precision in calculations.
Practical Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have a wide range of practical applications across various fields:
-
Construction and Engineering: Calculating distances, areas, and volumes often involves square roots. For example, determining the length of a diagonal of a rectangular building or the area of a triangular plot of land requires understanding square roots.
-
Physics: Square roots play a significant role in calculating velocity, acceleration, and energy in physics problems. For example, calculating the velocity of a falling object requires the use of the square root of the distance fallen.
-
Finance: Compound interest calculations and present value calculations often involve square roots, especially when dealing with complex financial instruments.
-
Statistics: Many statistical calculations, such as determining standard deviation and variance, make use of square roots.
-
Graphics and Game Development: Square roots are extensively used in computer graphics and game development for tasks such as calculating distances between points, normalizing vectors, and implementing physics engines.
Conclusion: Beyond the Decimal Approximation
While a calculator readily provides a decimal approximation of √31, understanding the underlying mathematical concepts is far more valuable. The journey to approximating √31 has revealed the nature of irrational numbers, the power of iterative algorithms, and the widespread applications of square roots in various fields. It's not just about getting a numerical answer; it's about appreciating the intricate beauty and practical significance of this fundamental mathematical concept. Whether you're a student, engineer, or simply curious about mathematics, grasping the essence of square roots and irrational numbers opens doors to a deeper understanding of the world around us. The seemingly simple question, "What is the square root of 31?", leads to a much richer and more rewarding exploration of mathematics than one might initially expect.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Corrosion A Physical Or Chemical Property
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 0 02 As A Fraction
Mar 23, 2025
-
2 5 As A Percentage And Decimal
Mar 23, 2025
-
In What Organelle Does Photosynthesis Take Place
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Is More Food Increase Carrying Capacity
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 31 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
