How Is More Food Increase Carrying Capacity
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
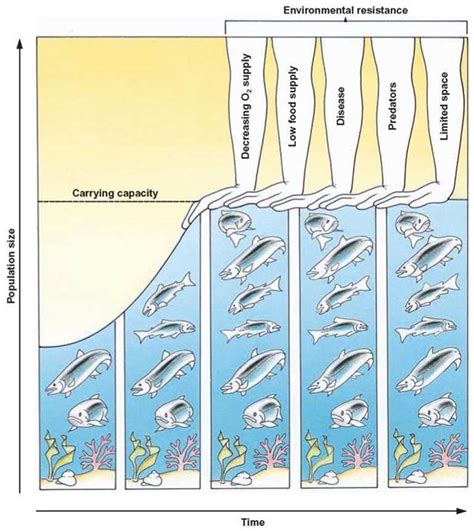
Table of Contents
How Increased Food Production Increases Carrying Capacity
Humanity's journey has been inextricably linked to its ability to produce and access food. Throughout history, advancements in food production have directly correlated with population growth and increased carrying capacity. Carrying capacity, in its simplest form, represents the maximum population size that a given environment can sustainably support. While other factors, such as disease, war, and resource availability beyond food, play a role, food production remains a fundamental limiting factor. This article delves into the multifaceted ways increased food production elevates carrying capacity, examining historical trends, technological advancements, and the ongoing challenges and complexities of this crucial relationship.
The Historical Interplay Between Food and Population
Throughout history, periods of agricultural innovation have consistently coincided with significant population booms. The Neolithic Revolution, marked by the transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to settled agriculture, represents a pivotal moment. The cultivation of crops and domestication of animals led to a more reliable food supply, drastically increasing carrying capacity and allowing for larger, denser human settlements. This surplus also facilitated specialization of labor, leading to advancements in other areas like technology and social structures.
The Green Revolution and its Impact
The 20th century witnessed another transformative period – the Green Revolution. The development and widespread adoption of high-yielding varieties of crops, coupled with increased use of fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation, dramatically increased food production worldwide. This revolution, while controversial due to its environmental impact, undeniably contributed to a significant increase in global carrying capacity, enabling a massive surge in the human population. The Green Revolution's success demonstrated the direct correlation between technological advancements in agriculture and increased capacity to support a larger population.
Technological Advancements Driving Increased Food Production
Several key technological innovations have played a crucial role in boosting food production and consequently, carrying capacity. These advancements encompass diverse aspects of the agricultural process:
1. High-Yielding Crop Varieties:
The development of genetically improved crops with higher yields per unit area is a cornerstone of increased food production. These varieties often feature traits such as disease resistance, enhanced nutrient uptake, and improved tolerance to environmental stresses like drought or salinity. This allows for more food to be grown on existing farmland, reducing pressure to expand agricultural land into natural habitats.
2. Improved Irrigation Techniques:
Efficient irrigation systems are essential for maximizing crop yields, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. Advances in drip irrigation, sprinkler systems, and water-harvesting techniques minimize water waste and ensure consistent water availability for crops, leading to improved yields and greater food security.
3. Precision Agriculture and Data Analytics:
Modern agriculture increasingly relies on technology like GPS, sensors, and data analytics to optimize farming practices. Precision agriculture enables farmers to tailor their approach to specific areas of their fields, adjusting irrigation, fertilization, and pesticide application based on real-time data. This precision approach minimizes resource waste and maximizes yields, contributing significantly to increased carrying capacity.
4. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering:
Biotechnology and genetic engineering offer powerful tools for improving crop characteristics and enhancing food production. Genetically modified (GM) crops often incorporate traits like pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, or enhanced nutritional value. While debates continue surrounding the safety and ethical implications of GM crops, their contribution to increased yields in some regions is undeniable.
5. Improved Livestock Management:
Advancements in animal husbandry, including selective breeding, improved feed formulations, and better disease management practices, have significantly increased the efficiency of livestock production. These advancements have resulted in greater meat, dairy, and egg production per animal, contributing to a greater food supply and increased carrying capacity.
6. Post-Harvest Technologies:
Reducing post-harvest losses is crucial for maximizing the availability of food. Advancements in storage technologies, transportation infrastructure, and processing techniques minimize spoilage and waste, ensuring that more food reaches consumers. This reduction in loss directly contributes to an increased effective carrying capacity.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Practices
While increased food production has undeniably increased carrying capacity, it's crucial to acknowledge the environmental consequences. Intensive agricultural practices can lead to soil degradation, water pollution from fertilizer runoff, biodiversity loss due to habitat destruction, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, sustainable agricultural practices are essential to ensure that increased food production doesn't compromise the long-term viability of the planet's ecosystems.
Sustainable Intensification:
Sustainable intensification focuses on increasing food production without expanding agricultural land or degrading the environment. This approach relies on strategies like integrated pest management, agroforestry, crop diversification, and improved nutrient management to enhance productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Reducing Food Waste:
A significant portion of food produced globally is lost or wasted throughout the supply chain. Reducing food waste, through improvements in storage, transportation, and consumer practices, is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of food production and enhancing carrying capacity sustainably.
Climate-Smart Agriculture:
Climate change poses significant threats to food production, including changes in rainfall patterns, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and rising temperatures. Climate-smart agriculture aims to adapt farming practices to mitigate the negative impacts of climate change and enhance the resilience of food systems.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in ensuring sufficient and sustainable food production to meet the needs of a growing global population. These include:
1. Climate Change:
Climate change is a major threat to food security, affecting crop yields, livestock production, and the availability of water resources. Adapting agriculture to climate change requires significant investment in research, technology, and policy.
2. Water Scarcity:
Many regions face water scarcity, limiting agricultural productivity. Efficient irrigation techniques and water conservation strategies are crucial to ensure sustainable water use in agriculture.
3. Soil Degradation:
Intensive agriculture can lead to soil degradation, reducing its fertility and productivity. Sustainable soil management practices, such as no-till farming and cover cropping, are essential for maintaining soil health.
4. Biodiversity Loss:
Agricultural intensification can lead to biodiversity loss, reducing the resilience of ecosystems and impacting the long-term sustainability of food production. Promoting biodiversity in agricultural landscapes is crucial for maintaining ecosystem services.
5. Food Distribution and Access:
Even with increased food production, unequal access to food remains a significant challenge. Improving food distribution systems and addressing poverty and inequality are crucial for ensuring food security for all.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Path Forward
Increased food production has been, and continues to be, a primary driver of increased carrying capacity for the human population. Technological advancements have played a pivotal role in this increase. However, the long-term sustainability of this trend requires a shift towards more environmentally friendly and equitable approaches to food production and distribution. Sustainable intensification, climate-smart agriculture, reduction of food waste, and improved access to food are crucial elements in ensuring that future generations have sufficient access to the food necessary to sustain a healthy and thriving human population. The challenge lies not merely in producing more food, but in producing it sustainably and equitably, ensuring a secure and prosperous future for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Water Molecules In A Drop
Mar 25, 2025
-
Derivative Of 2 Square Root X
Mar 25, 2025
-
Twice A Number Divided By 6 Is 42
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Sum Of Three Consecutive Integers Is
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Is In 3 Meters
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Is More Food Increase Carrying Capacity . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
