How To Find Axis Of Symmetry Parabola
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
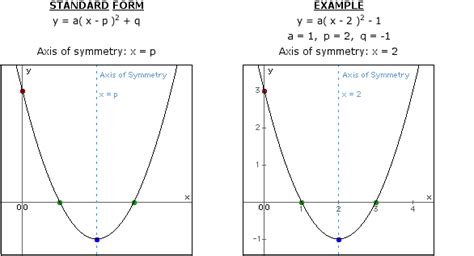
Table of Contents
How to Find the Axis of Symmetry of a Parabola: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the axis of symmetry of a parabola is a fundamental concept in algebra and is crucial for understanding and graphing quadratic functions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various methods to determine the axis of symmetry, regardless of how the parabola is presented – whether it's through an equation, a graph, or a set of points. We'll explore the underlying principles and provide numerous examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Axis of Symmetry
Before diving into the methods, let's establish a clear understanding of what the axis of symmetry actually is. The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that divides the parabola into two mirror images. In simpler terms, if you were to fold the parabola along this line, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This line of symmetry passes through the vertex of the parabola, which is the parabola's highest or lowest point, depending on whether the parabola opens upwards or downwards.
Knowing the axis of symmetry is invaluable for several reasons:
- Graphing parabolas: It helps accurately sketch the graph, as you only need to plot points on one side of the axis and then mirror them to the other side.
- Finding the vertex: The x-coordinate of the vertex lies directly on the axis of symmetry.
- Solving quadratic equations: The axis of symmetry can help you estimate the roots (x-intercepts) of the quadratic equation.
- Understanding the parabola's behavior: It reveals information about the parabola's orientation and range.
Methods to Find the Axis of Symmetry
We'll explore three primary methods to find the axis of symmetry, each suited to different scenarios:
Method 1: Using the Standard Form of a Quadratic Equation
The most common way to find the axis of symmetry is when the quadratic function is given in its standard form:
f(x) = ax² + bx + c
where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. The axis of symmetry is a vertical line with the equation:
x = -b / 2a
This formula directly derives from the process of completing the square to find the vertex form of the quadratic. Let's illustrate with examples:
Example 1:
Find the axis of symmetry for the parabola represented by the equation: f(x) = 2x² + 8x + 6
Here, a = 2, b = 8, and c = 6. Applying the formula:
x = -8 / (2 * 2) = -8 / 4 = -2
Therefore, the axis of symmetry is x = -2.
Example 2:
Find the axis of symmetry for the parabola represented by the equation: f(x) = -x² + 4x - 3
Here, a = -1, b = 4, and c = -3. Applying the formula:
x = -4 / (2 * -1) = -4 / -2 = 2
Therefore, the axis of symmetry is x = 2.
Method 2: Using the Vertex Form of a Quadratic Equation
The vertex form of a quadratic equation provides a more direct route to finding the axis of symmetry. The vertex form is:
f(x) = a(x - h)² + k
where (h, k) represents the coordinates of the vertex. The axis of symmetry is simply:
x = h
Example 3:
Find the axis of symmetry for the parabola represented by the equation: f(x) = 3(x + 1)² - 4
In this case, h = -1 and k = -4. Therefore, the axis of symmetry is x = -1.
Example 4:
Find the axis of symmetry for the parabola represented by the equation: f(x) = -2(x - 3)² + 5
Here, h = 3 and k = 5. Therefore, the axis of symmetry is x = 3.
The vertex form directly gives you the x-coordinate of the vertex, which is the axis of symmetry. This method is particularly efficient if the equation is already in vertex form.
Method 3: Using the Graph of a Parabola
If you have the graph of the parabola, finding the axis of symmetry is visual and straightforward. Simply locate the vertex of the parabola. The vertical line passing through the x-coordinate of the vertex is the axis of symmetry.
Example 5:
Imagine a parabola with its vertex at the point (1, 4). The axis of symmetry is the vertical line x = 1.
Example 6:
Consider a parabola whose vertex is at (-2, -3). The axis of symmetry is the vertical line x = -2.
This method is intuitive but relies on having an accurately drawn graph. Slight inaccuracies in the graph can lead to inaccuracies in determining the axis of symmetry.
Method 4: Using a Set of Points
If you are only given a set of points that lie on the parabola, finding the axis of symmetry requires a slightly more involved process. You need to determine the quadratic equation that fits these points, which can be achieved using techniques like solving a system of equations or using regression analysis (for a larger set of points). Once you have the quadratic equation, you can use Method 1 or Method 2 to find the axis of symmetry.
Example 7:
Suppose you have three points on a parabola: (1, 2), (2, 3), and (3, 2). This requires a more advanced method like solving simultaneous equations. This process typically involves substituting the x and y values of the points into the general equation, ax² + bx + c = y, creating a system of three equations with three unknowns (a, b, and c). Solving this system will give you the quadratic equation which you can then use to find the axis of symmetry via Method 1.
This method is the most challenging and generally requires a strong understanding of algebra and possibly the use of technology like a graphing calculator or software.
Advanced Considerations and Applications
The axis of symmetry has broader applications beyond simply graphing parabolas. It plays a crucial role in:
-
Optimization Problems: In real-world applications, quadratic functions often model optimization problems. The axis of symmetry helps locate the maximum or minimum value of the function, representing the optimal solution. For example, finding the maximum profit in a business scenario.
-
Projectile Motion: The trajectory of a projectile is often modeled using a quadratic equation. The axis of symmetry indicates the time at which the projectile reaches its maximum height.
-
Signal Processing: In signal processing, quadratic functions are used to represent various signal properties. The axis of symmetry plays a role in analyzing and manipulating these signals.
-
Data Analysis: Regression analysis often employs quadratic models to capture non-linear relationships in data. Understanding the axis of symmetry helps to interpret and understand the trends within the data.
Conclusion
Finding the axis of symmetry of a parabola is a crucial skill in mathematics with numerous practical applications. Whether you are given the equation in standard or vertex form, have a graph, or a set of points, the methods outlined above provide a robust framework for determining the axis of symmetry. Remember that understanding the underlying concepts will allow you to tackle more complex problems and real-world applications involving quadratic functions effectively. Mastering this fundamental concept will undoubtedly strengthen your problem-solving skills in mathematics and beyond. Continue practicing with various examples to solidify your understanding and improve your proficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Br
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Flywheel In The Form Of A Uniformly Thick Disk
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Inverse Of 2 5
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Absolute Value Of 4
Mar 19, 2025
-
Find The Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Axis Of Symmetry Parabola . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
