What Is The Absolute Value Of 4
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
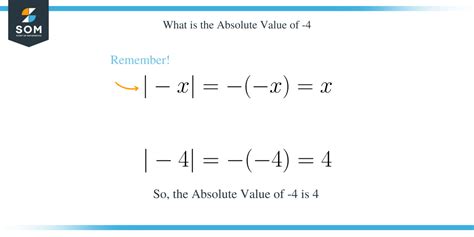
Table of Contents
What is the Absolute Value of 4? A Deep Dive into Absolute Value and its Applications
The seemingly simple question, "What is the absolute value of 4?" opens a door to a fascinating area of mathematics: absolute value. While the answer itself is straightforward – the absolute value of 4 is 4 – understanding the concept's nuances and its broader applications is crucial for anyone seeking a firm grasp of mathematics. This comprehensive article will explore the absolute value of 4, delve into the definition and properties of absolute value, and illustrate its significance across various mathematical fields and real-world applications.
Understanding Absolute Value: A Fundamental Concept
The absolute value of a number represents its distance from zero on the number line. It's always a non-negative value, regardless of the number's sign. The absolute value of a number x is denoted as |x|.
In simpler terms: Imagine you're standing at zero on a number line. The absolute value tells you how many steps you need to take to reach a specific number, regardless of whether you move to the left (negative direction) or right (positive direction).
Therefore, the absolute value of 4, denoted as |4|, is simply 4 because 4 is 4 units away from zero.
Defining Absolute Value Mathematically
We can formally define the absolute value function as follows:
|x| = { x, if x ≥ 0 {-x, if x < 0
This definition states that:
- If x is greater than or equal to zero (non-negative), the absolute value of x is x itself.
- If x is less than zero (negative), the absolute value of x is the negation of x (making it positive).
Let's illustrate this with a few examples:
- |5| = 5 (5 is non-negative)
- |-3| = -(-3) = 3 (-3 is negative, so we negate it)
- |0| = 0 (0 is non-negative)
- |-100| = 100
- |√2| = √2
- |-π| = π
As you can see, the absolute value function always returns a non-negative value. This property is crucial in many mathematical contexts.
Properties of the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function possesses several important properties that make it a powerful tool in mathematics:
- Non-negativity: |x| ≥ 0 for all real numbers x.
- Even Function: |x| = |-x| for all real numbers x. This means the function is symmetric about the y-axis.
- Multiplicative Property: |xy| = |x| |y| for all real numbers x and y. The absolute value of a product is the product of the absolute values.
- Triangle Inequality: |x + y| ≤ |x| + |y| for all real numbers x and y. This inequality is fundamental in many areas of mathematics, particularly in analysis and linear algebra. It essentially states that the absolute value of a sum is less than or equal to the sum of the absolute values.
These properties are not just theoretical; they have practical implications in various mathematical operations and problem-solving scenarios. Understanding them is key to mastering absolute value.
Applications of Absolute Value
The absolute value function is far from a mere theoretical construct; it has wide-ranging applications across diverse fields:
1. Distance and Measurement
The most intuitive application of absolute value is in representing distance. As mentioned earlier, |x| represents the distance between x and 0 on the number line. More generally, the distance between two points a and b on the number line is |a - b|. This concept extends to higher dimensions as well, forming the basis of distance calculations in geometry and other fields.
For example, if a car travels 10 miles east (positive direction) and then 5 miles west (negative direction), the total distance traveled is |10| + |-5| = 10 + 5 = 15 miles. However, the displacement (net change in position) is 10 - 5 = 5 miles east. Here, we see the distinction between distance (absolute value) and displacement (signed value).
2. Error and Tolerance
In engineering and science, absolute value is frequently used to represent error or tolerance. For instance, if a manufactured part is supposed to be 10 cm long, but its actual length is 10.2 cm, the error is |10.2 - 10| = 0.2 cm. This allows engineers to assess the accuracy of measurements and ensure that deviations remain within acceptable limits.
3. Inequalities and Equations
Absolute value plays a vital role in solving inequalities and equations. For example, solving the inequality |x - 2| < 5 involves considering two cases:
- x - 2 < 5 => x < 7
- -(x - 2) < 5 => -x + 2 < 5 => x > -3
Therefore, the solution is -3 < x < 7. Solving equations involving absolute value often requires similar case-by-case analysis.
4. Graphing Functions
Absolute value functions create unique graphs with sharp turns or corners. The graph of y = |x| is a V-shaped curve with its vertex at (0,0). Transformations of this basic function, such as y = |x - 2| + 3, shift and scale the graph, leading to diverse shapes with practical uses in modeling real-world phenomena.
5. Complex Numbers
In complex analysis, the absolute value of a complex number z = a + bi (where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit) is defined as |z| = √(a² + b²). This represents the distance of the complex number from the origin in the complex plane. This concept is fundamental in understanding the geometry of complex numbers and their applications in various branches of mathematics and physics.
6. Computer Science and Programming
Absolute value is a built-in function in most programming languages, frequently used in algorithms involving distance calculations, error handling, and numerical analysis. It plays a crucial role in tasks such as image processing, game development, and simulations.
7. Statistics and Probability
Absolute value appears in various statistical measures, such as mean absolute deviation, which quantifies the average distance of data points from the mean. This provides a measure of data dispersion or spread, alternative to the variance or standard deviation which utilize squared differences.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Applications
The applications of absolute value extend far beyond these introductory examples. It forms a fundamental building block in more advanced mathematical concepts such as:
- Metric spaces: Absolute value is the basis for defining distance in metric spaces, a crucial concept in topology and analysis.
- Functional analysis: Absolute value is used to define norms in vector spaces, leading to powerful tools for analyzing functions and operators.
- Optimization problems: Absolute value functions often appear in optimization problems, particularly those involving minimizing errors or deviations.
- Differential equations: Absolute value can appear in the formulation and solution of certain differential equations.
Conclusion: The Ubiquity of Absolute Value
While the absolute value of 4 is simply 4, understanding the broader concept of absolute value and its properties opens up a world of mathematical possibilities. Its applications extend far beyond basic arithmetic, permeating advanced mathematics, various scientific disciplines, and numerous real-world applications. Mastering absolute value is not just about knowing its definition but also about appreciating its power and versatility in problem-solving and mathematical modeling. Its seemingly simple nature belies its significance in a remarkably wide range of contexts. The next time you encounter the absolute value symbol, remember its profound role in shaping our understanding of numbers, distance, error, and many other fundamental concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Smallest Common Multiple Of 3 And 4
Mar 20, 2025
-
Distance From Nashville Tn To Atlanta Ga
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is 31 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 20, 2025
-
Columns In The Periodic Table Are Called
Mar 20, 2025
-
In Which Layer Of The Atmosphere Does The Weather Occur
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Absolute Value Of 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
