How To Convert Rev To Rad
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
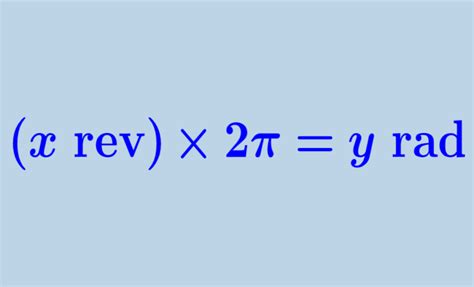
Table of Contents
How to Convert Revolutions to Radians: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to convert revolutions (rev) to radians (rad) is crucial in various fields, particularly in physics, engineering, and mathematics. Radians are the standard unit for measuring angles in many scientific and mathematical contexts, offering significant advantages in calculus and other advanced applications. Revolutions, on the other hand, are a more intuitive unit for describing rotational motion, representing a complete cycle of rotation. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to perform this conversion, along with explanations, examples, and practical applications.
Understanding Revolutions and Radians
Before delving into the conversion process, it's essential to understand the fundamental concepts of revolutions and radians.
What is a Revolution (rev)?
A revolution (rev) represents one complete rotation around a central point or axis. Think of a wheel turning once; that's one revolution. It's a straightforward unit, easy to visualize and understand in everyday contexts.
What is a Radian (rad)?
A radian (rad) is a unit of angular measurement defined by the ratio of the arc length to the radius of a circle. More specifically, one radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius. This definition is independent of the size of the circle.
Imagine a circle with a radius 'r'. If you take an arc along the circumference of the circle that is also of length 'r', the angle subtended at the center by that arc is exactly one radian. This is a crucial concept for understanding the relationship between revolutions and radians.
Because the circumference of a circle is 2πr, there are 2π radians in a complete circle (360 degrees). This fundamental relationship is the key to converting between revolutions and radians.
The Conversion Factor: The Bridge Between Revolutions and Radians
The core of converting revolutions to radians lies in the understanding that one revolution is equal to 2π radians. This is the crucial conversion factor we will use throughout our calculations.
1 rev = 2π rad
This simple equation is the foundation of all our conversion processes. We will use this factor to multiply the number of revolutions to get the equivalent angle in radians.
How to Convert Revolutions to Radians: A Step-by-Step Guide
The conversion process is straightforward: simply multiply the number of revolutions by 2π.
Steps:
-
Identify the number of revolutions: Determine the number of revolutions you want to convert. Let's denote this number as 'N'.
-
Apply the conversion factor: Multiply 'N' by 2π.
-
Calculate the result: The result of the multiplication will be the equivalent angle in radians.
Formula:
Radians = N * 2π
Where:
- Radians is the angle in radians
- N is the number of revolutions
Examples: Putting the Conversion into Practice
Let's illustrate the conversion process with some examples:
Example 1: Convert 3 revolutions to radians.
- N = 3 revolutions
- Radians = 3 * 2π = 6π radians
Therefore, 3 revolutions are equal to 6π radians (approximately 18.85 radians).
Example 2: Convert 0.5 revolutions to radians.
- N = 0.5 revolutions
- Radians = 0.5 * 2π = π radians
Therefore, 0.5 revolutions are equal to π radians (approximately 3.14 radians).
Example 3: A wheel rotates 10 times. Convert this to radians.
- N = 10 revolutions
- Radians = 10 * 2π = 20π radians
Therefore, 10 revolutions are equal to 20π radians (approximately 62.83 radians).
Example 4: A spinning top completes 2.75 revolutions. Convert this to radians.
- N = 2.75 revolutions
- Radians = 2.75 * 2π = 5.5π radians
Therefore, 2.75 revolutions are equal to 5.5π radians (approximately 17.28 radians).
Practical Applications of Revolutions to Radians Conversion
The conversion from revolutions to radians is vital in numerous real-world applications:
- Rotational mechanics: Calculating angular velocity, angular acceleration, and torque often requires working with radians.
- Circular motion: Determining the distance traveled along a circular path necessitates the use of radians.
- Physics and Engineering: Many physics equations, especially those involving rotational motion and oscillatory systems, use radians as the standard angular unit. For instance, calculating the angular frequency in simple harmonic motion requires using radians.
- Signal processing: Analyzing sinusoidal signals and waveforms frequently involves radians.
- Computer graphics and animation: Representing rotations and transformations in 3D graphics relies heavily on radians.
Beyond the Basics: Handling More Complex Scenarios
While the basic conversion is straightforward, some scenarios may require additional steps.
Dealing with fractional revolutions: As demonstrated in the examples, fractional revolutions are handled seamlessly using the same conversion factor. Simply multiply the fractional number of revolutions by 2π.
Converting from radians back to revolutions: To convert radians back to revolutions, simply divide the number of radians by 2π.
Choosing the Right Unit: Radians vs. Revolutions
While revolutions are intuitive for describing complete rotations, radians offer significant mathematical advantages. Many mathematical functions, particularly trigonometric functions, are defined and behave most naturally using radians. This is because the derivatives and integrals of trigonometric functions have simpler expressions when using radians, avoiding the need for additional conversion factors. Therefore, while revolutions are suitable for initial problem description, the conversion to radians is often necessary for mathematical analysis and calculations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Revolutions to Radians Conversion
Mastering the conversion between revolutions and radians is essential for anyone working with rotational motion, circular motion, or advanced mathematical concepts. The simple yet powerful conversion factor of 2π radians per revolution makes the process straightforward. By understanding the underlying concepts and practicing the conversion steps, you can confidently navigate these units in various applications and solve complex problems involving rotational systems. Remember, while revolutions offer an intuitive understanding of rotations, radians provide the mathematical foundation needed for more sophisticated calculations and analysis within various scientific disciplines. This conversion is a fundamental skill that will significantly enhance your ability to handle mathematical and physical problems related to rotational motion.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Electrons Are In A Carbon Atom
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Resonance Structures Can Be Drawn For Ozone O3
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 5 Out Of 25
Mar 21, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons In Aluminum
Mar 21, 2025
-
44 Is What Percent Of 50
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Convert Rev To Rad . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
