How Many Protons Does Strontium Have
listenit
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
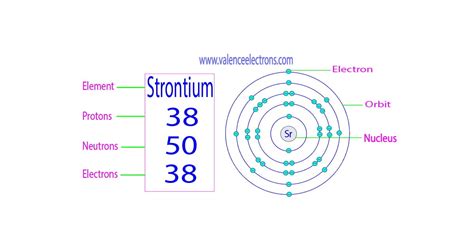
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Does Strontium Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Strontium, a fascinating element with a silvery-white metallic luster, holds a significant place in various scientific fields. But understanding its properties starts with a fundamental question: how many protons does strontium have? The answer, simply put, is 38. However, this seemingly straightforward response opens the door to a much deeper exploration of atomic structure, isotopes, and the periodic table. This article will delve into the intricacies of strontium, explaining not only its proton count but also its place within the broader context of chemistry and physics.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we delve into the specifics of strontium, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. An atom, the fundamental building block of matter, is composed of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located within the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The arrangement of these particles dictates an element's chemical properties and behavior. The positive charge of the protons in the nucleus is balanced by the negative charge of the electrons, resulting in a neutral atom. However, atoms can gain or lose electrons, forming ions with a net positive or negative charge.
Strontium's Position on the Periodic Table: Atomic Number 38
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. Strontium (Sr) is located in Group 2 (alkaline earth metals) and Period 5 of the periodic table. Its atomic number, 38, unequivocally states that every strontium atom possesses 38 protons. This fundamental characteristic dictates all of strontium's chemical and physical properties.
Isotopes of Strontium: Variations in Neutron Count
While the number of protons remains constant for a given element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Strontium has several naturally occurring isotopes, including:
- ⁸⁴Sr: This isotope contains 38 protons and 46 neutrons.
- ⁸⁶Sr: This isotope contains 38 protons and 48 neutrons.
- ⁸⁷Sr: This isotope contains 38 protons and 49 neutrons.
- ⁸⁸Sr: This isotope, the most abundant, contains 38 protons and 50 neutrons.
These isotopes exhibit similar chemical behavior due to the same number of protons and electrons, but their physical properties, such as mass and radioactive decay characteristics, differ slightly. The variation in neutron number affects the stability of the nucleus. For example, ⁸⁷Sr is a naturally occurring radioactive isotope, though it decays very slowly.
The Significance of Strontium's Proton Number in its Properties
The presence of 38 protons profoundly influences strontium's chemical and physical properties. Its position in Group 2 indicates that it readily loses two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, forming a +2 ion (Sr²⁺). This characteristic explains its reactivity and tendency to form ionic compounds with nonmetals.
Chemical Properties:
- Reactivity: Strontium is a reactive metal, readily reacting with water to produce strontium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. This reactivity is a direct consequence of its electron configuration and the ease with which it loses electrons.
- Ionic Bonding: Due to its tendency to form a +2 ion, strontium primarily forms ionic compounds through electrostatic attraction with anions. These compounds often have characteristic crystal structures and properties.
- Oxidation States: Strontium typically exhibits an oxidation state of +2.
Physical Properties:
- Metallic Luster: Strontium possesses a silvery-white metallic luster, characteristic of many alkaline earth metals.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Strontium has relatively low melting and boiling points compared to transition metals, reflecting its weaker metallic bonding.
- Density: Strontium has a relatively low density, contributing to its lightweight nature.
Strontium's Applications: Leveraging its Unique Properties
Understanding strontium's atomic structure and properties is crucial for appreciating its diverse applications:
- Pyrotechnics: Strontium salts, particularly strontium carbonate, are widely used in fireworks to produce a brilliant crimson red color. The specific emission spectrum of strontium ions during combustion gives rise to this distinctive color.
- Metallurgy: Strontium is sometimes added to alloys to improve their properties, such as malleability and strength.
- Medical Applications: Certain strontium isotopes have applications in medical imaging and therapy, taking advantage of their radioactive decay properties.
- Other Uses: Strontium compounds find applications in various fields, including ceramics, glass production, and refining of sugar.
Beyond the Basics: Nuclear Physics and Radioactive Isotopes
The study of strontium's isotopes extends beyond basic chemistry into the realm of nuclear physics. The radioactive decay of certain strontium isotopes, like ⁸⁷Sr and ⁹⁰Sr (a product of nuclear fission), provides valuable insights into geological processes, dating methods, and the impact of nuclear reactions on the environment. The understanding of these decay processes requires detailed knowledge of nuclear structure and interactions.
Conclusion: The Importance of Atomic Number
The answer to "how many protons does strontium have?" is 38. This seemingly simple number is the foundation upon which all of strontium's unique properties and applications are built. Understanding the atomic structure, isotopes, and chemical behavior of strontium not only provides a deeper understanding of this specific element but also illustrates the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of all matter. The study of strontium serves as a powerful example of how the basic building blocks of matter determine the macroscopic properties and applications we observe in the world around us. Further exploration into the realm of isotopes and nuclear physics reveals even more fascinating complexities and applications, solidifying the importance of understanding the fundamental composition of elements like strontium. The knowledge of strontium’s 38 protons is thus not merely a fact, but a key that unlocks a wealth of scientific understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Shape With 12 Edges And 6 Faces
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Graph Of A Quadratic Function Called
Mar 30, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 3
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Regular Decagon Have
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Does An Igneous Rock Become A Sedimentary Rock
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Does Strontium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
