How Many Neutrons Does Carbon 13 Have
listenit
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
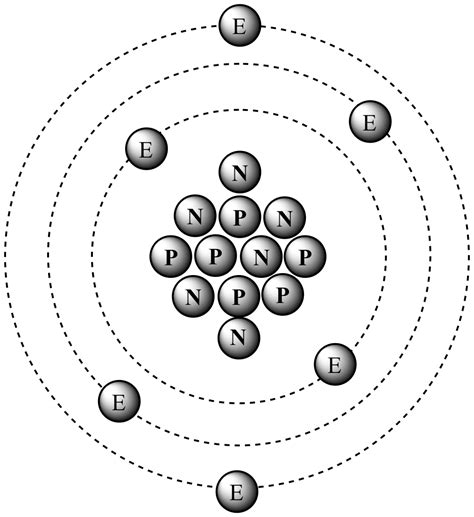
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Carbon-13 Have? Exploring Isotopes and Nuclear Structure
Carbon, the backbone of life as we know it, is a fascinating element with a rich isotopic story. While we often think of carbon as simply carbon, the reality is more nuanced. The element exists in various forms called isotopes, each differing in the number of neutrons within their atomic nuclei. This article delves into the specifics of carbon-13, exploring how many neutrons it possesses and delving into the broader concepts of isotopes, atomic structure, and their significance in various fields.
Understanding Isotopes: A Quick Refresher
Before diving into the neutron count of carbon-13, let's establish a fundamental understanding of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that share the same number of protons (defining the element) but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties, as chemical behavior is primarily determined by the electron configuration, which is directly related to the number of protons.
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is known as its atomic number. Carbon's atomic number is 6, meaning all carbon atoms have 6 protons. The mass number, on the other hand, represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. This is where isotopes become relevant. Carbon exists in several isotopic forms, including:
- Carbon-12 (¹²C): The most abundant isotope of carbon, with 6 protons and 6 neutrons (mass number = 12).
- Carbon-13 (¹³C): A stable, less abundant isotope with 6 protons and 7 neutrons (mass number = 13).
- Carbon-14 (¹⁴C): A radioactive isotope with 6 protons and 8 neutrons (mass number = 14), used in radiocarbon dating.
The Neutron Count of Carbon-13: The Answer
Now, to answer the central question: Carbon-13 has 7 neutrons.
This is derived from its mass number (13) and its atomic number (6). Since the mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons, subtracting the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number gives us the number of neutrons: 13 - 6 = 7.
The Significance of Carbon-13
While less abundant than carbon-12, carbon-13 plays a crucial role in various scientific fields. Its non-radioactive nature and relatively stable presence make it ideal for:
1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy:
Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy is a powerful technique used in chemistry and biochemistry to analyze the structure and dynamics of organic molecules. The difference in magnetic properties between carbon-12 and carbon-13 allows scientists to distinguish and study different carbon atoms within a molecule, providing valuable insights into its composition and behavior. The low natural abundance of carbon-13 often necessitates isotopic enrichment for improved NMR signal strength.
2. Stable Isotope Analysis:
Carbon-13 serves as a key tracer in stable isotope analysis, a technique used across diverse disciplines including ecology, archaeology, and paleoclimatology. The ratio of ¹³C to ¹²C in various materials can provide valuable information about past environments, dietary habits, metabolic processes, and much more. For example, variations in the ¹³C/¹²C ratio in plant tissues can indicate differences in photosynthetic pathways or environmental conditions.
3. Geochemical Studies:
The isotopic composition of carbon, including the abundance of carbon-13, provides critical insights into geochemical processes. Variations in the ¹³C/¹²C ratio in geological samples can help determine the source of carbon, the pathways of carbon cycling, and the ages of geological formations. These analyses often involve advanced mass spectrometry techniques.
4. Medical Applications:
While not as widely used as other isotopes, carbon-13 finds niche applications in medical imaging and research. Specific carbon-13 labeled compounds can be used as tracers to monitor metabolic processes and explore physiological functions in a non-invasive manner.
Beyond Carbon-13: Isotopic Abundance and Variations
The relative abundance of isotopes in nature is not uniform and can vary based on various factors. While carbon-12 is the most abundant isotope, constituting around 98.9% of natural carbon, carbon-13 makes up approximately 1.1%. This abundance ratio is relatively constant across the Earth, although minor variations can occur due to isotopic fractionation, which is the preferential enrichment or depletion of certain isotopes in different chemical processes.
Isotopic Fractionation:
Isotopic fractionation is a critical concept in understanding the distribution of isotopes in the environment. It refers to the phenomenon where different isotopes of an element partition differently during physical or chemical processes. This process can lead to variations in the isotopic ratios of an element between different materials or locations. For example, plants undergoing C3 photosynthesis often exhibit lower ¹³C/¹²C ratios compared to plants using C4 photosynthesis.
Conclusion: The Importance of Isotopes in Science
Understanding the number of neutrons in an isotope like carbon-13 is not merely an academic exercise; it is fundamental to comprehending the behavior of matter at the atomic and molecular levels. The existence of isotopes, with their variations in neutron numbers, has profound implications for various fields of study, from chemistry and biochemistry to geology, ecology, and even archaeology. The stable isotope carbon-13, with its seven neutrons, serves as a valuable tool for scientists investigating the complex processes that shape our world and life itself. By utilizing advanced techniques like NMR spectroscopy and stable isotope analysis, researchers continuously unlock new insights into the intricate world of isotopic variations and their implications for different scientific domains. Further research into isotopes promises to reveal even more about the fundamental building blocks of matter and their role in shaping our planet and universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
40 Is 60 Percent Of What Number
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Hco3
Apr 01, 2025
-
Indicate A Condensed Structural Formula For The Following Compound
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Subatomic Particle Determines The Identity Of An Atom
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is 5 Divided By 1 4
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Carbon 13 Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
