How Far Is Jupiter From Earth In Light Years
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
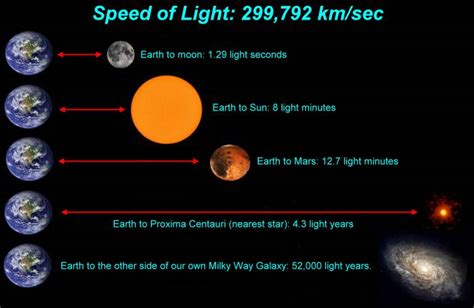
Table of Contents
How Far is Jupiter From Earth in Light Years? Understanding Astronomical Distances
The question "How far is Jupiter from Earth in light years?" might seem simple at first glance, but it reveals the complexities of measuring vast cosmic distances. While light years are a common unit for expressing interstellar distances, they aren't the most practical for measuring the comparatively smaller distances within our solar system. This article will delve into the intricacies of this question, exploring the actual distance between Jupiter and Earth, why light years aren't the ideal unit for this measurement, and explaining the various methods used to determine these distances.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU) and Light Years
Before we dive into the specifics of Jupiter's distance, let's clarify the units involved. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year – approximately 9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (5.878 × 10<sup>12</sup> miles). It's a colossal distance, perfectly suited for measuring distances to stars and galaxies.
However, for distances within our solar system, using light years would be unnecessarily cumbersome. Instead, astronomers use the Astronomical Unit (AU). One AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). This provides a more manageable scale for describing planetary distances.
The Variable Distance Between Jupiter and Earth
The distance between Jupiter and Earth is constantly changing due to the planets' elliptical orbits around the Sun. Jupiter's orbit is significantly larger than Earth's, resulting in a wide range of possible distances between the two planets.
At their closest approach, known as conjunction, Jupiter and Earth can be as close as approximately 365 million miles (588 million kilometers) or roughly 3.9 AU. Conversely, at their farthest point, or opposition, they can be over 600 million miles (966 million kilometers) apart, or about 6.2 AU.
Calculating the Distance in Light Years (Approximation)
To answer the initial question directly, while not practical, we can calculate an approximate distance in light years. Let's use the closest approach distance of 588 million kilometers. To convert this to light years, we divide the distance in kilometers by the number of kilometers in a light year:
588,000,000 km / 9,461,000,000,000 km/light-year ≈ 0.000062 light years
Therefore, at its closest point, Jupiter is approximately 0.000062 light years away from Earth. This minuscule fraction highlights why light years are unsuitable for measuring distances within our solar system.
Methods for Determining Planetary Distances
Astronomers use various techniques to determine the distances to planets, including:
-
Radar: For closer planets like Venus and Mars, radar signals are bounced off their surfaces. By measuring the time it takes for the signal to return, astronomers can precisely calculate the distance. This method isn't feasible for outer planets like Jupiter due to the significant signal attenuation over such vast distances.
-
Parallax: This method involves observing a planet from two different points on Earth's orbit, six months apart. The slight shift in the planet's apparent position against the background stars allows astronomers to calculate the distance using trigonometry. While effective for nearby planets, its accuracy decreases for more distant objects.
-
Kepler's Laws: Johannes Kepler's laws of planetary motion provide a fundamental framework for understanding planetary orbits. By carefully observing a planet's orbital period and its average distance from the sun, we can determine its distance with high precision. The application of Newton's Law of Gravitation further refines these calculations.
-
Transit method: The transit method, primarily used for exoplanet detection, can also help refine the understanding of the orbits and distances of planets in our own Solar System. Observing the slight dimming of the sun's light as a planet transits across its face allows us to determine orbital parameters, which then translates to distance.
Why Light Years are Better Suited for Interstellar Distances
While impractical for planetary distances, light years are crucial for understanding the vast expanse of space beyond our solar system. The distances to stars and galaxies are so immense that using kilometers or even AUs would result in unwieldy, extremely large numbers. Light years provide a more manageable and intuitive scale for grasping these astronomical distances.
For example, the nearest star to our Sun, Proxima Centauri, is approximately 4.24 light years away. This means that the light we see from Proxima Centauri today left the star 4.24 years ago. Using light years allows us to comprehend not only the distance but also the time it takes for light to travel across interstellar space.
The Importance of Understanding Cosmic Distances
Accurate measurement of distances, whether within our solar system or beyond, is fundamental to our understanding of the universe. This understanding is crucial for:
-
Planetary exploration: Precise knowledge of planetary distances is essential for planning and executing space missions.
-
Cosmology: Understanding distances to galaxies and other celestial objects is critical for studying the universe's expansion, structure, and evolution.
-
Astrophysics: Precise distance measurements are crucial for calibrating astronomical observations and determining the physical properties of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects.
Conclusion: Putting it All Together
While the distance between Jupiter and Earth is not practically measured in light years—its closest approach being approximately 0.000062 light years— understanding this conversion highlights the vast difference in scale between interplanetary and interstellar distances. Astronomical units (AU) serve as a much more practical unit for measuring distances within our solar system. Different sophisticated methods, from radar to Kepler's laws and transit methods, are employed to determine these distances with remarkable precision. Ultimately, a firm grasp of these measurement techniques and units is critical for our continued exploration and comprehension of the universe's magnificent expanse. The seemingly simple question of how far Jupiter is from Earth reveals a profound depth in the science of astronomy and the challenge of measuring cosmic scales.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Most Fossils Are Found In What Type Of Rock
Mar 24, 2025
-
Cis 1 4 Dimethylcyclohexane Chair Conformation
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Charge Of Nickel
Mar 24, 2025
-
Derivative Of 1 Square Root Of X
Mar 24, 2025
-
When Pressure Increases Then The Volume Must
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Far Is Jupiter From Earth In Light Years . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
