Cis 1 4 Dimethylcyclohexane Chair Conformation
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
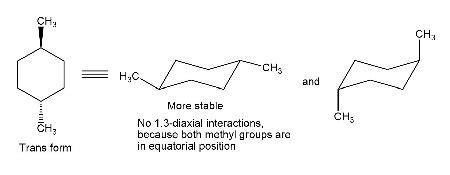
Table of Contents
Cis-1,4-Dimethylcyclohexane Chair Conformation: A Deep Dive
The conformational analysis of cyclohexane derivatives is a cornerstone of organic chemistry, offering insights into the interplay between steric interactions and molecular stability. Among these derivatives, cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane presents a particularly instructive case study, highlighting the subtle yet significant effects of substituent positioning on chair conformer equilibrium. This article delves into the intricacies of cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane's chair conformations, exploring their relative stabilities, energy differences, and the underlying principles governing their existence.
Understanding Cyclohexane Conformations
Before examining cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane specifically, it's crucial to establish a firm understanding of cyclohexane's fundamental conformations. Cyclohexane, a six-membered ring, exists primarily in two chair conformations that readily interconvert through a process involving ring flips. These chair conformations are characterized by alternating axial and equatorial positions for the ring hydrogens.
Axial and Equatorial Positions: The Key Difference
The distinction between axial and equatorial positions is vital. Axial hydrogens are oriented perpendicular to the plane of the ring, while equatorial hydrogens lie roughly in the plane of the ring. This difference in orientation significantly impacts steric interactions when substituents are attached to the cyclohexane ring. Axial substituents experience greater steric hindrance due to their proximity to other axial hydrogens on the same side of the ring (1,3-diaxial interactions). Equatorial substituents, on the other hand, experience less steric crowding.
Cis-1,4-Dimethylcyclohexane: Introducing the Isomer
Cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane refers to the stereoisomer where both methyl groups are on the same side of the cyclohexane ring. This cis configuration dictates the relative orientations of the methyl groups in the chair conformations.
Chair Conformations of Cis-1,4-Dimethylcyclohexane
Cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane possesses two chair conformations that are interconvertible:
- Conformer A: In this conformer, one methyl group is axial and the other is equatorial.
- Conformer B: In this conformer, the positions of the methyl groups are reversed – one equatorial and one axial.
Analyzing Conformer A: One Axial, One Equatorial
In Conformer A, the 1,3-diaxial interactions involving the axial methyl group contribute to its higher energy state. This interaction is significantly destabilizing compared to the equatorial methyl group, which experiences minimal steric hindrance.
Analyzing Conformer B: One Axial, One Equatorial (Mirror Image)
Conformer B is essentially a mirror image of Conformer A. The positions of the axial and equatorial methyl groups are simply swapped. Therefore, the energy considerations are identical; one methyl group experiences 1,3-diaxial interactions, raising the energy level.
Relative Stability of the Chair Conformers
A critical question arises: Which conformer is more stable? The answer, surprisingly, is that both conformers possess essentially the same energy. This is because the steric interactions in Conformer A and Conformer B perfectly mirror each other. The 1,3-diaxial interactions in one conformer are offset by the equivalent interactions in the other. Therefore, the equilibrium between these conformers favors a roughly 50:50 ratio. There is no significant energy difference driving a preference for one conformer over the other.
The Impact of Steric Strain: 1,3-Diaxial Interactions
The key to understanding the energy equivalence lies in the 1,3-diaxial interactions. These interactions are responsible for the energy penalty associated with having a substituent in the axial position. In cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane, the presence of one axial methyl group in each conformer counterbalances the other.
Comparison with Other Dimethylcyclohexane Isomers
To further illuminate the unique characteristics of cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane, it's helpful to compare it with other dimethylcyclohexane isomers:
- Trans-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane: In this isomer, the methyl groups are on opposite sides of the ring. The most stable conformation has both methyl groups in equatorial positions, resulting in significantly lower energy and a strong preference for this conformation.
- Cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane: This isomer also shows a preference for one conformer over the other due to the unequal distribution of steric strain between the two chair conformations.
- Trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane: Similar to cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane, the unequal distribution of steric strain leads to a preference for one specific chair conformation.
Experimental Evidence and Spectroscopic Techniques
The energy equivalence of the cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane conformers has been experimentally verified using various spectroscopic techniques, such as NMR spectroscopy. NMR provides information about the chemical environment of the protons, allowing for the identification and relative quantification of different conformers present in a sample. The spectral data reflects the roughly equal population of both chair conformers.
Computational Chemistry and Molecular Modeling
Computational chemistry methods, including molecular mechanics and density functional theory (DFT) calculations, are powerful tools for studying conformational preferences. These computational approaches can provide accurate predictions of relative energies and geometries of different conformers, further corroborating the experimental findings on cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane. These methods allow researchers to visualize and quantify steric interactions, providing a deeper understanding of the subtle balance of forces determining the equilibrium.
Implications and Applications
Understanding the conformational analysis of molecules like cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane is crucial in various fields:
- Drug Design: Understanding steric interactions is fundamental in designing drugs that can effectively bind to their target receptors. The conformational flexibility of molecules significantly impacts their ability to interact with biological macromolecules.
- Polymer Chemistry: The conformational properties of monomers influence the properties of the resulting polymers. Understanding conformational equilibria is key to designing polymers with specific physical and chemical characteristics.
- Materials Science: The arrangement of molecules in materials significantly affects their macroscopic properties. Understanding conformational preferences is crucial in designing materials with desirable properties.
Conclusion: A Balancing Act of Steric Forces
Cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane stands as a compelling example of how seemingly minor differences in molecular structure can have a substantial impact on conformational preferences. The approximately equal energy of its two chair conformations underscores the delicate balance between steric interactions. This understanding highlights the importance of considering steric effects when predicting molecular behavior and designing molecules with specific properties. The analysis of this molecule provides invaluable insights into the complexities of conformational analysis and its broad relevance across various scientific disciplines. Further research continues to refine our understanding of these subtle but important energy differences and their impact on the macroscopic properties of systems containing these molecules. The ongoing development of computational tools promises even more detailed and accurate predictions, leading to a deeper appreciation of the intricate dance of steric forces that govern molecular conformations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 8 In Fraction Form
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Find Z Score For Percentile
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration Of N
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Long Is 9 Feet In Meters
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 48 And 84
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cis 1 4 Dimethylcyclohexane Chair Conformation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
