Derivative Of Log With Base Other Than E
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
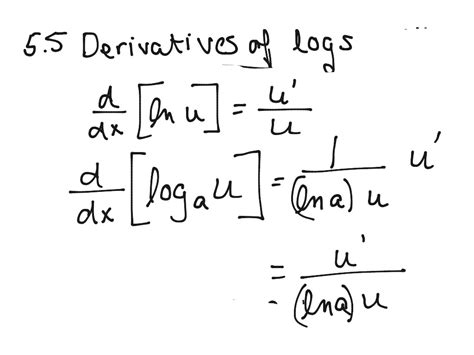
Table of Contents
The Derivative of Logarithms with Bases Other Than e
The natural logarithm, denoted as ln(x) or logₑ(x), holds a special place in calculus due to its elegant derivative: 1/x. However, we frequently encounter logarithms with bases other than e, such as log₂(x), log₁₀(x), or even logₐ(x) where 'a' is any positive number not equal to 1. Understanding how to find the derivative of these logarithms is crucial for various applications in mathematics, science, and engineering. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of deriving these logarithmic functions, providing a clear and step-by-step approach.
Understanding the Change of Base Formula
Before diving into differentiation, it's essential to grasp the change of base formula for logarithms. This formula allows us to convert a logarithm from one base to another, a critical step in simplifying the derivative process. The formula is:
logₐ(x) = logₓ(x) / logₐ(b)
Where:
- 'a' is the original base.
- 'b' is the new base (often e for simplicity in calculus).
- 'x' is the argument of the logarithm.
This formula is incredibly powerful because it lets us express any logarithm in terms of the natural logarithm (base e), which we already know how to differentiate.
Deriving the Derivative Using the Chain Rule and Change of Base
Let's consider the general case: finding the derivative of logₐ(x). We'll utilize the change of base formula to express it in terms of the natural logarithm:
logₐ(x) = ln(x) / ln(a)
Notice that 1/ln(a) is a constant. Now, we can apply the chain rule of differentiation, which states that the derivative of a composite function is the derivative of the outer function (with the inside function left alone) times the derivative of the inner function.
Let y = logₐ(x) = (1/ln(a)) * ln(x)
Applying the chain rule:
dy/dx = (1/ln(a)) * (d/dx) [ln(x)]
Since the derivative of ln(x) with respect to x is 1/x, we get:
dy/dx = (1/ln(a)) * (1/x)
Therefore, the derivative of logₐ(x) is:
d/dx [logₐ(x)] = 1 / (x * ln(a))
This is the fundamental formula for the derivative of a logarithm with any base 'a'.
Examples: Differentiating Logarithms with Different Bases
Let's solidify our understanding with some concrete examples:
Example 1: Finding the derivative of log₂(x)
In this case, a = 2. Using the formula derived above:
d/dx [log₂(x)] = 1 / (x * ln(2))
Example 2: Finding the derivative of log₁₀(x)
Here, a = 10. Applying the formula:
d/dx [log₁₀(x)] = 1 / (x * ln(10))
Example 3: Differentiating a more complex function
Let's find the derivative of f(x) = x² * log₃(x³)
First, we simplify the logarithmic term using the properties of logarithms:
f(x) = x² * 3log₃(x)
Now, we apply the product rule and our derived formula for the derivative of a logarithmic function:
f'(x) = d/dx [x²] * 3log₃(x) + x² * d/dx [3log₃(x)]
f'(x) = 2x * 3log₃(x) + x² * 3 * [1 / (x * ln(3))]
Simplifying:
f'(x) = 6xlog₃(x) + 3x / ln(3)
Applications of the Derivative
The derivative of logarithmic functions with bases other than e finds numerous applications across various fields:
-
Optimization problems: In many optimization problems, particularly in engineering and economics, logarithmic functions with different bases are used to model phenomena such as growth, decay, and resource allocation. Finding the derivative helps determine the optimal values that maximize or minimize certain quantities.
-
Rate of change analysis: The derivative provides the instantaneous rate of change of a logarithmic function. This is valuable when analyzing how a quantity changes with respect to another variable, for instance, analyzing the rate of change of population growth (often modeled using logarithmic functions).
-
Curve fitting and modeling: Logarithmic functions, with appropriately chosen bases, are often used to model real-world data. The derivative assists in fitting curves to data and making predictions based on the model.
-
Solving differential equations: Certain differential equations involve logarithmic functions, and understanding their derivatives is essential for finding solutions to these equations, which are critical in many scientific and engineering applications.
-
Financial mathematics: Logarithmic functions frequently appear in finance models related to interest rates, returns on investments, and option pricing. The derivative allows for analyzing the sensitivity of these models to changes in underlying parameters.
Beyond the Basics: Derivatives of More Complex Logarithmic Functions
The principles discussed above can be extended to more complex scenarios. For instance:
-
Logarithms of functions: If we have logₐ(f(x)), we employ the chain rule: d/dx [logₐ(f(x))] = f'(x) / (f(x) * ln(a)).
-
Implicit differentiation: When a logarithmic function is implicitly defined within an equation, we use implicit differentiation techniques combined with the derivative formula derived earlier to find the derivative.
Conclusion: Mastering Logarithmic Differentiation
Understanding the derivative of logarithmic functions with bases other than e is a fundamental skill for anyone working with calculus. By mastering the change of base formula and applying the chain rule effectively, we can readily differentiate a wide range of logarithmic expressions. The applications of this knowledge are extensive, extending to various scientific, engineering, and financial domains. Through diligent practice and the application of these principles to diverse problem sets, you can build a strong foundation in this crucial aspect of calculus. Remember that practice is key to mastering these concepts; solving various problems, from simple to complex, will greatly improve your understanding and proficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
11 Out Of 15 In Percentage
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Protons Does Magensiuum Ion Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
Domain And Range Of Arcsin X
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Protons Does Titanium Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
Group 3 12 Elements Are Called
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Derivative Of Log With Base Other Than E . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
