A Conical Tank With Vertex Down
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
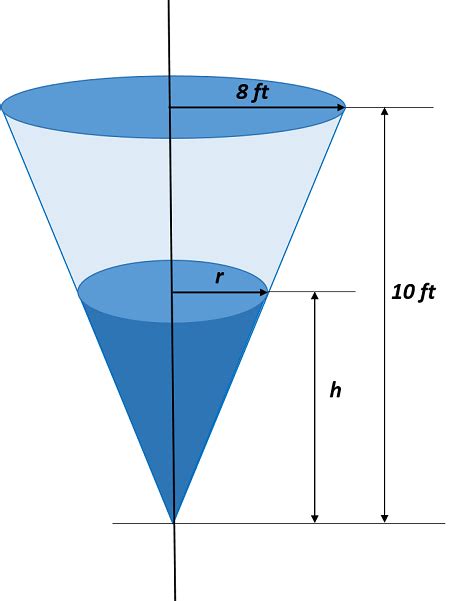
Table of Contents
- A Conical Tank With Vertex Down
- Table of Contents
- A Conical Tank with Vertex Down: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Geometry of a Conical Tank
- Calculating the Volume of a Conical Tank with Varying Liquid Levels
- Applications and Real-World Scenarios
- Fluid Dynamics in a Conical Tank
- Advanced Considerations
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Conical Tank with Vertex Down: A Comprehensive Guide
A conical tank with its vertex pointing downwards presents unique challenges and considerations in various engineering and mathematical applications. Understanding its properties, particularly its volume calculation and fluid dynamics, is crucial for accurate design and efficient operation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of conical tanks with a vertex-down orientation, covering various aspects from basic geometry to advanced applications.
Understanding the Geometry of a Conical Tank
Before tackling more complex calculations, let's establish a firm grasp of the fundamental geometry involved. A conical tank, in its simplest form, is a right circular cone. This means it has a circular base and a vertex directly above the center of that base. Key geometric parameters include:
- Radius (r): The radius of the circular base of the cone.
- Height (h): The perpendicular distance from the vertex to the base.
- Slant height (s): The distance from the vertex to any point on the circumference of the base. This can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
s = √(r² + h²). - Volume (V): The capacity of the tank, given by the formula:
V = (1/3)πr²h.
Understanding these parameters is essential for performing accurate calculations relating to the tank's capacity and the behavior of fluids within it. Accurate measurements of the radius and height are the foundation for all subsequent calculations.
Calculating the Volume of a Conical Tank with Varying Liquid Levels
One of the most common applications of understanding conical tank geometry is determining the volume of liquid contained within the tank at any given liquid level. This is not simply a case of using the standard volume formula because the filled portion also forms a cone, albeit with a smaller radius and height.
Here's how to approach this:
1. Similar Triangles: The key to solving this problem lies in the principle of similar triangles. The filled portion of the tank forms a smaller cone that is similar to the entire cone. This means the ratio of corresponding sides remains constant.
2. Proportions: Let's denote:
r: the radius of the entire tank's baseh: the height of the entire tankx: the radius of the liquid's surfacey: the height of the liquid in the tank
The proportion between the radii and heights of the similar triangles is: x/y = r/h. This allows us to express x in terms of y: x = (r/h)y.
3. Volume Calculation: Now, we can substitute this expression for x into the volume formula for a cone:
V(y) = (1/3)πx²y = (1/3)π((r/h)y)²y = (1/3)π(r²/h²)y³
This formula, V(y) = (1/3)π(r²/h²)y³, gives the volume of liquid in the tank as a function of the liquid's height (y). This is incredibly useful for monitoring liquid levels, controlling filling and emptying processes, and various other applications.
Applications and Real-World Scenarios
The knowledge of calculating the volume of a partially filled conical tank is critical in many real-world applications:
- Water storage: In agriculture and water management, conical tanks are sometimes used for storing water. The ability to precisely calculate the volume of water allows for efficient irrigation scheduling and monitoring of water resources.
- Industrial Processes: Conical tanks find use in various industrial processes, such as mixing chemicals or storing liquids. Precise volume calculations are vital for maintaining accurate ratios and preventing overflows or underfills.
- Waste Management: Conical tanks are employed in waste management systems. Understanding their volume capacities is crucial for efficient waste disposal and environmental safety.
- Chemical Reactors: In chemical engineering, conical reactors are sometimes used. The ability to accurately model the fluid dynamics and volume is critical for optimizing reaction rates and yields.
Fluid Dynamics in a Conical Tank
Understanding the fluid dynamics within a conical tank adds another layer of complexity. The shape of the cone influences the flow of liquid as it enters or exits. Several factors impact the fluid dynamics:
- Inlet/Outlet Location: The position of the inlet and outlet significantly influences the flow patterns. A bottom outlet will cause a faster flow rate at the bottom than at the top.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of the liquid affects how easily it flows. High-viscosity liquids will flow more slowly than low-viscosity liquids.
- Flow Rate: The rate at which the liquid enters or exits the tank will determine the flow patterns and the time taken to fill or empty the tank.
Modeling Fluid Dynamics: Accurate modeling of fluid dynamics in conical tanks often requires computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. These simulations can predict flow patterns, pressure distributions, and other relevant parameters, especially helpful in complex scenarios involving multiple inlets or outlets, or non-Newtonian fluids.
Advanced Considerations
- Tank Material and Stress Analysis: The material chosen for the conical tank must be able to withstand the pressure exerted by the liquid. Stress analysis is necessary to ensure the tank's structural integrity, especially for large tanks or those containing heavy liquids.
- Temperature Effects: Temperature changes can affect the volume of the liquid and the dimensions of the tank, potentially leading to inaccuracies in volume calculations. These effects must be accounted for in precise applications.
- Leakage: Leakage from a conical tank can lead to significant losses, especially in large tanks. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to minimize leakage and ensure the tank's integrity.
Conclusion
Understanding the properties and characteristics of a conical tank with its vertex down is vital for accurate calculations, efficient design, and safe operation. From calculating the volume of the contained liquid to analyzing the complexities of fluid dynamics, a thorough understanding of the geometry and principles involved is crucial across diverse engineering and industrial applications. By utilizing the formulas provided and considering the advanced considerations outlined above, engineers and designers can ensure the efficient and reliable use of conical tanks in various settings. This detailed guide serves as a valuable resource for professionals and students alike, providing a comprehensive overview of this essential piece of engineering equipment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Two Square Roots Of 64
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Percent Of 64 Is 48
Mar 23, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons In Bromine
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Percent Of 80 Is 18
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Krypton
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Conical Tank With Vertex Down . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
