What Is The Electron Configuration For Krypton
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
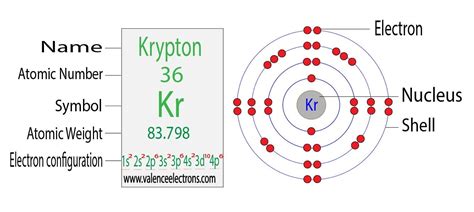
Table of Contents
- What Is The Electron Configuration For Krypton
- Table of Contents
- What is the Electron Configuration for Krypton? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
- Understanding Electron Configuration
- The Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule
- Determining Krypton's Electron Configuration
- The Significance of Krypton's Full Valence Shell
- Applications of Krypton
- Krypton's Isotopes and Nuclear Physics
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Electron Configuration for Krypton? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Krypton, a noble gas with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36, holds a special place in the periodic table. Its unique electron configuration is the key to understanding its inert nature and various applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the electron configuration of krypton, exploring its underlying principles, implications, and relevance in chemistry and physics. We'll also touch upon related concepts and answer frequently asked questions.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before we dive into krypton's specific configuration, let's establish a foundational understanding of what electron configuration represents. Electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in the various energy levels and sublevels within an atom. It's a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for predicting an element's chemical properties and behavior. These properties are directly linked to the number and arrangement of electrons in the outermost shell, known as the valence electrons.
The Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule
The process of determining electron configuration follows specific rules:
- The Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. This means electrons occupy orbitals with the lowest possible energy before moving to higher energy levels.
- Hund's Rule: Within a subshell, electrons will individually occupy each orbital before pairing up. This minimizes electron-electron repulsion.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms). This means each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
Determining Krypton's Electron Configuration
Krypton (Kr) has an atomic number of 36, meaning it has 36 protons and, in a neutral atom, 36 electrons. To determine its electron configuration, we follow the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule.
The order of filling orbitals is generally: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p... and so on. Each orbital designation has a specific meaning:
- n: Principal quantum number (energy level) – represents the shell number (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- l: Azimuthal quantum number (sublevel) – indicates the shape of the orbital (s, p, d, f). 's' orbitals are spherical, 'p' orbitals are dumbbell-shaped, and 'd' and 'f' orbitals have more complex shapes.
- ml: Magnetic quantum number – specifies the orientation of the orbital in space.
- ms: Spin quantum number – indicates the spin of the electron (+1/2 or -1/2).
Following this order, krypton's electron configuration is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶.
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: Two electrons in the 1s orbital (lowest energy level).
- 2s²: Two electrons in the 2s orbital.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons in the three 2p orbitals (each holding two electrons).
- 3s²: Two electrons in the 3s orbital.
- 3p⁶: Six electrons in the three 3p orbitals.
- 4s²: Two electrons in the 4s orbital.
- 3d¹⁰: Ten electrons in the five 3d orbitals.
- 4p⁶: Six electrons in the three 4p orbitals.
This configuration shows that all krypton's orbitals are completely filled. This completely filled outermost shell is responsible for krypton's inertness.
The Significance of Krypton's Full Valence Shell
Krypton's full valence shell (4s²4p⁶) is the reason it is a noble gas and highly unreactive. Noble gases, also known as inert gases, are characterized by their extremely low reactivity. This low reactivity is because their outermost electron shell is completely filled, meaning there is no tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The stable octet of electrons in the valence shell makes them chemically inert under normal conditions.
Applications of Krypton
Despite its inert nature, krypton does have some notable applications:
- Lighting: Krypton is used in some specialized lighting applications, such as high-intensity arc lamps and fluorescent lights. It produces a bright, white light and extends the lifespan of the lamps.
- Lasers: Krypton-based lasers are used in various applications, including surgery and spectroscopy, due to their specific wavelengths of light.
- Photography: Krypton flash tubes provide a very bright and intense light for high-speed photography.
- Plasma displays: Certain plasma displays use krypton gas in their construction.
Krypton's Isotopes and Nuclear Physics
Krypton has several stable isotopes, but also some radioactive isotopes, which are used in studies of nuclear reactions. These radioactive isotopes are critical in research, helping to deepen our understanding of nuclear processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can krypton form compounds?
A: While krypton is generally considered inert, under extreme conditions (high pressure, high energy) it can form compounds with highly electronegative elements like fluorine. These compounds are extremely unstable and rare.
Q: How does krypton's electron configuration compare to other noble gases?
A: Other noble gases, like argon (Ar), neon (Ne), and xenon (Xe), also have completely filled valence electron shells, contributing to their inertness. The number of electrons and energy levels differs, but the principle of a complete valence shell remains the same.
Q: What is the difference between the electron configuration and the orbital diagram for krypton?
A: The electron configuration shows the total number of electrons in each subshell, while the orbital diagram provides a more visual representation of the electrons' arrangement within individual orbitals, including their spins. The electron configuration for krypton is a concise summary; the orbital diagram would show each electron in its specific orbital with its spin indicated.
Q: What are the limitations of the Aufbau principle?
A: While the Aufbau principle is a useful guideline, it doesn't always perfectly predict the electron configuration of all elements, particularly transition metals and some heavier elements. Electron-electron repulsion and other quantum mechanical effects can influence the order of electron filling.
Q: How is krypton extracted?
A: Krypton is extracted from the air through a process of fractional distillation of liquid air. This separates the various components of air based on their boiling points. Krypton, being a noble gas, is present in relatively small quantities in air.
Conclusion
Krypton's electron configuration, 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶, is a crucial aspect of its chemical properties and applications. Its completely filled valence shell explains its inert nature, making it suitable for specific uses in lighting, lasers, and other technologies. This article provided a detailed examination of its electron configuration and related concepts, hopefully providing a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable element. Further research into quantum mechanics and nuclear chemistry will provide a deeper appreciation of the complexities involved in atomic structure and the unique properties of elements like krypton.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Common Factors Of 18 And 24
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Find Exponential Function From Two Points
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Organelle Is Found In Plant Cells But Not Animal
Mar 26, 2025
-
6 Of 15 Is What Percent
Mar 26, 2025
-
Systems Of Equations With Three Variables
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electron Configuration For Krypton . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
