Number Of Valence Electrons In Bromine
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
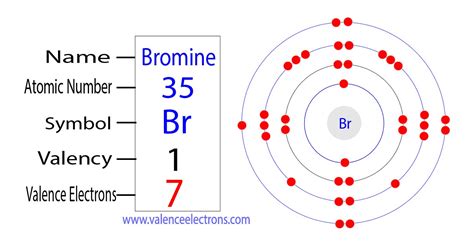
Table of Contents
The Enigmatic Valence Electrons of Bromine: A Deep Dive
Bromine, a vibrant reddish-brown liquid element, holds a fascinating place in the periodic table. Its chemical behavior, reactivity, and unique properties are all intricately linked to a single, crucial aspect: its valence electrons. Understanding the number of valence electrons in bromine is fundamental to grasping its chemical interactions and the compounds it forms. This comprehensive article will explore this topic in depth, covering everything from basic atomic structure to the implications of bromine's valence electrons in various chemical contexts.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Bonding
Before we delve into the specifics of bromine, let's establish a clear understanding of what valence electrons are. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. These electrons are the primary players in chemical reactions, determining how an atom will interact with other atoms to form chemical bonds. They are responsible for an element's reactivity and its ability to form compounds. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses dictates its bonding capacity and the types of bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, metallic). Understanding the distribution and behavior of valence electrons is, therefore, paramount to understanding chemistry.
Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons: Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
Bromine (Br) is a halogen, residing in Group 17 (or VIIA) of the periodic table. The periodic table itself is a powerful tool for predicting the number of valence electrons an element possesses. Group numbers (using the IUPAC numbering system) directly indicate the number of valence electrons for main group elements (elements not in the transition metal or inner transition metal blocks).
Bromine's atomic number is 35. This means a neutral bromine atom has 35 protons and 35 electrons. To determine the number of valence electrons, we need to examine its electron configuration. The electron configuration of bromine is:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵
The valence electrons are those in the outermost energy level, which, for bromine, is the fourth energy level (n=4). This level contains the 4s² and 4p⁵ electrons. Adding these together, we find that bromine has 7 valence electrons.
This also aligns with its position in Group 17. Elements in this group all have 7 valence electrons, contributing to their similar chemical behaviors.
The Significance of Seven Valence Electrons: Reactivity and Bonding
The presence of seven valence electrons profoundly influences bromine's chemical properties. Atoms tend to strive for a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas (elements in Group 18 with full valence shells). This tendency is described by the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve eight electrons in their outermost shell.
Bromine, with its seven valence electrons, is one electron short of achieving a stable octet. This makes bromine highly reactive, readily participating in chemical reactions to gain that extra electron. This is typically achieved through one of two primary methods:
-
Ionic Bonding: Bromine readily accepts an electron from another atom, typically a metal, forming a bromide ion (Br⁻). This process results in an ionic bond, a strong electrostatic attraction between the positively charged metal cation and the negatively charged bromide anion. Examples include sodium bromide (NaBr) and potassium bromide (KBr).
-
Covalent Bonding: Alternatively, bromine can share an electron pair with another atom, forming a covalent bond. This is particularly common with other nonmetals. Bromine forms single covalent bonds with other halogens (e.g., Br₂, BrCl), and it can form multiple bonds (though less common) with elements such as carbon.
Bromine's Diverse Compounds: A Testament to its Valence Electrons
The versatility of bromine's bonding capabilities, driven by its seven valence electrons, leads to a wide array of compounds with diverse applications. Some notable examples include:
-
Bromide salts: These salts, formed through ionic bonding, have various applications, from flame retardants to photographic chemicals (silver bromide, AgBr).
-
Organic bromine compounds: Bromine readily incorporates itself into organic molecules, forming a vast array of compounds used in agriculture (as pesticides), medicine, and industrial applications (as solvents and catalysts).
-
Bromine gas (Br₂): In its elemental form, bromine exists as a diatomic molecule (Br₂), where two bromine atoms share an electron pair via a covalent bond, completing their octets.
The Role of Valence Electrons in Bromine's Physical Properties
While chemical properties are primarily determined by valence electrons, the number of valence electrons also subtly influences an element's physical properties. For instance, bromine's seven valence electrons contribute to its relatively high electronegativity. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Bromine's high electronegativity results in its strong attraction to other atoms, contributing to its high reactivity and its ability to form strong bonds.
Furthermore, the arrangement of electrons in its valence shell influences bromine's relatively low melting and boiling points compared to other halogens. The intermolecular forces between bromine molecules are relatively weak, leading to these lower points.
Advanced Concepts: Oxidation States and Beyond
The concept of valence electrons extends to the understanding of oxidation states. The oxidation state of an atom represents the hypothetical charge it would have if all bonds were completely ionic. Bromine, with its seven valence electrons, commonly exhibits oxidation states ranging from -1 (in bromide ions) to +7 (in compounds such as perbromates). These varying oxidation states further expand the range of chemical compounds bromine can form.
Applications and Industrial Relevance: A Broader Perspective
The unique properties of bromine, stemming from its seven valence electrons, have led to its widespread application in diverse fields:
-
Agriculture: Bromine-containing compounds are used as pesticides and fumigants to control pests and diseases.
-
Medicine: Bromine compounds are used in various medications and treatments, although some are being phased out due to environmental concerns.
-
Industry: Bromine compounds are crucial in various industrial applications, including flame retardants, water treatment, and the production of various chemicals.
-
Photography: Silver bromide (AgBr) is a vital component in traditional photographic film.
Environmental Considerations: Responsible Use of Bromine
Due to the widespread use of bromine compounds, their environmental impact is an important concern. Some bromine-containing compounds can persist in the environment, accumulating in organisms and potentially harming ecosystems. Therefore, responsible handling and disposal practices are crucial to mitigate potential risks and ensure the sustainable use of bromine resources.
Conclusion: A Powerful Element Defined by its Valence Electrons
The number of valence electrons in bromine, seven, serves as the cornerstone for understanding its chemical behavior and its diverse applications. Its reactivity, bonding characteristics, and the wide range of compounds it forms are all direct consequences of this key feature. From basic ionic and covalent bonding to the more nuanced concepts of oxidation states and environmental considerations, the influence of bromine's seven valence electrons extends across numerous aspects of chemistry and beyond. Understanding valence electrons is fundamental to comprehending the behavior of all elements, and bromine provides a compelling illustration of the power of this concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does The Modern Theory Of Plate Tectonics State
Mar 25, 2025
-
Where Is The Majority Of Fresh Water Found On Earth
Mar 25, 2025
-
25 Out Of 31 As A Percentage
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Do Pulleys Make Work Easier
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Has The Largest Atomic Radius
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Valence Electrons In Bromine . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
