What Are The Two Square Roots Of 64
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
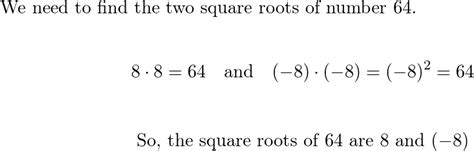
Table of Contents
What Are the Two Square Roots of 64? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Their Applications
The question, "What are the two square roots of 64?" seems simple at first glance. The immediate answer, 8, is often the only one considered. However, a deeper understanding of square roots reveals a more nuanced answer: 8 and -8. This article will delve into the concept of square roots, explore why 64 has two square roots, and examine the broader applications of square roots in various fields.
Understanding Square Roots
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. This is often represented as √9 = 3. But this only tells part of the story.
The Concept of Squaring
Before diving deeper into square roots, let's solidify the concept of squaring a number. Squaring a number simply means multiplying the number by itself. For example:
- 2² = 2 x 2 = 4
- 5² = 5 x 5 = 25
- (-3)² = (-3) x (-3) = 9
Notice that squaring a negative number results in a positive number. This is a crucial concept when understanding the two square roots of a number.
Why Two Square Roots?
The key to understanding why 64 has two square roots lies in the nature of multiplication. When we ask, "What number multiplied by itself equals 64?", we are essentially solving the equation x² = 64. This equation has two solutions:
- x = 8: Because 8 x 8 = 64
- x = -8: Because (-8) x (-8) = 64
Therefore, both 8 and -8 are square roots of 64. The principal square root (often denoted by √64) is 8, the positive square root. However, it's vital to remember that every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
Beyond 64: Exploring Square Roots of Other Numbers
The concept of two square roots applies to all positive numbers. Let's examine some examples:
- √25 = ±5: Both 5 and -5 are square roots of 25 because 5 x 5 = 25 and (-5) x (-5) = 25.
- √100 = ±10: Similarly, 10 and -10 are square roots of 100.
- √1 = ±1: The square roots of 1 are 1 and -1.
However, the square root of 0 is unique:
- √0 = 0: Zero only has one square root, which is itself.
And what about negative numbers? The square root of a negative number involves complex numbers, which are beyond the scope of this introductory exploration. However, it's important to note that they are an extension of the real number system and are extensively used in advanced mathematics and physics.
Practical Applications of Square Roots
Square roots are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have widespread practical applications in various fields:
1. Geometry and Measurement
Square roots are fundamental in geometry for calculating distances, areas, and volumes. For example:
-
Pythagorean Theorem: This theorem, a cornerstone of geometry, uses square roots to determine the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle (a² + b² = c², where c is the hypotenuse). Many real-world applications, from surveying land to constructing buildings, rely on this theorem.
-
Calculating the area of a square: If you know the area of a square, finding the length of its side involves taking the square root of the area.
-
Calculating the radius of a circle: If you know the area of a circle, you can calculate its radius using the formula r = √(A/π), where A is the area.
2. Physics and Engineering
Square roots are crucial in various physics and engineering calculations:
-
Speed and Velocity Calculations: Understanding the relationship between distance, time, and velocity often involves working with square roots. For instance, calculating the final velocity of an object under constant acceleration necessitates using square roots.
-
Calculating energy: In physics, calculating the kinetic energy of a moving object involves squaring the velocity; the inverse calculation uses square roots.
-
Electrical Engineering: In circuit analysis and other electrical engineering calculations, impedance and other properties frequently involve square roots.
3. Data Analysis and Statistics
Square roots play a role in statistical analysis:
-
Standard Deviation: Calculating the standard deviation of a dataset involves taking the square root of the variance. The standard deviation measures the spread or dispersion of data points around the mean.
-
Root Mean Square (RMS): This statistical measure is commonly used in signal processing, acoustics, and other fields to find the effective value of a varying quantity. It involves taking the square root of the mean of the squares of the values.
4. Computer Graphics and Game Development
Square roots are essential in computer graphics and game development for various operations:
-
Distance Calculations: Determining the distance between two points on a screen or in a 3D game environment uses the distance formula, which involves square roots.
-
Vector Normalization: Normalizing vectors, a common task in graphics programming, requires calculating the magnitude of the vector, which uses a square root.
-
Lighting and Shadow Calculations: Realistic lighting and shadow effects in computer games frequently use algorithms that depend on square root calculations.
Advanced Concepts Related to Square Roots
While we've focused on the basics, several more advanced concepts build upon the understanding of square roots:
-
Nth Roots: Square roots are a specific case of nth roots, where n is the index of the root. For example, the cube root (∛) is a third root, and the fourth root is a fourth root, and so on. These higher-order roots find application in various mathematical and scientific fields.
-
Irrational Numbers: Many square roots, such as √2 or √3, are irrational numbers—numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. These numbers have an infinite number of non-repeating decimal places, and their importance in mathematics and its applications cannot be overstated.
-
Radical Expressions: Expressions containing square roots or other roots are called radical expressions. Manipulating and simplifying these expressions is a crucial skill in algebra and calculus.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Square Roots
The seemingly straightforward question of finding the square roots of 64 opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts and their applications. Understanding that 64 has two square roots—8 and -8—is critical for grasping the broader implications of square roots in various fields. From basic geometry to advanced physics and computer science, square roots are an indispensable tool, highlighting the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their power to describe and solve real-world problems. The more we delve into these fundamental ideas, the more we appreciate their elegance and utility. So, next time you encounter a square root, remember that the answer may be more complex, and perhaps more interesting, than you first imagined.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Chambers Does The Frog Heart Have
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Oz Is A Quarter Lb
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Oxygen Released During Photosynthesis Comes From Where
Mar 25, 2025
-
Substance That Speeds Up The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which State Of Matter Has Highest Kinetic Energy
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Two Square Roots Of 64 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
