X 3 4x 2 4x 16
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
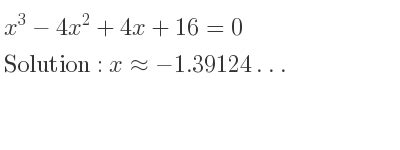
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: A Deep Dive into x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16
The expression x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16 presents a fascinating challenge in algebra. At first glance, it might seem like a simple cubic polynomial, but a closer examination reveals opportunities for factorization and deeper mathematical understanding. This article will dissect this expression, exploring various methods of simplification, highlighting crucial mathematical concepts, and unveiling the hidden elegance within this seemingly straightforward algebraic puzzle.
Understanding the Basics: Cubic Polynomials and Factorization
Before delving into the specifics of x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16, let's establish a firm foundation in the fundamentals. A cubic polynomial is a polynomial of degree three, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 3. These polynomials can be expressed in the general form: ax³ + bx² + cx + d, where a, b, c, and d are constants.
Factorization, a critical process in algebra, involves expressing a polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials. This process is crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and gaining a deeper understanding of the polynomial's behavior. Factoring a cubic polynomial can be more challenging than factoring quadratic expressions, often requiring a combination of techniques.
Approaches to Factoring x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16
Several methods can be employed to tackle the factorization of x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16. Let's explore some common strategies:
1. Factoring by Grouping
One common approach is factoring by grouping. This technique involves grouping terms with common factors and then factoring out these common factors. Let's see if this method works for our expression:
x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16 can be grouped as: (x³ + 4x²) + (4x + 16)
Factoring out common factors from each group, we get: x²(x + 4) + 4(x + 4)
Notice that (x + 4) is a common factor in both terms. Factoring this out, we obtain: (x + 4)(x² + 4)
This factorization reveals a crucial aspect of the original expression. It's now expressed as the product of a linear factor (x + 4) and a quadratic factor (x² + 4).
2. The Rational Root Theorem
The Rational Root Theorem provides a systematic way to identify potential rational roots of a polynomial. This theorem states that any rational root of a polynomial with integer coefficients can be expressed in the form p/q, where p is a factor of the constant term and q is a factor of the leading coefficient.
In our case, the constant term is 16, and the leading coefficient is 1. Therefore, the potential rational roots are the factors of 16: ±1, ±2, ±4, ±8, ±16. We can test these values by substituting them into the polynomial. If we find a root, we can then perform polynomial division to find the remaining factor.
Testing the potential roots reveals that x = -4 is a root because:
(-4)³ + 4(-4)² + 4(-4) + 16 = -64 + 64 - 16 + 16 = 0
This confirms that (x + 4) is a factor, which aligns with our findings using factoring by grouping.
3. Polynomial Long Division
After identifying a factor using the Rational Root Theorem or other methods, polynomial long division can be used to find the other factor(s). Dividing x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16 by (x + 4) yields the quadratic factor x² + 4.
This method provides a systematic way to verify and obtain the remaining factors after finding one root.
Analyzing the Factors: x + 4 and x² + 4
Now that we've factored the expression into (x + 4)(x² + 4), let's examine each factor:
-
(x + 4): This is a simple linear factor. Setting it to zero gives us the root x = -4. This indicates that the graph of the cubic polynomial intersects the x-axis at x = -4.
-
(x² + 4): This is a quadratic factor. Notice that it cannot be factored further using real numbers. To find the roots, we can set it to zero: x² + 4 = 0 => x² = -4 => x = ±2i, where 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1). These are complex roots, indicating that the graph of the quadratic (and consequently the cubic) does not intersect the x-axis at any other points in the real plane.
Graphical Representation and Implications
The factorization allows for a clearer understanding of the polynomial's graphical behavior. The real root x = -4 represents an x-intercept. The complex roots (±2i) indicate that the graph does not intersect the x-axis beyond this point. The cubic polynomial will have a single real root and exhibit a characteristic shape influenced by the presence of complex roots.
Applications and Extensions
This seemingly simple algebraic exercise demonstrates powerful techniques applicable in various mathematical contexts. Understanding factorization, polynomial division, and the Rational Root Theorem are fundamental skills in fields like:
- Calculus: Finding roots and analyzing polynomial behavior are crucial for optimization problems, curve sketching, and understanding function behavior.
- Engineering: Polynomial expressions are used extensively in modeling physical systems, where understanding roots and behavior is vital for design and analysis.
- Physics: Many physical phenomena can be described using polynomial models, making factorization and root-finding techniques indispensable.
- Computer Science: Algorithmic efficiency often hinges on techniques for manipulating and simplifying polynomials.
Conclusion: Beyond the Surface
The seemingly straightforward expression x³ + 4x² + 4x + 16 reveals a wealth of mathematical depth. By applying various factorization techniques, we've uncovered its underlying structure, revealing real and complex roots, and gaining insights into its graphical representation. This exploration emphasizes the importance of mastering algebraic tools and highlights the interconnectedness of seemingly disparate mathematical concepts. The journey from a simple polynomial to its factored form is a testament to the beauty and power of algebraic manipulation and its applications in a wide range of scientific and engineering disciplines. This deep dive underscores the significance of thorough algebraic understanding, reminding us that even seemingly simple expressions can hold fascinating mathematical secrets. The techniques learned in this analysis will prove invaluable in tackling more complex polynomial expressions and related mathematical challenges. Furthermore, understanding the underlying principles of factorization and root-finding allows for more efficient and effective problem-solving across various disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
This Type Of Reaction Requires Energy In Order To Proceed
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 57
Mar 15, 2025
-
C 5 9 F 32 Solve For F
Mar 15, 2025
-
2 3 Divided By 1 2
Mar 15, 2025
-
Density Of Water At 4 Degrees Celsius
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 4x 2 4x 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
