X 3 3x 2 16x 48
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
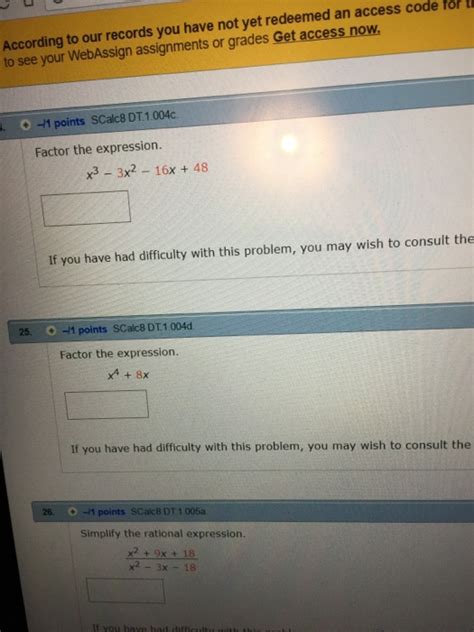
Table of Contents
Deconstructing the Expression: x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48
This article delves deep into the mathematical expression x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48, exploring its various facets, including factorization, solving for x, graphical representation, and its applications within different mathematical contexts. We'll dissect this cubic polynomial, revealing its hidden secrets and demonstrating practical techniques for understanding and manipulating similar expressions.
Understanding the Basics: Cubic Polynomials
Before we embark on analyzing x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48, let's lay a strong foundation by revisiting the fundamentals of cubic polynomials. A cubic polynomial is a polynomial of degree three, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is three. The general form of a cubic polynomial is ax³ + bx² + cx + d, where a, b, c, and d are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. Our expression, x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48, fits this description perfectly, with a=1, b=3, c=16, and d=48.
Factorization Techniques: Unveiling the Factors
Factorization is a crucial step in simplifying and solving polynomial equations. The goal is to express the polynomial as a product of simpler expressions. For our cubic polynomial, we can employ several techniques:
1. Factoring by Grouping
This method is particularly effective when the polynomial can be grouped into pairs of terms that share common factors. Let's try this approach with x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48:
We can group the terms as follows: (x³ + 3x²) + (16x + 48)
Now, factor out the common factor from each group: x²(x + 3) + 16(x + 3)
Notice that (x + 3) is a common factor in both terms. We can factor this out: (x + 3)(x² + 16)
Therefore, the factorization of x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48 is (x + 3)(x² + 16).
2. The Rational Root Theorem
The Rational Root Theorem helps identify potential rational roots (solutions) of a polynomial equation. It states that any rational root of the polynomial will be of the form p/q, where p is a factor of the constant term (48 in our case) and q is a factor of the leading coefficient (1 in our case).
This means potential rational roots are factors of 48: ±1, ±2, ±3, ±4, ±6, ±8, ±12, ±16, ±24, ±48. We can test these values by substituting them into the polynomial. If the result is zero, then that value is a root, and (x - root) is a factor. In this case, substituting x = -3 yields:
(-3)³ + 3(-3)² + 16(-3) + 48 = -27 + 27 - 48 + 48 = 0
This confirms that x = -3 is a root, and (x + 3) is a factor, aligning with our finding using factoring by grouping.
3. Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is a streamlined method for dividing a polynomial by a linear factor (x - r), where 'r' is a potential root. It's particularly useful when we already have a potential root from the Rational Root Theorem. Performing synthetic division with x = -3 on our polynomial confirms that (x + 3) is indeed a factor and the quotient is x² + 16.
Solving for x: Finding the Roots
Now that we've factored the polynomial into (x + 3)(x² + 16), we can find the roots (values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero).
-
From (x + 3) = 0: This gives us x = -3 as one real root.
-
From (x² + 16) = 0: This gives us x² = -16, which results in two complex roots: x = 4i and x = -4i, where 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1).
Therefore, the complete set of roots for the equation x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48 = 0 is {-3, 4i, -4i}.
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Polynomial
The graph of a cubic polynomial can reveal valuable information about its roots, behavior, and overall characteristics. Plotting the function y = x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48 reveals the following:
-
The graph intersects the x-axis at x = -3, visually confirming our real root.
-
The graph does not intersect the x-axis at any other points, indicating the presence of complex roots, which are not visible on a standard real-number Cartesian plane.
-
The overall shape of the cubic curve demonstrates its increasing nature as x moves towards positive infinity and its decreasing nature as x moves towards negative infinity.
Applications and Extensions
The cubic polynomial x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48, while seemingly simple, holds relevance in various mathematical applications:
-
Modeling Real-World Phenomena: Cubic polynomials can model various real-world phenomena, including the trajectory of a projectile, the growth of populations, or the volume of a three-dimensional object. The specific context dictates the interpretation of the roots and the significance of the polynomial's overall behavior.
-
Calculus Applications: Finding derivatives and integrals of cubic polynomials is a fundamental aspect of calculus. The derivative of x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48 is 3x² + 6x + 16, which can be used to find critical points and analyze the function's rate of change.
-
Higher-Order Polynomial Equations: The techniques used to analyze this cubic polynomial (factoring, synthetic division, solving for roots) are applicable, with necessary modifications, to higher-order polynomial equations. Understanding the fundamentals laid out here provides a solid base for tackling more complex mathematical problems.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concepts of factorization and roots extend into abstract algebra, where polynomials are studied in more general settings. Understanding the factorization of x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48 provides a concrete example to further appreciate these abstract concepts.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding
This comprehensive analysis of x³ + 3x² + 16x + 48 reveals that even seemingly straightforward mathematical expressions can harbor rich layers of complexity. By exploring its factorization, roots, graphical representation, and applications, we gain a deeper understanding of cubic polynomials and their significance in mathematics and beyond. The techniques employed here—factoring by grouping, the Rational Root Theorem, synthetic division, and the graphical analysis of the polynomial—serve as fundamental tools for tackling a wide range of mathematical challenges. The journey of understanding this particular expression showcases the beauty and power of mathematical exploration, revealing how seemingly simple equations can lead to intricate insights and practical applications. The process of dissecting this cubic polynomial underscores the importance of a methodical approach to problem-solving, emphasizing the interconnectedness of different mathematical concepts. It is through this careful exploration that we can appreciate the elegance and utility of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Simplest Form Of 4 12
Mar 28, 2025
-
Find The Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 9
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 1 10 Of 10
Mar 28, 2025
-
Points Of View Or Point Of Views
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Cl
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 3x 2 16x 48 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
