Which Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Occur In
listenit
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
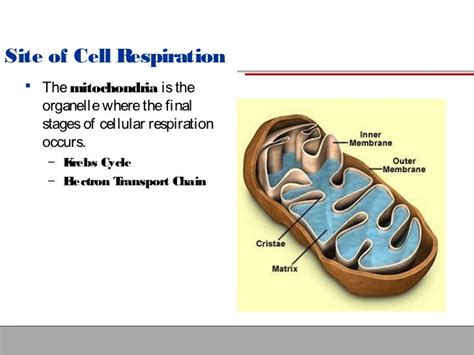
Table of Contents
Which Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Occur In? A Deep Dive into the Mitochondria
Cellular respiration, the process that fuels life, is a complex series of biochemical reactions that convert nutrients into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). But where, precisely, within the cell does this vital process unfold? The answer is the mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell. This article will delve deep into the structure and function of mitochondria, exploring their crucial role in cellular respiration and highlighting the intricate mechanisms that make life possible.
The Mighty Mitochondria: Structure and Function
Mitochondria are double-membrane-bound organelles found in most eukaryotic cells. Their unique structure is intimately linked to their function in cellular respiration. Let's break down the key structural components:
1. Outer Mitochondrial Membrane: The Gatekeeper
The outer mitochondrial membrane is a relatively porous membrane, permeable to small molecules and ions. This permeability is due to the presence of porins, protein channels that allow for the free passage of substances. This characteristic distinguishes it from the inner membrane, which is much less permeable.
2. Intermembrane Space: A Crucial Compartment
Between the outer and inner membranes lies the intermembrane space, a narrow region that plays a critical role in the electron transport chain, a key step in cellular respiration. The proton gradient established across this space is fundamental to ATP synthesis.
3. Inner Mitochondrial Membrane: The Site of ATP Production
The inner mitochondrial membrane is highly folded into structures called cristae. These folds significantly increase the surface area available for the electron transport chain and ATP synthase, maximizing the efficiency of ATP production. The inner membrane is impermeable to most ions and molecules, maintaining the crucial proton gradient. It is studded with numerous protein complexes involved in the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation.
4. Mitochondrial Matrix: The Central Hub
The mitochondrial matrix, enclosed by the inner membrane, contains the enzymes necessary for the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle), a crucial step in cellular respiration. It also houses mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), mitochondrial ribosomes, and tRNA molecules, enabling the mitochondria to synthesize some of its own proteins.
The Stages of Cellular Respiration: A Mitochondrial Journey
Cellular respiration is a multi-stage process that can be broadly divided into four main stages:
1. Glycolysis: The Preparatory Stage
Glycolysis, although not strictly occurring within the mitochondria, is the initial step in cellular respiration. It takes place in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. This process generates a small amount of ATP and NADH, a crucial electron carrier that will later play a significant role in the mitochondria.
2. Pyruvate Oxidation: Entering the Mitochondria
Pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, is transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Here, it undergoes oxidative decarboxylation, a process that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA. This step releases carbon dioxide and generates NADH.
3. The Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle or TCA Cycle): The Central Metabolic Hub
The acetyl-CoA produced during pyruvate oxidation enters the citric acid cycle, a cyclical series of reactions that occur in the mitochondrial matrix. This cycle generates ATP, NADH, FADH2 (another electron carrier), and releases carbon dioxide. The citric acid cycle is a central metabolic hub, connecting various metabolic pathways within the cell.
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation: ATP Synthesis
Oxidative phosphorylation, the final and most significant stage of cellular respiration, occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This process involves two key components:
-
Electron Transport Chain (ETC): The electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are passed along a series of protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. As electrons move through the chain, protons (H+) are pumped from the matrix into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient.
-
Chemiosmosis: The proton gradient established by the ETC drives the synthesis of ATP through a process called chemiosmosis. Protons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase, an enzyme that utilizes the energy of the proton gradient to phosphorylate ADP, forming ATP. This is where the majority of ATP is generated during cellular respiration.
The Importance of Mitochondrial Function
The efficient functioning of mitochondria is crucial for various cellular processes and overall health. Dysfunction in these organelles can lead to a range of diseases and conditions, including:
-
Mitochondrial diseases: These are a group of disorders that affect the mitochondria's ability to produce energy, leading to a wide range of symptoms depending on which tissues or organs are primarily affected.
-
Neurodegenerative diseases: Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in several neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. The high energy demand of the brain makes it particularly vulnerable to mitochondrial impairment.
-
Cancer: Mitochondria play a complex role in cancer development. Changes in mitochondrial function can contribute to cancer initiation and progression.
-
Aging: Mitochondrial dysfunction is thought to contribute to the aging process, as the accumulation of damage to mitochondria over time can lead to a decline in cellular function.
Beyond Cellular Respiration: Other Mitochondrial Roles
While cellular respiration is the primary function of mitochondria, they are also involved in several other vital cellular processes:
-
Calcium homeostasis: Mitochondria play a significant role in regulating calcium levels within the cell. They can store and release calcium ions, influencing various cellular processes.
-
Apoptosis (programmed cell death): Mitochondria are involved in the initiation of apoptosis, a process of programmed cell death crucial for development and the removal of damaged or unwanted cells. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria is a key signal in the apoptotic pathway.
-
Heme synthesis: Mitochondria are involved in the synthesis of heme, a crucial component of hemoglobin and other proteins.
-
Steroid hormone synthesis: In certain cell types, mitochondria participate in the synthesis of steroid hormones.
Conclusion: The Powerhouse Within
The mitochondria are far more than just the "powerhouses" of the cell; they are dynamic organelles with diverse functions critical for life. Their intricate structure, with its double membrane, cristae, and matrix, is perfectly tailored for carrying out cellular respiration, a process that provides the energy needed for all cellular activities. Understanding the structure and function of mitochondria is essential for comprehending the complexities of cellular biology, health, and disease. Further research continues to unveil the intricacies of these fascinating organelles, revealing their ever-expanding roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis and overall organismal health. Their pivotal role in energy production makes them a critical focus in various fields of biomedical research, aiming to develop novel treatments for diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. The exploration of the mitochondria's functions continues to unveil new facets of their importance in the intricate machinery of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Half Life Of Potassium 40
Apr 04, 2025
-
7 Is What Percent Of 15
Apr 04, 2025
-
6 Is 25 Of What Number
Apr 04, 2025
-
Organism That Cannot Produce Its Own Food
Apr 04, 2025
-
Least Common Factor Of 12 And 36
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Occur In . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
