Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Cell Membrane
listenit
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
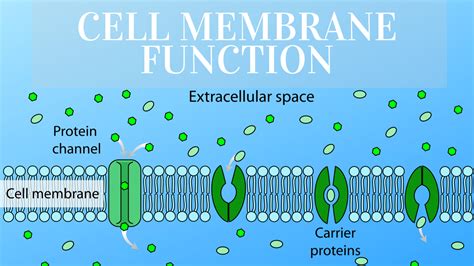
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Function of the Cell Membrane? A Deep Dive into Cellular Structure and Function
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a vital component of all living cells. It's far more than just a passive barrier; it's a dynamic, selectively permeable gatekeeper orchestrating a complex interplay of processes crucial for cell survival and function. Understanding its functions is fundamental to grasping the intricacies of cellular biology. This article will explore the multifaceted roles of the cell membrane, addressing the question of its functions in detail.
The Cell Membrane: A Dynamic Barrier
Before diving into the specific functions, let's establish a basic understanding of the cell membrane's structure. It's primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer, a double layer of phospholipid molecules. These molecules have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and two hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails. This arrangement creates a selectively permeable barrier, allowing some substances to pass through while restricting others. Embedded within this bilayer are various proteins, cholesterol molecules, and glycolipids, each contributing to the membrane's diverse functionalities.
1. Regulation of Transport: The Gatekeeper of the Cell
One of the most critical functions of the cell membrane is regulating the transport of substances across it. This involves both passive and active transport mechanisms.
Passive Transport: This type of transport doesn't require energy. It includes:
- Simple Diffusion: Movement of small, nonpolar molecules (like oxygen and carbon dioxide) directly across the phospholipid bilayer, from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- Facilitated Diffusion: Movement of larger or polar molecules (like glucose and amino acids) across the membrane with the help of membrane proteins. These proteins act as channels or carriers, facilitating the passage of specific molecules down their concentration gradient.
- Osmosis: The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration). This process is crucial for maintaining cell turgor and preventing cell lysis (bursting) or plasmolysis (shrinking).
Active Transport: This type of transport requires energy, typically in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). It's used to move molecules against their concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Examples include:
- Sodium-Potassium Pump: This crucial pump maintains the electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane by actively transporting sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell and potassium ions (K+) into the cell. This gradient is essential for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
- Endocytosis: The process by which the cell takes in substances from its external environment by engulfing them. There are different types of endocytosis, including phagocytosis ("cell eating"), pinocytosis ("cell drinking"), and receptor-mediated endocytosis (targeted uptake of specific molecules).
- Exocytosis: The process by which the cell releases substances from its interior to the external environment. This is important for secretion of hormones, neurotransmitters, and waste products.
2. Cell Signaling and Communication: The Communication Hub
The cell membrane plays a crucial role in cell signaling and communication. Receptors embedded in the membrane bind to specific signaling molecules (ligands), initiating intracellular signaling cascades that regulate various cellular processes. These signaling pathways can trigger changes in gene expression, metabolism, cell growth, and even cell death.
- Receptor Proteins: These transmembrane proteins span the cell membrane and have specific binding sites for signaling molecules. Upon ligand binding, they undergo conformational changes, triggering downstream signaling events.
- Second Messengers: These intracellular molecules amplify the signal initiated by ligand binding to receptors. Examples include cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium ions (Ca2+).
- Cell Junctions: Specialized structures in the cell membrane that connect adjacent cells, facilitating communication and coordination between cells in tissues and organs. These include tight junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes.
3. Cell Adhesion and Recognition: Maintaining Tissue Integrity
The cell membrane is essential for cell adhesion and recognition. Specific molecules on the cell surface, such as cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) and glycoproteins, mediate interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix (ECM). This is vital for maintaining tissue structure and function.
- Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs): These proteins mediate cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions, contributing to tissue organization and stability.
- Glycoproteins: These carbohydrate-protein complexes on the cell surface play a crucial role in cell recognition and interaction, allowing cells to distinguish between self and non-self. This is critical for immune responses and tissue development.
4. Maintaining Cell Shape and Structure: The Cellular Scaffold
The cell membrane contributes to maintaining cell shape and structure. The cytoskeleton, a network of protein filaments within the cell, interacts with the membrane, providing structural support and influencing cell morphology. This interaction is particularly important for maintaining the integrity of cells that experience significant mechanical stress.
5. Enzymatic Activity: Catalyzing Cellular Reactions
Some membrane proteins possess enzymatic activity, catalyzing specific biochemical reactions. These enzymes can be involved in various cellular processes, including metabolism, signal transduction, and transport.
6. Selective Permeability: Protecting the Cellular Environment
The selective permeability of the cell membrane is a cornerstone of its function. It allows the cell to maintain a unique internal environment distinct from its surroundings. This control over what enters and exits the cell is crucial for preserving homeostasis and preventing damage from harmful substances.
The Cell Membrane: A Complex and Dynamic Organelle
In conclusion, the cell membrane is far from a simple barrier. Its intricate structure and diverse components empower it to perform a wide range of critical functions. From regulating transport and facilitating communication to mediating cell adhesion and catalyzing enzymatic reactions, the cell membrane is a dynamic and essential organelle that orchestrates cellular processes vital for life itself. Understanding its multifaceted roles is fundamental to comprehending the complexities of cellular biology and disease mechanisms. Further research continuously unravels more details about the intricate mechanisms of the cell membrane, highlighting its ongoing importance in biological studies. The exploration of membrane proteins, lipid rafts, and their interactions promises even greater insight into this fundamental component of life.
Further research into the cell membrane continues to yield exciting discoveries. For example, the role of lipid rafts – specific microdomains within the membrane – in signal transduction and membrane trafficking is an area of intense study. Similarly, ongoing investigations into the complexities of membrane protein interactions and their dynamics are deepening our understanding of cellular processes. The cell membrane's intricate structure and diverse functions make it a captivating subject of ongoing research. The more we learn about this essential component of life, the more we appreciate its crucial role in cellular health and disease. The ongoing studies on membrane-related diseases and the development of novel therapeutic strategies are further testament to the importance of this essential cellular structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
X 3 2x 2 X 2 0
Apr 02, 2025
-
1 3 Divided By 1 6 As A Fraction
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Determine Zeros Of A Function
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Are Four Principles Of Natural Selection
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is 9 To The Power Of 0
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Cell Membrane . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
